序列解包
序列解包: *针对可迭代对象的解包 ** 针对字典的 解包
格式:变量a,变量b....(多个变量)= 可迭代对象
案例: info = "guohan|222|20" a,b,c = info.split("|") info.split("|")成为列表:可迭代 将guohan 222 20 赋值给a b c
比如将info以|分割后的元素变成字典的value:
info = "guohan|123|20"
name,pwd,age = info.split("|")
a = {"Name":name,"Pwd":pwd,"Age":age} #变量的使用在其定义后前即不可以将2 3两行换位置
print(a)
>>>{'Name': 'guohan', 'Pwd': '123', 'Age': '20'}列表元组解包:
# 列表解包
data = [10, 20, 30]
a, b, c = data
print(a) # 输出: 10
print(b) # 输出: 20
print(c) # 输出: 30
# 元组解包
info = ("Alice", 25, "Engineer")
name, age, job = info
print(name) # 输出: Alice
print(age) # 输出: 25
print(job) # 输出: Engineer字符串解包:
text = "ABC"
x, y, z = text
print(x) # 输出: A
print(y) # 输出: B
print(z) # 输出: C解包时忽略部分元素:如果只需要序列中部分元素 可以用_进行占位忽略掉部分元素
data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
first, _, third, _, fifth = data
print(first) # 输出: 1
print(third) # 输出: 3
print(fifth) # 输出: 5解包不定长度的序列:用*捕获多个元素(会被打包成列表),其余元素按顺序赋值
# 捕获前两个元素,剩余元素给 rest
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
a, b, *rest = numbers
print(a) # 输出: 1
print(b) # 输出: 2
print(rest) # 输出: [3, 4, 5]
# 捕获中间元素
data = ["Alice", 25, "Engineer", "New York"]
name, *details, city = data
print(name) # 输出: Alice
print(details) # 输出: [25, "Engineer"]
print(city) # 输出: New York
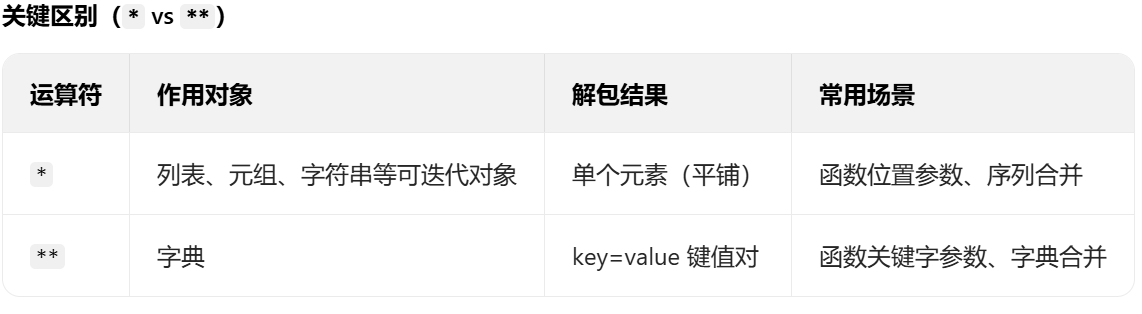
关于* / **
*
* 是 Python 的序列解包运算符(对应 ** 字典解包),专门用于列表、元组、字符串等可迭代对象,核心作用是:把可迭代对象 “拆成单个元素”,直接平铺使用。
1. 函数传参(位置参数平铺)
2. 合并序列(列表 / 元组拼接)
3. 字符串解包(拆成单个字符)
避坑提醒
核心记住 3 点:
- 用
*开头,只针对可迭代对象(列表、元组、字符串等); - 解包后是单个独立元素(平铺格式);
- 不能单独写
*对象(会报错),必须跟在函数括号里或容器大括号里(列表 / 元组 / 集合)。
**
字典解包(** 语法)一句话总结:把字典 {'key1': val1, 'key2': val2} 拆成 key1=val1, key2=val2 的形式,只能用在「函数传参」或「合并字典」里。
1. 函数传参(Flask 模板用的场景 render_template('login.html',**locals()))
题目:函数的定义+数据类型+序列解包
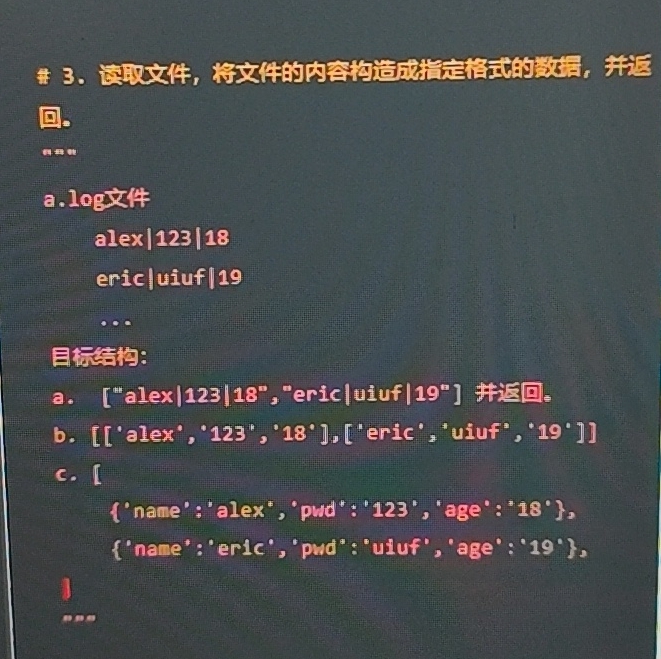
#打开文件并指定格式函数
#打开文件并指定格式函数
def get_file(file_path):
a_list = list()
with open(file_path,"r",encoding = "utf-8") as result:
for line in result:
line.strip()
a_list.append(line.strip())
print(a_list)
def get_file1(file_path):
a_list = list()
with open(file_path,"r",encoding = "utf-8") as result:
for line in result:
line.strip().split("|")
a_list.append(line.strip().split("|"))
print(a_list)
def get_file2(file_path):
a_list = list()
with open(file_path,"r",encoding = "utf-8") as result:
for line in result:
line.strip().split("|")
name,pwd,age = line.strip().split("|")
data = {"Name":name,"Pwd":pwd,"Age":age}
a_list.append(data)
print(a_list)
get_file("np.txt")
get_file1("np.txt")
get_file2("np.txt")



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号