§4.5 Setting Up DI
Before getting started with unit testing, it’s worth putting your DI infrastructure into place. This will deal with resolving dependencies between components.(e.g., ProductsController’s dependency on an IProductsRepository) For this example, you’ll use the popular open source DI container Ninject, which you’ll configure by adding some code to your Global.asax.cs file.
A DI component can be any .NET object or type that you choose. All your controllers are going to be DI components, and so are your repositories. Each time you instantiate a component, the DI container will resolve its dependencies automatically. So, if a controller depends on a repository—perhaps by demanding an instance as a constructor parameter—the DI container will supply a suitable instance. Once you see the code, you’ll realize that it’s actually quite simple!
First, download Ninject from its web site, ninject.org/.10 All you need is its main assembly, Ninject.dll, so put this somewhere convenient on disk and then reference it from your SportsStore.WebUI project
§4.5.1 Creating a Custom Controller Factory
First, create a new folder in your SportsStore.WebUI project called Infrastructure. Inside that folder, create a class called NinjectControllerFactory:
namespace SportsStore.Infrastructure { public class NinjectControllerFactory : DefaultControllerFactory { // A Ninject "kernel" is the thing that can supply object instances private IKernel kernel = new StandardKernel(new SportsStoreServices()); // ASP.NET MVC calls this to get the controller for each request protected override IController GetControllerInstance(RequestContext context, Type controllerType) { if (controllerType == null) return null; return (IController)kernel.Get(controllerType); } // Configures how abstract service types are mapped to concrete implementations private class SportsStoreServices : NinjectModule { public override void Load() { // We'll add some configuration here in a moment } } } }Next, instruct ASP.NET MVC to use your new controller factory by calling SetControllerFactory() inside the Application_Start handler in Global.asax.cs:
§4.5.2 Using Your DI Container
The whole point of bringing in a DI container is that you can use it to eliminate hard-coded dependencies between components. Right now, you’re going to eliminate ProductsController’s current hard-coded dependency on SqlProductsRepository (which, in turn, means you’ll eliminate the hardcoded connection string, soon to be configured elsewhere). The advantages will soon become clear.
When a DI container instantiates an object (e.g., a controller class), it inspects that type’s list of constructor parameters (a.k.a. dependencies) and tries to supply a suitable object for each one. So, if you edit ProductsController, adding a new constructor parameter as follows:public ProductsController(IProductsRepository productsRepository) { //string connString = "Data Source=(local)\\SQL2005; Initial Catalog=SportsStore;Integrated Security=True;"; this.productsRepository = productsRepository; }Let us back to NinjectControllerFactory,and registered any IProductsRepository with the DI container
// Configures how abstract service types are mapped to concrete implementations private class SportsStoreServices : NinjectModule { public override void Load() { Bind<IProductsRepository>() .To<SqlProductsRepository>() .WithConstructorArgument("connectionString", ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["AppDb"].ConnectionString ); } }As you can see, this code tries to fetch a connection string named AppDb using .NET’s standard ConfigurationManager API, which in turn will look for it in your Web.config file. To make this work, add a <connectionStrings> node inside Web.config’s root node, as follows:
<connectionStrings> <add name="AppDb" connectionString="Data Source=(local)\SQL2005; Initial Catalog=SportsStore;Integrated Security=True;"/> </connectionStrings>So that’s it—you’ve set up a working DI system. No matter how many DI components and dependencies you need to add, the plumbing is already done.Nothing chaged like before
§4.5 Creating Unit Tests
Almost all the foundational pieces of infrastructure are now in place—a solution and project structure, a basic domain model and LINQ to SQL repository system, a DI container—so now you can do the real job of writing application behavior and tests!
ProductsController currently produces a list of every product,let us improve it into a paged list of products.In this section we’ll combine NUnit, Moq, and your component-oriented architecture to design new application behaviors using unit tests, starting with that paged list.
TDD: Getting Started
Download Nunit from www.nunit.org and Moq from http://code.google.com/p/moq/.
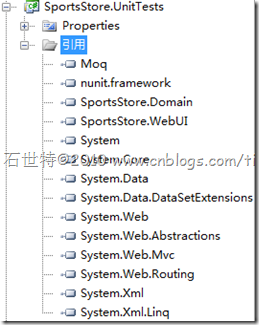
and Add references from your SportsStore.UnitTests project to all these assemblies:
Choosing Our Own Syntax
To make our unit tests easier to understand at a glance, we’ll build up a small library of static methods that enable a readable ASP.NET MVC unit testing syntax.
namespace SportsStore.UnitTests { public static class UnitTestHelpers { public static void ShouldEqual<T>(this T actualValue, T expectedValue) { Assert.AreEqual(expectedValue, actualValue); } } }Adding the First Unit Test
To hold the first unit test, create a new class called CatalogBrowsing in your SportsStore.UnitTests project.
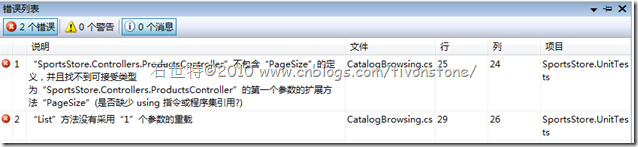
Following the BDD idea of describe a behavior,our first test will be called Can_View_A_Single_Page_Of_Products
namespace SportsStore.UnitTests { [TestFixture] public class CatalogBrowsing { [Test] public void Can_View_A_Single_Page_Of_Products() { // Arrange: If there are 5 products in the repository... IProductsRepository repository = UnitTestHelpers.MockProductsRepository( new Product { Name = "P1" }, new Product { Name = "P2" }, new Product { Name = "P3" }, new Product { Name = "P4" }, new Product { Name = "P5" } ); var controller = new ProductsController(repository); controller.PageSize = 3; // This property doesn't yet exist, but by // accessing it, you're implicitly forming // a requirement for it to exist // Act: ... then when the user asks for the second page (PageSize=3)... var result = controller.List(2); // Assert: ... they'll just see the last two products. var displayedProducts = (IList<Product>)result.ViewData.Model; displayedProducts.Count.ShouldEqual(2); displayedProducts[0].Name.ShouldEqual("P4"); displayedProducts[1].Name.ShouldEqual("P5"); } } }To obtain a mock repository, it tries to call UnitTestHelpers.MockProductsRepository()
public static IProductsRepository MockProductsRepository(params Product[] prods) { // Generate an implementer of IProductsRepository at runtime using Moq var mockProductsRepos = new Mock<IProductsRepository>(); mockProductsRepos.Setup(x => x.Products).Returns(prods.AsQueryable()); return mockProductsRepos.Object; }It’s far easier, tidier, and faster to do this than to actually load real rows into a SQL Server database for testing, and it’s only possible because ProductsController accesses its repository only through an abstract interface.
Check That You Have a Red Light First
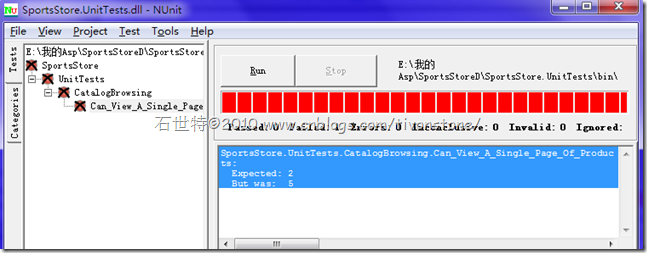
Running the Test Suite in NUnit GUI
Now you can add the paging behavior for real. This used to be a tricky task before LINQ (yes, SQL Server 2005 can return paged data sets, but it’s hardly obvious how to do it), but with LINQ it’s a single, elegant C# code statement. Update the List() method once again:
public ViewResult List(int page) { return View(productsRepository.Products.ToList() .Skip((page - 1) * PageSize) .Take(PageSize) .ToList() ); }
Now, if you’re doing unit tests, recompile and rerun the test in NUnit GUI. Behold . . . a green light!
作者:石世特
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/TivonStone/
希望本文对你有所帮助,想转随便转,心情好的话给我的文章留个链接.o(. .)o


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号