Request被处理到ActionInvoker时,ActionInvoker找到目标Action,方法列表的参数是怎么传递的? 这就需要理解Model Binding过程了。
看一个普通的action:
{
var myPerson = new Person();
return View(myPerson);
}
请求http://mydomain.com/Home/Person/1 经过Route系统解析后,执行到Person。id的参数值解析过程为: Request.Form["id"] -> RouteData.Values["id"] -> Request.QueryString["id"] -> Request.Files["id"]。 当然了,这里解析完第RouteData后就找到目标,退出后边的解析了。
看参数的一般解析过程:
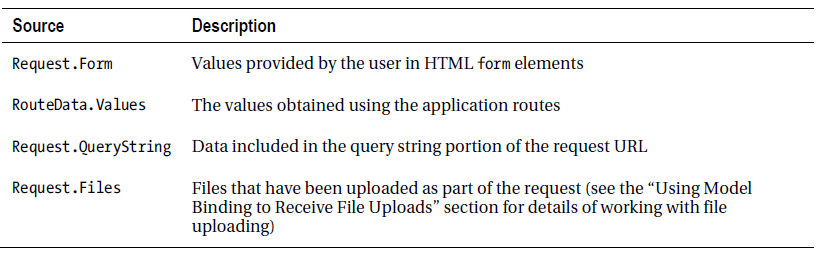
执行过程从上到下,找到即中止,直到找到;否则,如果参数为值类型,并且必选,则报错。另外,参数解析过程中,对于简单类型,DefaultModelBinder利用System.ComponentModel.TypeDescriptor类将解析出的字符串转换为目标类型。如果转换失败,model binding失败。
对于上述Person方法,加入对应的view为:
@model Person
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Person";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
@{
var myPerson = new Person() {FirstName = "Jane", LastName = "Doe"};
}
@using (Html.BeginForm()) {
@Html.EditorFor(m => myPerson)
@Html.EditorForModel()
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
}
标黄部分,实际上render了2个Person对象实例。那么它的postback对应的action方法怎么写?
public ActionResult Person(Person firstPerson, [Bind(Prefix = "myPerson")] Person secondPerson) //Exclude="IsApproved, Role" //FirstName,LastName
{
//do sth.
return Content("Success");
}
它可以接收2个Person实例参数。其中,第二个参数加了一个Bind设置,Prefix后还可以加入Exclude、Include设置。它们分别表示model所绑定的数据来源前缀、忽略赋值的属性、必须赋值的属性。
如果要传值多个字符串,因为是同类型,可以讲它们作为数组传值么?先看view:
@using (Html.BeginForm()) {
@Html.TextBox("movies", "m1", new{id="m1", name="m1"})
@Html.TextBox("movies", "m2", new { id = "m2", name = "m2" })
@Html.TextBox("movies", "m3", new { id = "m3", name="m3" })
<input type="submit" />
}
对应的action为:
public ActionResult Movies(string[] movies)
{
return Content("done");
}
测试成功。Asp.net MVC Framework貌似足够强大,它model binding系统能够智能识别和提取model参数。看model为多个对象实例的list时:
@{
ViewBag.Title = "PersonList";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
for (int i = 0; i < Model.Count; i++)
{
<h4>Person Number: @i</h4>
@:First Name: @Html.EditorFor(m => m[i].FirstName)
@:Last Name: @Html.EditorFor(m => m[i].LastName)
}
<input type="submit"/>
}
对应的action为:
public ActionResult PersonList(List<Person> list)
{
return Content("done");
}
view中的多个person配置,在页面被postback会server后,就被model binding为List<Person>类型的list了。
如果要手动来触发绑定,改进如下:
[ActionName("PersonList")]
public ActionResult PersonListResult()
{
var list = new List<Person>();//Person myPerson = (Person)DependencyResolver.Current.GetService(typeof(Person));
UpdateModel(list);
return Content("done");
}
可以看到,参数占位已经被移除,然后在action内部,先创建一个list,然后调用controller基类的UpdateModel方法来更新list。而UpdateModel方法作用就是根据request传回来的值,同步model。基于之前讲述的model binding寻值的4个源,这里可以直接配置数据源。将上面标黄的代码改为:
即可。这时,model数据源直接从Form中获取。
因为FormCollection实现了IValueProvider接口,上面的实现还可以继续改进为:
[ActionName("PersonList")]
public ActionResult PersonListResult(FormCollection formData)
{
var list = new List<Person>();
//UpdateModel(list, formData);
if(TryUpdateModel(list, formData))
{
return Content("done");
}
else
{
//...provide UI feedback based on ModelState
//var isValid = ModelState.IsValid;
return View();
}
//return Content("done");
}
其中,TryUpdateModel方法可以避免binding失败时抛出异常。
利用Model Binding,怎么来上传文件?如下:
Upload a photo: <input type="file" name="photo" />
<input type="submit" />
</form>
action的写法:
public ActionResult UploadFile(HttpPostedFileBase file)
{
// Save the file to disk on the server
string filename = "myfileName"; // ... pick a filename
file.SaveAs(filename);
//// ... or work with the data directly
//byte[] uploadedBytes = new byte[file.ContentLength];
//file.InputStream.Read(uploadedBytes, 0, file.ContentLength);
//// Now do something with uploadedBytes
return Content("done");
}
最后,来自己定义Model Binding系统吧。先基于IValueProvider接口,实现一个:
{
public bool ContainsPrefix(string prefix)
{
return string.Compare("CurrentTime", prefix, true) == 0;
}
public ValueProviderResult GetValue(string key)
{
return ContainsPrefix(key)
? new ValueProviderResult(DateTime.Now, null, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)
: null;
}
}
创建一个factory:
{
public override IValueProvider GetValueProvider(ControllerContext controllerContext)
{
return new CurrentTimeValueProvider();
}
}
Application_Start中注册:
因为它的位置为0,优先被利用。看一个action:
{
return Content("The time is " + currentTime.ToLongTimeString());
}
显然,它需要一个datetime参数,但是通过http://mydomain.com/home/clock/ 可以访问,这就是CurrentTimeValueProvider的功劳。
自定义一个Dependency-Aware(不知道怎么翻译)的ModelBinder:
{
protected override object CreateModel(ControllerContext controllerContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext, Type modelType)
{
return DependencyResolver.Current.GetService(modelType) ??
base.CreateModel(controllerContext, bindingContext, modelType);
}
}
注册使用:
为Person创建一个专用的ModelBinder:
{
public object BindModel(ControllerContext controllerContext, ModelBindingContext bindingContext)
{
// see if there is an existing model to update and create one if not
Person model = (Person)bindingContext.Model ?? (Person)DependencyResolver.Current.GetService(typeof(Person));
// find out if the value provider has the required prefix
bool hasPrefix = bindingContext.ValueProvider.ContainsPrefix(bindingContext.ModelName);
string searchPrefix = (hasPrefix) ? bindingContext.ModelName + "." : "";
// populate the fields of the model object
model.PersonId = int.Parse(GetValue(bindingContext, searchPrefix, "PersonId"));
model.FirstName = GetValue(bindingContext, searchPrefix, "FirstName");
model.LastName = GetValue(bindingContext, searchPrefix, "LastName");
model.BirthDate = DateTime.Parse(GetValue(bindingContext, searchPrefix, "BirthDate"));
model.IsApproved = GetCheckedValue(bindingContext, searchPrefix, "IsApproved");
model.Role = (Role)Enum.Parse(typeof(Role), GetValue(bindingContext, searchPrefix, "Role"));
return model;
}
private string GetValue(ModelBindingContext context, string prefix, string key)
{
ValueProviderResult vpr = context.ValueProvider.GetValue(prefix + key);
return vpr == null ? null : vpr.AttemptedValue;
}
private bool GetCheckedValue(ModelBindingContext context, string prefix, string key)
{
bool result = false;
ValueProviderResult vpr = context.ValueProvider.GetValue(prefix + key);
if (vpr != null)
{
result = (bool)vpr.ConvertTo(typeof(bool));
}
return result;
}
}
注册使用:
自定义一个ModelBindProvider:
{
public IModelBinder GetBinder(Type modelType)
{
return modelType == typeof(Person) ? new PersonModelBinder() : null;
}
}
注册使用:
基于上面的代码,你也可以直接给对象类加上Model Binding:
public class Person
源码download




