D. Artsem and Saunders
Artsem has a friend Saunders from University of Chicago. Saunders presented him with the following problem.
Let [n] denote the set {1, ..., n}. We will also write f: [x] → [y] when a function f is defined in integer points 1, ..., x, and all its values are integers from 1 to y.
Now then, you are given a function f: [n] → [n]. Your task is to find a positive integer m, and two functions g: [n] → [m], h: [m] → [n], such that g(h(x)) = x for all 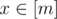 , and h(g(x)) = f(x) for all
, and h(g(x)) = f(x) for all  , or determine that finding these is impossible.
, or determine that finding these is impossible.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105).
The second line contains n space-separated integers — values f(1), ..., f(n) (1 ≤ f(i) ≤ n).
If there is no answer, print one integer -1.
Otherwise, on the first line print the number m (1 ≤ m ≤ 106). On the second line print n numbers g(1), ..., g(n). On the third line print m numbers h(1), ..., h(m).
If there are several correct answers, you may output any of them. It is guaranteed that if a valid answer exists, then there is an answer satisfying the above restrictions.
3
1 2 3
3
1 2 3
1 2 3
3
2 2 2
1
1 1 1
2
2
2 1
-1
思路:由h(g(x)) = f(x),假设f(x1) = f(x2);
那么有h(g(x1)) = h(g(x2)),那么我们假设g(x1)!=g(x2),那么就有h中存在两个相等的数,那么g(h(g(x1))) = g(x1),g(h(g(x2))) = g(x2)
就有个g(x1) = g(x2)所以假设不成立,那么h中的数都是不一样的,那么就为f中的不同种类数,m就确定了。
于是确定h(x),那么h(x)有许多的排列,假设x1,x2,h(x1) = a,h(x2) = b,f(y1) = a,f(y2) = b;
通过条件1求出g,h(g(a)) = f(a),h(g(b)) = f(b);-> g(a) = x1,g(b) = x2,那么有h(x1) = f(a),h(x2) = f(b);
那么假设h(x1) = b,h(x2) = a,可以推得g(a) = x2,g(b) = x1,有h(x2) = f(a),h(x1) = f(b),总是可以的f(a)= a,f(b) = b;
所以h的序列任意排序即可,然后求出g,在通过第二个条件验证即可。
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #include<queue> 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 #include<iostream> 6 #include<string.h> 7 #include<set> 8 #include<map> 9 using namespace std; 10 typedef long long LL; 11 set<int>vec; 12 set<int>::iterator it; 13 int ans[1000006]; 14 int g[1000006]; 15 int h[1000006]; 16 map<int,int>my; 17 int main(void) 18 { 19 int n; 20 scanf("%d",&n); 21 int cn = 0; 22 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 23 scanf("%d",&ans[i]),vec.insert(ans[i]); 24 for(it = vec.begin(); it!=vec.end(); it++) 25 { 26 h[++cn] = *it; 27 my[*it] = cn; 28 g[h[cn]] = cn; 29 } 30 int flag = 0; 31 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 32 { 33 if(g[i] == 0) 34 { 35 g[i] = my[ans[i]]; 36 } 37 else if(h[g[i]]!=ans[i]) 38 flag = 1; 39 } 40 if(flag == 1) 41 printf("-1\n"); 42 else 43 { 44 printf("%d\n",cn); 45 printf("%d",g[1]); 46 for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) 47 printf(" %d",g[i]); 48 printf("\n"); 49 printf("%d",h[1]); 50 for(int i = 2; i <= cn; i++) 51 printf(" %d",h[i]); 52 } 53 return 0; 54 }


