第二周作业
github地址:https://github.com/violetshellz/software_wc
1.项目简介
基本功能:
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数 wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的单词总数 wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的总行数 wc.exe -o outputFile.txt //将结果输出到指定文件outputFile.txt
注意:
空格,水平制表符,换行符,均算字符。
由空格或逗号分割开的都视为单词,且不做单词的有效性校验,例如:thi#,that视为用逗号隔开的2个单词。
-c, -w, -l参数可以共用同一个输入文件,形如:wc.exe –w –c file.c 。
-o 必须与文件名同时使用,且输出文件必须紧跟在-o参数后面,不允许单独使用-o参数。
扩展功能:
wc.exe -s //递归处理目录下符合条件的文件 wc.exe -a file.c //返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行) wc.exe -e stopList.txt // 停用词表,统计文件单词总数时,不统计该表中的单词
[file_name]: 文件或目录名,可以处理一般通配符。
其中,
代码行:本行包括多于一个字符的代码。
空 行:本行全部是空格或格式控制字符,如果包括代码,则只有不超过一个可显示的字符,例如“{”。
注释行:本行不是代码行,并且本行包括注释。一个有趣的例子是有些程序员会在单字符后面加注释:
}//注释
在这种情况下,这一行属于注释行。
-e 必须与停用词文件名同时使用,且停用词文件必须紧跟在-e参数后面,不允许单独使用-e参数。
stopList.txt中停用词可以多于1个,单词之间以空格分割,不区分大小写,形如:while if switch
高级功能
wc.exe -x //该参数单独使用,如果命令行有该参数,则程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、单词数、行数等全部统计信息。
2.代码分析
(1)根据传达给judge()的参数判断要调用的功能:
当par=='-c',返回文件的字符数;当par==‘-w’时,返回文件单词数;当par==‘l’时,返回文件的行数;当par==‘a’时,返回文件的代码、空格、注释行数。
def judge(par, file, out='result.txt'): if par == '-c': with open(file, 'r') as f: count = 0 while f.read(1): count += 1 with open(out, 'a') as fm: fm.write(file + ',字符数:' + str(count) + '\n') if par == '-w': with open(file, 'r') as f: count = 0 for line in f: sp = re.split(',|\x20', line) for i in sp: if i not in table: count += 1 with open(out, 'a') as fn: fn.write(file + ',单词数:' + str(count) + '\n') if par == '-l': with open(file, 'r') as f: count = 0 for line in f: count += 1 with open(out, 'a') as fl: fl.write(file + ',行数:' + str(count) + '\n') if par == '-a': with open(file,'r') as f: c1,c2,c3=0,0,0 for line in f: pattern2 = re.compile(r'.?\n') if pattern2.match(line): c2+=1 else: line=line.strip() pattern3 = re.compile(r'^(})?//') pattern4 = re.compile(r'^(})?/\*') pattern5 = re.compile(r'^\*/$') if pattern3.match(line) or pattern4.match(line) or pattern5.match(line): c3 += 1 else: c1 += 1 with open(out,'a') as fo: fo.write(file + ',代码行/空行/注释行:' + str(c1) +'/' + str(c2)+ '/'+str(c3) + '\n')
(2)实现高级功能
wc.exe -x
该参数单独使用,如果命令行有该参数,则程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、单词数、行数等全部统计信息。
if i <=(LEN-1) and sys.argv[i] == '-x': default_dir = r"CC:\Python27\PyInstaller-3.3.1\wc\dist" # 设置默认打开目录 fname = tkFileDialog.askopenfilename(title=u"选择文件", initialdir=(os.path.expanduser(default_dir))) for i2 in ['-c','-w','-l','-a']: judge(i2,fname,'outputFile.txt') os._exit(0)
(3)实现停用词表
wc.exe -e stopList.txt // 停用词表,统计文件单词总数时,不统计该表中的单词
if i <= (LEN - 1) and sys.argv[i] == '-e': i += 1 if i <= (LEN - 1): with open(sys.argv[i], 'r') as f: i += 1 for line in f: for SP in re.split(',|\x20', line): table.append(SP) else: print("输入错误")
(4)
将结果输入到制定文件夹 wc.exe -o outputFile.txt
实现递归处理目录下符合条件的文件 wc.exe -s
if i <= (LEN - 1) and sys.argv[i] == '-o': # print sys.argv[i] i += 1 if i <= (LEN - 1): if '-s' not in para: for j in para: judge(j, sys.argv[ip], sys.argv[i]) else: para.remove('-s') # files = os.listdir(sys.argv[ip]) FILES = [] for root, dirs, files in os.walk(sys.argv[ip], topdown=True): for name in files: FILES.append(os.path.join(root, name)) res = [] for file in FILES: pattern = re.compile(r'.*\.c') if pattern.match(file): res.append(file) for j in para: for k in res: judge(j, k, sys.argv[i]) else: print("输入错误") else: if '-s' not in para: for j in para: judge(j, sys.argv[ip]) else: para.remove('-s') # files = os.listdir(sys.argv[ip]) FILES = [] for root, dirs, files in os.walk(sys.argv[ip], topdown=True): for name in files: FILES.append(os.path.join(root, name)) res = [] for file in FILES: pattern = re.compile(r'.*\.c') if pattern.match(file): res.append(file) for j in para: for k in res: judge(j, k)
3.测试用例
运行测试脚本wc\BIN\ceshi.py,结果在result.txt内
若测试脚本不能用:①在BIN目录下shift+鼠标右键打开命令行(也许需要管理员模式)②在命令行下一个个测试下面os.system()函数中的命令
(1)统计字符
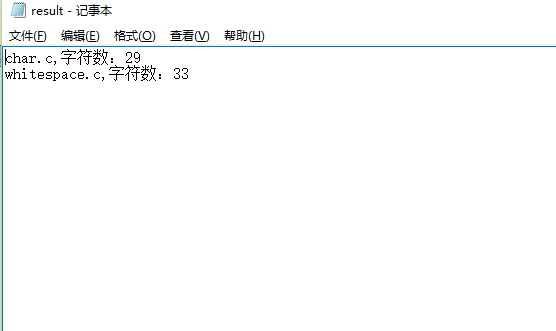
import os os.system(r'wc.exe -c char.c')
os.system(r'wc.exe -c whitespace.c')
(2)单词数和行数
os.system(r'wc.exe –w –l wordtest.c')

(3)
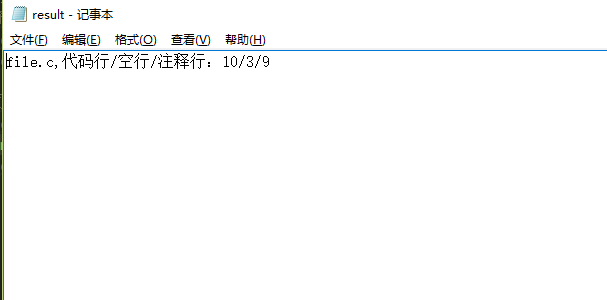
1.统计代码行、空行、注释行
os.system(r'wc.exe –a atest.c')
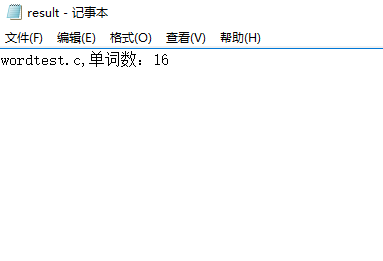
2. 停用词表
os.system('wc.exe –w stoptest.c –e stoplist.txt')
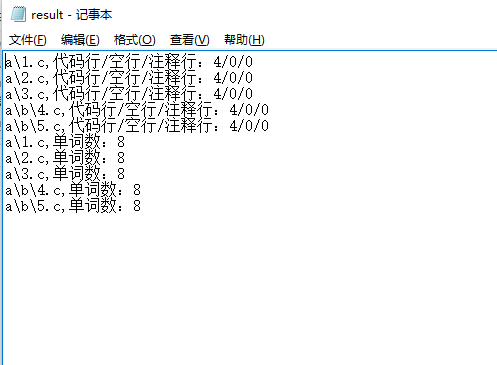
3.文件夹遍历
遍历当前文件夹下 a目录下所有 .c结尾文件
os.system('wc.exe -s -a –w a')
(4)高级功能
以图形界面输入文件
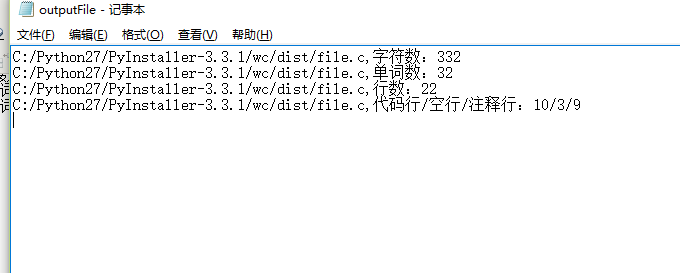
wc.exe -x 会返回字符、单词、行数、注释代码空格行数(结果在outputFile.txt中)
os.system('wc.exe –x')
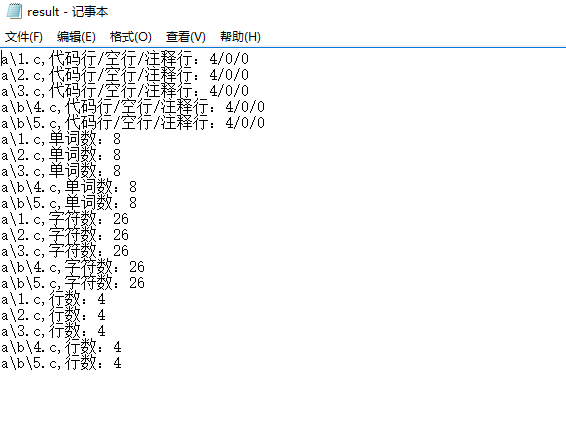
(5)输出测试(结果在result.txt内)
os.system('wc.exe –s –a –w –c –l a')
4.PSP
| PSP阶段 | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
| 计划 | 20 | 30 |
| 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 15 | 20 |
| 开发 | 300 | 600 |
| 需求分析(包括学习新技术) | 60 | 120 |
| 生产设计文档 | 60 | 60 |
| 设计复审(和同事审核设计文档) | 30 | 50 |
| 代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 40 |
| 具体设计 | 20 | 40 |
| 具体编码 | 120 | 300 |
| 代码复审 | 30 | 100 |
| 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 100 | 200 |
| 报告 | 120 | 150 |
| 测试报告 | 20 | 60 |
| 计算工作量 | 30 | 40 |
| 事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 30 |
| 合计 | 975 | 1840 |
4.参考文件
https://www.cnblogs.com/zxyfanta/p/4032093.html
http://blog.csdn.net/woshisangsang/article/details/73230433
http://www.runoob.com/python/att-string-split.html
https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/308587899.html
http://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-os-walk.html

