SQL Server自动化运维系列——监控性能指标脚本(Power Shell)
需求描述
一般在生产环境中,有时候需要自动的检测指标值状态,如果发生异常,需要提前预警的,比如发邮件告知,本篇就介绍如果通过Power shell实现状态值监控
监控值范围
根据经验,作为DBA一般需要监控如下系统能行指标
cpu: \Processor(_Total)\% Processor Time \Processor(_Total)\% Privileged Time \SQLServer:SQL Statistics\Batch Requests/sec \SQLServer:SQL Statistics\SQL Compilations/sec \SQLServer:SQL Statistics\SQL Re-Compilations/sec \System\Processor Queue Length \System\Context Switches/sec Memory: \Memory\Available Bytes \Memory\Pages/sec \Memory\Page Faults/sec \Memory\Pages Input/sec \Memory\Pages Output/sec \Process(sqlservr)\Private Bytes \SQLServer:Buffer Manager\Buffer cache hit ratio \SQLServer:Buffer Manager\Page life expectancy \SQLServer:Buffer Manager\Lazy writes/sec \SQLServer:Memory Manager\Memory Grants Pending \SQLServer:Memory Manager\Target Server Memory (KB) \SQLServer:Memory Manager\Total Server Memory (KB) Disk: \PhysicalDisk(_Total)\% Disk Time \PhysicalDisk(_Total)\Current Disk Queue Length \PhysicalDisk(_Total)\Avg. Disk Queue Length \PhysicalDisk(_Total)\Disk Transfers/sec \PhysicalDisk(_Total)\Disk Bytes/sec \PhysicalDisk(_Total)\Avg. Disk sec/Read \PhysicalDisk(_Total)\Avg. Disk sec/Write SQL Server: \SQLServer:Access Methods\FreeSpace Scans/sec \SQLServer:Access Methods\Full Scans/sec \SQLServer:Access Methods\Table Lock Escalations/sec \SQLServer:Access Methods\Worktables Created/sec \SQLServer:General Statistics\Processes blocked \SQLServer:General Statistics\User Connections \SQLServer:Latches\Total Latch Wait Time (ms) \SQLServer:Locks(_Total)\Lock Timeouts (timeout > 0)/sec \SQLServer:Locks(_Total)\Lock Wait Time (ms) \SQLServer:Locks(_Total)\Number of Deadlocks/sec \SQLServer:SQL Statistics\Batch Requests/sec \SQLServer:SQL Statistics\SQL Re-Compilations/sec
上述指标含义,可以参照我上一篇文章:SQL Server需要监控哪些计数器
监控脚本
$server = "(local)" $uid = "sa" $db="master" $pwd="password" $mailprfname = "SendEmail" $recipients = "787449667@qq.com" $subject = "数据库指标异常了!" $computernamexml = "f:\computername.xml" $alter_cpuxml = "f:\alter_cpu.xml" function GetServerName($xmlpath) { $xml = [xml] (Get-Content $xmlpath) $return = New-Object Collections.Generic.List[string] for($i = 0;$i -lt $xml.computernames.ChildNodes.Count;$i++) { if ( $xml.computernames.ChildNodes.Count -eq 1) { $cp = [string]$xml.computernames.computername } else { $cp = [string]$xml.computernames.computername[$i] } $return.Add($cp.Trim()) } $return } function GetAlterCounter($xmlpath) { $xml = [xml] (Get-Content $xmlpath) $return = New-Object Collections.Generic.List[string] $list = $xml.counters.Counter $list } function CreateAlter($message) { $SqlConnection = New-Object System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection $CnnString ="Server = $server; Database = $db;User Id = $uid; Password = $pwd" $SqlConnection.ConnectionString = $CnnString $CC = $SqlConnection.CreateCommand(); if (-not ($SqlConnection.State -like "Open")) { $SqlConnection.Open() } $cc.CommandText=" EXEC msdb..sp_send_dbmail @profile_name = '$mailprfname' ,@recipients = '$recipients' ,@body = '$message' ,@subject = '$subject' " $cc.ExecuteNonQuery()|out-null $SqlConnection.Close(); } $names = GetServerName($computernamexml) $pfcounters = GetAlterCounter($alter_cpuxml) foreach($cp in $names) { $p = New-Object Collections.Generic.List[string] $report = "" foreach ($pfc in $pfcounters) { $b = "" $counter ="\\"+$cp+$pfc.get_InnerText().Trim() $p.Add($counter) } $count = Get-Counter $p for ($i = 0; $i -lt $count.CounterSamples.Count; $i++) { $v = $count.CounterSamples.Get($i).CookedValue $pfc = $pfcounters[$i] #$pfc.get_InnerText() $b = "" $lg = "" if($pfc.operator -eq "lt") { if ($v -ge [double]$pfc.alter) {$b = "alter" $lg = "Greater Than"} } elseif ($pfc.operator -eq "gt") { if( $v -le [double]$pfc.alter) {$b = "alter" $lg = "Less Than"} } if($b -eq "alter") { $path = "\\"+$cp+$pfc.get_InnerText() $item = "{0}:{1};{2} Threshold:{3}" -f $path,$v.ToString(),$lg,$pfc.alter.Trim() $report += $item + "`n" } } if($report -ne "") { #生产警告 参数 计数器,阀值,当前值 CreateAlter $report } }
其中涉及到2个配置文件:computernamexml,alter_cpuxml分别如下:
<computernames>
<computername>
wuxuelei-pc
</computername>
</computernames>
<Counters>
<Counter alter = "10" operator = "gt" >\Processor(_Total)\% Processor Time</Counter>
<Counter alter = "10" operator = "gt" >\Processor(_Total)\% Privileged Time</Counter>
<Counter alter = "10" operator = "gt" >\SQLServer:SQL Statistics\Batch Requests/sec</Counter>
<Counter alter = "10" operator = "gt" >\SQLServer:SQL Statistics\SQL Compilations/sec</Counter>
<Counter alter = "10" operator = "gt" >\SQLServer:SQL Statistics\SQL Re-Compilations/sec</Counter>
<Counter alter = "10" operator= "lt" >\System\Processor Queue Length</Counter>
<Counter alter = "10" operator= "lt" >\System\Context Switches/sec</Counter>
</Counters>
其中 alter 就是阀值,如第一条,如果 阀值 > 性能计数器值,就会发出警告。
其实这种自定义配置的方式,实现了灵活多变的自动化监控标准:
1、比如可以检测磁盘空间大小
2、检测运行峰值状态
3、定时的根据历史运行值,更改生产系统中的阀值大小,也就是所谓的运行基线
警告实现方式
1、SQL Agent配置Job方式实现
2、计划任务
以上两种配置方式,可以灵活掌握,操作还是蛮简单的,如果不会,可自行google。当然,如果不想干预正常的生产系统,可以添加一个Server专门用来自动化运维检测来用,实现远程监控。
后续文章中会分析关于Power Shell的远程调用,并且能实现事故当前状态下,自动化截图....自动Send Email......为DBA现场取证第一手材料...方便诊断问题...
效果图如下
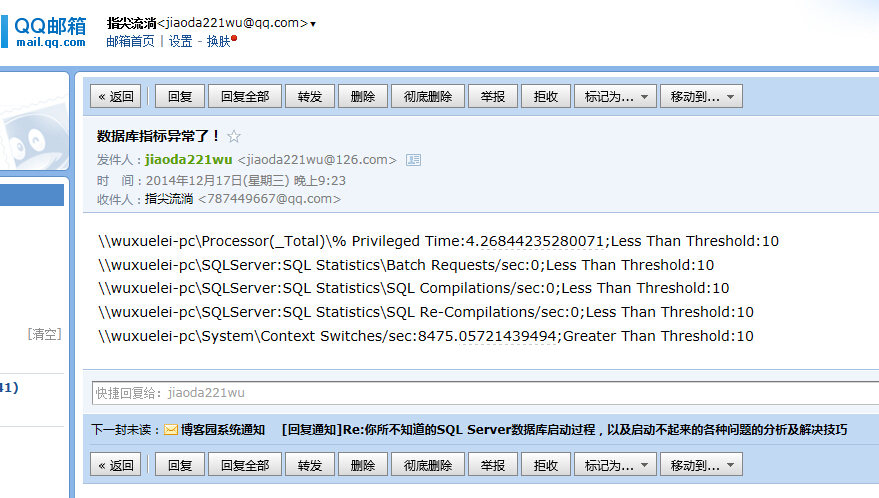
以上只提供实现方式,如需要内容更新,自己灵活更新。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号