Codeforces 895.E Eyes Closed
Vasya and Petya were tired of studying so they decided to play a game. Before the game begins Vasya looks at array a consisting of n integers. As soon as he remembers all elements of a the game begins. Vasya closes his eyes and Petya does q actions of one of two types:
1) Petya says 4 integers l1, r1, l2, r2 — boundaries of two non-intersecting segments. After that he swaps one random element from the [l1, r1]segment with another random element from the [l2, r2] segment.
2) Petya asks Vasya the sum of the elements of a in the [l, r] segment.
Vasya is a mathematician so he answers Petya the mathematical expectation of the sum of the elements in the segment.
Your task is to write a program which will answer the second type questions as Vasya would do it. In other words your program should print the mathematical expectation of the sum of the elements of a in the [l, r] segment for every second type query.
The first line contains two integers n, q (2 ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the number of elements in the array and the number of queries you need to handle.
The second line contains n integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — elements of the array.
The next q lines contain Petya's actions of type 1 or 2.
If it is a type 1 action then the line contains 5 integers 1, l1, r1, l2, r2 (1 ≤ l1 ≤ r1 ≤ n, 1 ≤ l2 ≤ r2 ≤ n).
If it is a type 2 query then the line contains 3 integers 2, l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n).
It is guaranteed that there is at least one type 2 query and segments [l1, r1], [l2, r2] don't have common elements.
For each type 2 query print one real number — the mathematical expectation of the sum of elements in the segment.
Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error doesn't exceed 10 - 4 — formally, the answer is correct if 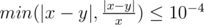 where x is jury's answer and y is yours.
where x is jury's answer and y is yours.
4 4
1 1 2 2
1 2 2 3 3
2 1 2
1 1 2 3 4
2 1 2
3.0000000
3.0000000
10 5
1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2
1 1 5 6 10
2 1 5
1 1 5 6 10
1 1 5 6 10
2 6 10
6.0000000
8.0400000
10 10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1 1 5 6 10
1 1 5 6 10
2 1 5
1 1 3 6 9
2 1 3
1 5 7 8 10
1 1 1 10 10
2 1 5
2 7 10
2 1 10
23.0000000
14.0000000
28.0133333
21.5733333
55.0000000
大致题意:两种操作。
1. [l1, r1]之间随机一个数,[l2, r2]之间随机一个数,把两个交换
2. 问[l, r]区间和的数学期望是多少。
分析:直接分析每个数对整体的影响很难,先分析个体.设len1 = r1 - l1 + 1,len2 = r2 - l2 + 1.那么对于第一个区间的数x,有1/len1的概率随机到.还有(len1 - 1)/len1的概率不会随机到.右边有1/len2的概率随机到y,那么既随机到x又随机到y的概率为1/(len1*len2),枚举第二个区间的每一个数y,那么x对第一个区间的期望的贡献就变成了[(len1 - 1)/len1] * x + sum2 / (len1 * len2).整个区间的期望和就是把所有x的期望加起来.可以利用线段树来维护:区间乘,区间加,区间求和,对于第二个区间也是差不多这样的.
对期望的概念理解的还不是非常深入.直接算整体的不好算可以先考虑算局部的贡献.
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn = 100010; int n,q,L[maxn << 2],R[maxn << 2]; double sum[maxn << 2],add[maxn << 2],mul[maxn << 2]; void pushup(int o) { sum[o] = sum[o * 2] + sum[o * 2 + 1]; } void pushdown(int o) { sum[o * 2] = sum[o * 2] * mul[o] + add[o] * (R[o * 2] - L[o * 2] + 1); sum[o * 2 + 1] = sum[o * 2 + 1] * mul[o] + add[o] * (R[o * 2 + 1] - L[o * 2 + 1] + 1); add[o * 2] = add[o * 2] * mul[o] + add[o]; add[o * 2 + 1] = add[o * 2 + 1] * mul[o] + add[o]; mul[o * 2] = mul[o * 2] * mul[o]; mul[o * 2 + 1] = mul[o * 2 + 1] * mul[o]; mul[o] = 1; add[o] = 0; } void build(int o,int l,int r) { L[o] = l; R[o] = r; add[o] = 0; mul[o] = 1; if (l == r) { cin >> sum[o]; return; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; build(o * 2,l,mid); build(o * 2 + 1,mid + 1,r); pushup(o); } double query(int o,int l,int r,int x,int y) { if (x <= l && r <= y) return sum[o]; pushdown(o); int mid = (l + r) >> 1; double res = 0.0; if (x <= mid) res += query(o * 2,l,mid,x,y); if (y > mid) res += query(o * 2 + 1,mid + 1,r,x,y); return res; } void update1(int o,int l,int r,int x,int y,double v) { if (x <= l && r <= y) { sum[o] += v * (r - l + 1); add[o] += v; return; } pushdown(o); int mid = (l + r) >> 1; if (x <= mid) update1(o * 2,l,mid,x,y,v); if (y > mid) update1(o * 2 + 1,mid + 1,r,x,y,v); pushup(o); } void update2(int o,int l,int r,int x,int y,double v) { if (x <= l && r <= y) { add[o] *= v; sum[o] *= v; mul[o] *= v; return; } pushdown(o); int mid = (l + r) >> 1; if (x <= mid) update2(o * 2,l,mid,x,y,v); if (y > mid) update2(o * 2 + 1,mid + 1,r,x,y,v); pushup(o); } int main() { scanf("%d%d",&n,&q); build(1,1,n); while (q--) { int l1,r1,l2,r2; int id; scanf("%d",&id); if (id == 1) { scanf("%d%d%d%d",&l1,&r1,&l2,&r2); double sum1 = query(1,1,n,l1,r1),sum2 = query(1,1,n,l2,r2); double len1 = r1 - l1 + 1,len2 = r2 - l2 + 1; update2(1,1,n,l1,r1,(len1 - 1) / len1); update2(1,1,n,l2,r2,(len2 - 1) / len2); update1(1,1,n,l1,r1,1.0 / len1 * (sum2 / len2)); update1(1,1,n,l2,r2,1.0 / len2 * (sum1 / len1)); } else { scanf("%d%d",&l1,&r1); printf("%.7lf\n",query(1,1,n,l1,r1)); } } return 0; }



