一、继承条件下构造方法的调用
测试代码一:
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
//super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
测试结果:

测试代码二:
class Grandparent
{
public Grandparent()
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
}
public Grandparent(String string)
{
System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent
{
public Parent()
{
super("Hello.Grandparent.");
System.out.println("Parent Created");
// super("Hello.Grandparent.");
}
}
测试结果:

测试代码三:
1 //编译错误
2 class Grandparent
3 {
4 public Grandparent()
5 {
6 System.out.println("GrandParent Created.");
7 }
8 public Grandparent(String string)
9 {
10 System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string);
11 }
12 }
13
14 class Parent extends Grandparent
15 {
16 public Parent()
17 {
18 //super("Hello.Grandparent.");
19 System.out.println("Parent Created");
20 super("Hello.Grandparent."); //报错
21 }
22 }
测试结果:
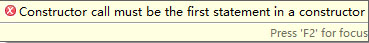
(构造函数调用必须在构造函数第一条语句)
结论:子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须调用父类的构造方法。
原因:构造函数的作用为初始化,当被继承的父类未初始化时,无法生成子类对象。
二、ParentChildTest
程序代码:
package ParentChild;
public class ParentChildTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
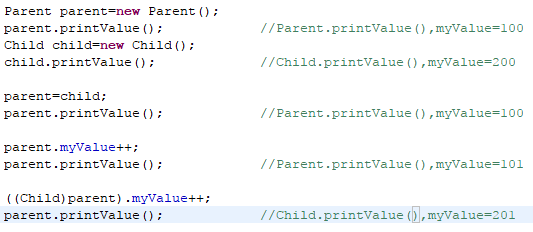
Parent parent=new Parent();
parent.printValue();
Child child=new Child();
child.printValue();
parent=child;
parent.printValue();
parent.myValue++;
parent.printValue();
((Child)parent).myValue++;
parent.printValue();
}
}
class Parent{
public int myValue=100;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
class Child extends Parent{
public int myValue=200;
public void printValue() {
System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue);
}
}
预测输出结果:
实际执行结果:
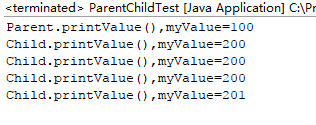
原因分析:
当子类与父类具有相同名称的成员时,调用子类对象,默认调用的是子类中的成员,即父类同名成员被隐藏。
当父类变量引用一个子类对象时,使用父类还是子类成员,由对象自己的“真实”类型所决定



