Windows Phone Mango:MVVM十分钟入门
在这篇文章中,我将谈一下在windows phone 7.1 Mango应用程序中使用MVVM设计模式。用较少的理论、更多的示例,在10分钟内来解释MVVM模式。
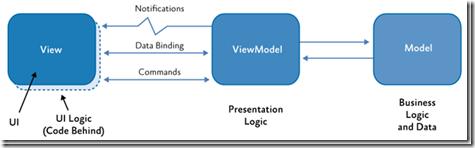
在开始之前,先简短介绍一下什么是MVVM:Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM)模式提供了一种灵活的方式,通过将应用程序分隔成三部分来创建windows phone应用程序。
a:View:放置XAML文件。
b:ViewModel:放置连接UI和数据的显示逻辑层。
c:放置数据模型和业务对象。
有关更多信息,看参阅官方MSDN文档。
为什么选择MVVM?有什么好处?
-
视图和显示逻辑层分离:从显示逻辑层分离出来View/XAML,可以使开发者只关注Code,而设计人员只关注XAML。
-
自动单元测试:视图/逻辑分离大大改进了表现逻辑层的自动单元测试。
-
代码重用:因为显示逻辑层在独立的组件或类中,和View(XAML)分离开来,你可以按照你喜欢的方式,通过继承和组合使它们结合起来。
-
设计时数据支持: 你可以在Blend中看到UI的样子,也就是说,设计人员可以使用样本数据来测试UI,甚至可以模拟实际场景数据。
-
多视图: 依据用户角色,同一ViewModel可以在不同的多视图中展现。
入门开始:
我们需要Windows Phone 7.1 Mango工程项目。在这个实例中,我们会使用上篇文章 为Windows Phone Mango MVVM 应用创建可复用 ICommand 实现类 所创建的DelegateCommand。请注意:commanding是伴随mango更新的新特性。(commanding意味着一些控件不支持Commands)。
MODEL
首先我们需要定义Model。在示例中,我们创建Person类,有两个属性:Name和Age。在这里,最重要的就是要实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口,因为,当Person对象发现变化时,需要通知给UI。(本例中,当按下Save Changes时,更新ListBox,更多信息参阅下面部分中的View)
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Ink;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Animation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
using System.ComponentModel;
namespace WPMangoMVVMSample
{
public class Person : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private string name;
private int age;
public string Name
{
get
{
return name;
}
set
{
if (this.name != value)
{
this.name = value;
this.RaisePropertyChanged("Name");
}
}
}
public int Age
{
get
{
return this.age;
}
set
{
if (this.age != value)
{
this.age = value;
this.RaisePropertyChanged("Age");
}
}
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
private void RaisePropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
PropertyChangedEventHandler handler = this.PropertyChanged;
if (handler != null)
{
handler(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
}
}
VIEW MODEL
下一步就是创建PersonViewModel,主要包含以下部分:
- SaveChangesCommand - 保存用户选择Person对象所引发的修改。
- LoadDataCommand - 此命令是用来填充ObservableCollection(Person对象)。
- SelectedName - 此属性表示选中的Person对象的名称。
- SelectedAge - 此属性表示选中的Person对象的年龄。
- SelectedPerson - 此属性表示所选中的Person对象。
PersonViewModel也实现了INotifyPropertyChanged,所有当某些属性更新时,UI会接到通知。 代码如下:
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Ink;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Animation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
namespace WPMangoMVVMSample
{
public class PersonViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
private string name;
private int age;
private ObservableCollection<Person> personDataSource;
private ICommand loadDataCommand;
private ICommand saveChangesCommand;
public PersonViewModel()
{
this.loadDataCommand = new DelegateCommand(this.LoadDataAction);
this.saveChangesCommand = new DelegateCommand(this.SaveChangesAction);
}
private void LoadDataAction(object p)
{
this.DataSource.Add(new Person() { Name = "John", Age = 32 });
this.DataSource.Add(new Person() { Name = "Kate", Age = 27 });
this.DataSource.Add(new Person() { Name = "Sam", Age = 30 });
}
private void SaveChangesAction(object p)
{
if (this.SelectedPerson != null)
{
this.SelectedPerson.Name = this.name;
this.SelectedPerson.Age = this.age;
}
}
public ICommand LoadDataCommand
{
get
{
return this.loadDataCommand;
}
}
public ICommand SaveChangesCommand
{
get
{
return this.saveChangesCommand;
}
}
public ObservableCollection<Person> DataSource
{
get
{
if (this.personDataSource == null)
{
this.personDataSource = new ObservableCollection<Person>();
}
return this.personDataSource;
}
}
public string SelectedName
{
get
{
if (this.SelectedPerson != null)
{
return this.SelectedPerson.Name;
}
return string.Empty;
}
set
{
this.name = value;
}
}
public int SelectedAge
{
get
{
if (this.SelectedPerson != null)
{
return this.SelectedPerson.Age;
}
return 0;
}
set
{
this.age = value;
}
}
private Person selectedPerson;
public Person SelectedPerson
{
get
{
return this.selectedPerson;
}
set
{
if (this.selectedPerson != value)
{
this.selectedPerson = value;
if (this.selectedPerson != null)
{
this.name = this.selectedPerson.Name;
this.age = this.selectedPerson.Age;
}
this.RaisePropertyChanged("SelectedName");
this.RaisePropertyChanged("SelectedAge");
}
}
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
private void RaisePropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
PropertyChangedEventHandler handler = this.PropertyChanged;
if (handler != null)
{
handler(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
}
}
VIEW
最后一步就是创建View。 我们仍然使用 MainPage.xaml。我们将创建:
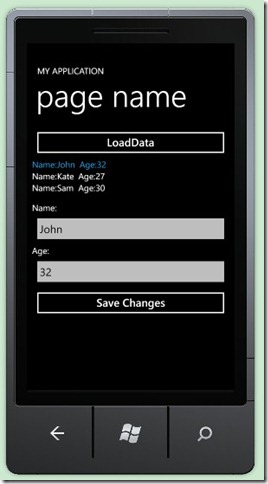
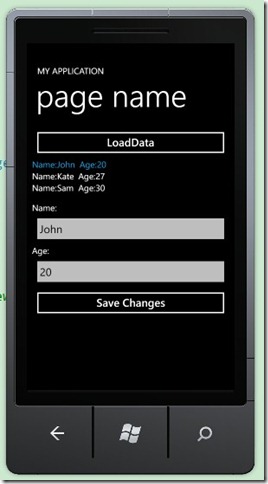
- "LoadData" 按钮: 调用LoadDataCommand填充数据源。
- ListBox 绑定PersonViewModel,两个TextBox用来编辑选择的Person对象: 姓名和年龄。
- "Save Changes" 调用SaveChangesCommand保存修改信息。
注意: TextBox的Binding 数据流向:Mode=TwoWay ,可以编辑和更新值。
<StackPanel x:Name="ContentPanel" Grid.Row="1" Margin="12,0,12,0">
<Button Content="LoadData" Command="{Binding LoadDataCommand}" />
<ListBox ItemsSource="{Binding DataSource}" SelectedItem="{Binding SelectedPerson, Mode=TwoWay}" Height="100">
<ListBox.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal">
<TextBlock Text="Name:"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Name}" />
<TextBlock Text="Age:" Margin="10,0,0,0"/>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding Age}" />
</StackPanel>
</DataTemplate>
</ListBox.ItemTemplate>
</ListBox>
<TextBlock Text="Name:"/>
<TextBox Text="{Binding SelectedName, Mode=TwoWay}" />
<TextBlock Text="Age:"/>
<TextBox Text="{Binding SelectedAge, Mode=TwoWay}" />
<Button Content="Save Changes" Command="{Binding SaveChangesCommand}" />
</StackPanel>
绑定view至view model简单方法就是设置DataContext:
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
// simple way to bind the view to the view model
this.DataContext = new PersonViewModel();
}
效果图:
由于本人翻译水平有限,有些地方欠妥,请园友们不吝指教!