第七篇、os、sys、random、time、datetime、logging
一、sys
用于提供对Python解释器相关的操作:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0)sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息sys.maxint 最大的Int值sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称sys.stdin 输入相关sys.stdout 输出相关sys.stderror 错误相关 |
二、os
用于提供系统级别的操作:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cdos.curdir 返回当前目录: ('.')os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:('..')os.makedirs('dir1/dir2') 可生成多层递归目录os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推os.mkdir('dirname') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirnameos.rmdir('dirname') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirnameos.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印os.remove() 删除一个文件os.rename("oldname","new") 重命名文件/目录os.stat('path/filename') 获取文件/目录信息os.sep 操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\",Linux下为"/"os.linesep 当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\t\n",Linux下为"\n"os.pathsep 用于分割文件路径的字符串os.name 字符串指示当前使用平台。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix'os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示,不能保存执行结果<br>os.popen("bash command").read() 运行shell命令,可以保存执行结果os.environ 获取系统环境变量os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回Falseos.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回Trueos.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回Falseos.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回Falseos.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间 |
三、random
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import random print(random.random()) # 生成0-1之间的随机小数print(random.randint(1, 20)) #生成1到20的整数包括20print random.uniform(10, 20) #生成10到20之间的浮点数print(random.randrange(1, 10)) #生成1到10的证书不包括10,第3个参数可以指定步长print(random.choice(["JGood", "is", "a", "handsome", "boy"])) # 从序列中随机选一个数# 每次对序列随机排序p = ["Python", "is", "powerful", "simple"]random.shuffle(p)print(p) |
随机验证码
import random
li = []
for i in range(6):
r = random.randint(0, 4)
if r == 2 or r == 4:
num = random.randrange(0, 10)
li.append(str(num))
else:
temp = random.randrange(65,91)
c = chr(temp)
li.append(c)
result = "".join(li)
print(result)
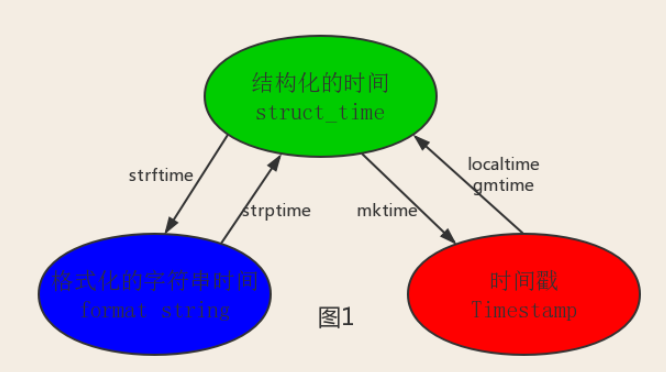
四、时间相关的操作,时间有三种表示方式:
- 时间戳 1970年1月1日之后的秒,即:time.time()
- 格式化的字符串 2014-11-11 11:11, 即:time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
- 结构化时间 元组包含了:年、日、星期等... time.struct_time 即:time.localtime()
time
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
import timeprint(time.clock()) #返回处理器时间,3.3开始已废弃print(time.process_time()) #返回处理器时间,3.3开始已废弃<br>print(time.time()) #返回当前系统时间戳输出:1471161757.5214906print(time.ctime()) #输出字符串格式时间:Sun Aug 14 16:04:02 2016 ,当前系统时间print(time.ctime(time.time()-86640)) #将时间戳转为字符串格式<br>print(time.gmtime()) #获取结构化时间print(time.gmtime(time.time()-86640)) #将时间戳转换成struct_time格式print(time.localtime(time.time()-86640)) #将时间戳转换成struct_time格式,但返回的本地时间print(time.mktime(time.localtime())) #与time.localtime()功能相反,将struct_time格式转回成时间戳格式time.sleep(4) #睡上4秒print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.gmtime()) ) #将struct_time格式转成指定的字符串格式print(time.strptime("2016-01-28","%Y-%m-%d") ) #将字符串格式转换成struct_time格式 |
datetime
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import datetimeprint(datetime.date.today()) #输出格式 2016-01-26print(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time()-864400) ) #2016-01-16 将时间戳转成日期格式current_time = datetime.datetime.now() #print(current_time) #输出2016-01-26 19:04:30.335935print(current_time.timetuple()) #返回struct_time格式 #datetime.replace([year[, month[, day[, hour[, minute[, second[, microsecond[, tzinfo]]]]]]]])print(current_time.replace(2014,9,12)) #输出2014-09-12 19:06:24.074900,返回当前时间,但指定的值将被替换 str_to_date = datetime.datetime.strptime("21/11/06 16:30", "%d/%m/%y %H:%M") #将字符串转换成日期格式new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=10) #比现在加10天new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(days=-10) #比现在减10天new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(hours=-10) #比现在减10小时new_date = datetime.datetime.now() + datetime.timedelta(seconds=120) #比现在+120sprint(new_date) |
时间转换关系:
logging模块
用于便捷记录日志且线程安全的模块
CRITICAL = 50
FATAL = CRITICAL
ERROR = 40
WARNING = 30
WARN = WARNING
INFO = 20
DEBUG = 10
NOTSET = 0

import logging logging.debug('调试debug') logging.info('消息info') logging.warning('警告warn') logging.error('错误error') logging.critical('严重critical') ''' WARNING:root:警告warn ERROR:root:错误error CRITICAL:root:严重critical '''

#======介绍 可在logging.basicConfig()函数中可通过具体参数来更改logging模块默认行为,可用参数有 filename:用指定的文件名创建FiledHandler(后边会具体讲解handler的概念),这样日志会被存储在指定的文件中。 filemode:文件打开方式,在指定了filename时使用这个参数,默认值为“a”还可指定为“w”。 format:指定handler使用的日志显示格式。 datefmt:指定日期时间格式。 level:设置rootlogger(后边会讲解具体概念)的日志级别 stream:用指定的stream创建StreamHandler。可以指定输出到sys.stderr,sys.stdout或者文件,默认为sys.stderr。若同时列出了filename和stream两个参数,则stream参数会被忽略。 format参数中可能用到的格式化串: %(name)s Logger的名字 %(levelno)s 数字形式的日志级别 %(levelname)s 文本形式的日志级别 %(pathname)s 调用日志输出函数的模块的完整路径名,可能没有 %(filename)s 调用日志输出函数的模块的文件名 %(module)s 调用日志输出函数的模块名 %(funcName)s 调用日志输出函数的函数名 %(lineno)d 调用日志输出函数的语句所在的代码行 %(created)f 当前时间,用UNIX标准的表示时间的浮 点数表示 %(relativeCreated)d 输出日志信息时的,自Logger创建以 来的毫秒数 %(asctime)s 字符串形式的当前时间。默认格式是 “2003-07-08 16:49:45,896”。逗号后面的是毫秒 %(thread)d 线程ID。可能没有 %(threadName)s 线程名。可能没有 %(process)d 进程ID。可能没有 %(message)s用户输出的消息 #========使用 import logging logging.basicConfig(filename='access.log', format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s -%(module)s: %(message)s', datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p', level=10) logging.debug('调试debug') logging.info('消息info') logging.warning('警告warn') logging.error('错误error') logging.critical('严重critical') #========结果 access.log内容: 2017-07-28 20:32:17 PM - root - DEBUG -test: 调试debug 2017-07-28 20:32:17 PM - root - INFO -test: 消息info 2017-07-28 20:32:17 PM - root - WARNING -test: 警告warn 2017-07-28 20:32:17 PM - root - ERROR -test: 错误error 2017-07-28 20:32:17 PM - root - CRITICAL -test: 严重critical

import logging formatter=logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s -%(module)s: %(message)s', datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p',) fh1=logging.FileHandler('test1.log') fh2=logging.FileHandler('test2.log') fh3=logging.FileHandler('test3.log') ch=logging.StreamHandler() fh1.setFormatter(formatter) #也可以是不同的formater fh2.setFormatter(formatter) fh3.setFormatter(formatter) ch.setFormatter(formatter) logger=logging.getLogger(__name__) logger.setLevel(40) logger.addHandler(fh1) logger.addHandler(fh2) logger.addHandler(fh3) logger.addHandler(ch) logger.debug('debug') logger.info('info') logger.warning('warning') logger.error('error') logger.critical('critical')
logging的实际应用,使用的时候套入就是了

""" logging配置 """ import os import logging.config # 定义三种日志输出格式 开始 standard_format = '[%(asctime)s][%(threadName)s:%(thread)d][task_id:%(name)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]' \ '[%(levelname)s][%(message)s]' #其中name为getlogger指定的名字 simple_format = '[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]%(message)s' id_simple_format = '[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s] %(message)s' # 定义日志输出格式 结束 logfile_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) # log文件的目录 logfile_name = 'all2.log' # log文件名 # 如果不存在定义的日志目录就创建一个 if not os.path.isdir(logfile_dir): os.mkdir(logfile_dir) # log文件的全路径 logfile_path = os.path.join(logfile_dir, logfile_name) # log配置字典 LOGGING_DIC = { 'version': 1, 'disable_existing_loggers': False, 'formatters': { 'standard': { 'format': standard_format }, 'simple': { 'format': simple_format }, }, 'filters': {}, 'handlers': { #打印到终端的日志 'console': { 'level': 'DEBUG', 'class': 'logging.StreamHandler', # 打印到屏幕 'formatter': 'simple' }, #打印到文件的日志,收集info及以上的日志 'default': { 'level': 'DEBUG', 'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件 'formatter': 'standard', 'filename': logfile_path, # 日志文件 'maxBytes': 1024*1024*5, # 日志大小 5M 'backupCount': 5, 'encoding': 'utf-8', # 日志文件的编码,再也不用担心中文log乱码了 }, }, 'loggers': { #logging.getLogger(__name__)拿到的logger配置 '': { 'handlers': ['default', 'console'], # 这里把上面定义的两个handler都加上,即log数据既写入文件又打印到屏幕 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': True, # 向上(更高level的logger)传递 }, }, } def load_my_logging_cfg(): logging.config.dictConfig(LOGGING_DIC) # 导入上面定义的logging配置 logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) # 生成一个log实例 logger.info('It works!') # 记录该文件的运行状态 if __name__ == '__main__': load_my_logging_cfg()

""" MyLogging Test """ import time import logging import my_logging # 导入自定义的logging配置 logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) # 生成logger实例 def demo(): logger.debug("start range... time:{}".format(time.time())) logger.info("中文测试开始。。。") for i in range(10): logger.debug("i:{}".format(i)) time.sleep(0.2) else: logger.debug("over range... time:{}".format(time.time())) logger.info("中文测试结束。。。") if __name__ == "__main__": my_logging.load_my_logging_cfg() # 在你程序文件的入口加载自定义logging配置 demo()

#! /usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # __author__ = "Q1mi" # Date: 2017/7/28 LOGGING = { 'version': 1, 'disable_existing_loggers': False, 'formatters': { 'standard': { 'format': '[%(asctime)s][%(threadName)s:%(thread)d][task_id:%(name)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]' '[%(levelname)s][%(message)s]' }, 'simple': { 'format': '[%(levelname)s][%(asctime)s][%(filename)s:%(lineno)d]%(message)s' }, 'collect': { 'format': '%(message)s' } }, 'filters': { 'require_debug_true': { '()': 'django.utils.log.RequireDebugTrue', }, }, 'handlers': { #打印到终端的日志 'console': { 'level': 'DEBUG', 'filters': ['require_debug_true'], 'class': 'logging.StreamHandler', 'formatter': 'simple' }, #打印到文件的日志,收集info及以上的日志 'default': { 'level': 'INFO', 'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切 'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_info.log"), # 日志文件 'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 5, # 日志大小 5M 'backupCount': 3, 'formatter': 'standard', 'encoding': 'utf-8', }, #打印到文件的日志:收集错误及以上的日志 'error': { 'level': 'ERROR', 'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切 'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_err.log"), # 日志文件 'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 5, # 日志大小 5M 'backupCount': 5, 'formatter': 'standard', 'encoding': 'utf-8', }, #打印到文件的日志 'collect': { 'level': 'INFO', 'class': 'logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler', # 保存到文件,自动切 'filename': os.path.join(BASE_LOG_DIR, "xxx_collect.log"), 'maxBytes': 1024 * 1024 * 5, # 日志大小 5M 'backupCount': 5, 'formatter': 'collect', 'encoding': "utf-8" } }, 'loggers': { #logging.getLogger(__name__)拿到的logger配置 '': { 'handlers': ['default', 'console', 'error'], 'level': 'DEBUG', 'propagate': True, }, #logging.getLogger('collect')拿到的logger配置 'collect': { 'handlers': ['console', 'collect'], 'level': 'INFO', } }, } # ----------- # 用法:拿到俩个logger logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) #线上正常的日志 collect_logger = logging.getLogger("collect") #领导说,需要为领导们单独定制领导们看的日志
详细介绍

import logging ''' 一:如果不指定filename,则默认打印到终端 二:指定日志级别: 指定方式: 1:level=10 2:level=logging.ERROR 日志级别种类: CRITICAL = 50 FATAL = CRITICAL ERROR = 40 WARNING = 30 WARN = WARNING INFO = 20 DEBUG = 10 NOTSET = 0 三:指定日志级别为ERROR,则只有ERROR及其以上级别的日志会被打印 ''' logging.basicConfig(filename='access.log', format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s -%(module)s: %(message)s', datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p', level=10) logging.debug('debug') logging.info('info') logging.warning('warning') logging.error('error') logging.critical('critical') logging.log(10,'log') #如果level=40,则只有logging.critical和loggin.error的日志会被打印
打印到终端又打印到文件
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_
__author__ = 'Linhaifeng'
import logging
formater=logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s -%(module)s: %(message)s',
datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p',)
fh=logging.FileHandler('aaaaaaaaaaaa.log')
ch=logging.StreamHandler()
fh.setFormatter(formater)
ch.setFormatter(formater)
log1=logging.getLogger()
log1.setLevel(logging.ERROR)
log1.addHandler(fh)
log1.addHandler(ch)
log1.debug('deubug')
log1.info('info')
log1.warning('warn')
log1.error('erro')
log1.critical('critical')
可在logging.basicConfig()函数中通过具体参数来更改logging模块默认行为,可用参数有
filename:用指定的文件名创建FiledHandler(后边会具体讲解handler的概念),这样日志会被存储在指定的文件中。
filemode:文件打开方式,在指定了filename时使用这个参数,默认值为“a”还可指定为“w”。
format:指定handler使用的日志显示格式。
datefmt:指定日期时间格式。
level:设置rootlogger(后边会讲解具体概念)的日志级别
stream:用指定的stream创建StreamHandler。可以指定输出到sys.stderr,sys.stdout或者文件,默认为sys.stderr。若同时列出了filename和stream两个参数,则stream参数会被忽略。点击查看更详细
日志格式
|
%(name)s |
Logger的名字,并非用户名,详细查看 |
|
%(levelno)s |
数字形式的日志级别 |
|
%(levelname)s |
文本形式的日志级别 |
|
%(pathname)s |
调用日志输出函数的模块的完整路径名,可能没有 |
|
%(filename)s |
调用日志输出函数的模块的文件名 |
|
%(module)s |
调用日志输出函数的模块名 |
|
%(funcName)s |
调用日志输出函数的函数名 |
|
%(lineno)d |
调用日志输出函数的语句所在的代码行 |
|
%(created)f |
当前时间,用UNIX标准的表示时间的浮 点数表示 |
|
%(relativeCreated)d |
输出日志信息时的,自Logger创建以 来的毫秒数 |
|
%(asctime)s |
字符串形式的当前时间。默认格式是 “2003-07-08 16:49:45,896”。逗号后面的是毫秒 |
|
%(thread)d |
线程ID。可能没有 |
|
%(threadName)s |
线程名。可能没有 |
|
%(process)d |
进程ID。可能没有 |
|
%(message)s |
用户输出的消息 |




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号