XML以及相关的XSLT,XPath,XSD工具在数据层面为我们提供了极大的灵活性和便利.我们游戏协议的代码自动生成就是首先使用XSD工具设计了协议的Schema,然后使用.net的xsd工具直接生成实体类,然后就直接在工具中操作对象就可以了,协议的XML文件也可以通过事先的Schema检查来校验数据规范性;Erlang类库提供了对于XML的支持,可能你在STDLIB中并没有找到,这是因为这部分被独立在:http://www.erlang.org/doc/apps/xmerl/index.html
如果已经忘记了XML中常用的概念,最好还是在维基百科中做一下回顾:
我们可以在"\erl5.9.1\lib\xmerl-1.3.1\include\xmerl.hrl"头文件中看到XML的上述各种概念在Erlang中的表达形式;
%% XML Element %% content = [#xmlElement()|#xmlText()|#xmlPI()|#xmlComment()|#xmlDecl()] -record(xmlElement,{ name, % atom() expanded_name = [], % string() | {URI,Local} | {"xmlns",Local} nsinfo = [], % {Prefix, Local} | [] namespace=#xmlNamespace{}, parents = [], % [{atom(),integer()}] pos, % integer() attributes = [], % [#xmlAttribute()] content = [], language = "", % string() xmlbase="", % string() XML Base path, for relative URI:s elementdef=undeclared % atom(), one of [undeclared | prolog | external | element] }).
Erlang官方解决方案从模块划分上看是五脏俱全的:xmerl_scan,xmerl,xmerl_xs,xmerl_eventp,xmerl_xpath,xmerl_xsd,xmerl_sax_parser;但是官方文档上并没有给出足够低门槛的demo代码,仅有的两段示例代码可能由于搜索引擎收录的问题,并不容易找到,其实他们是在:
http://erlang.org/doc/apps/xmerl/xmerl_xs_examples.html
http://www.erlang.org/doc/apps/xmerl/xmerl_xs_examples.html
解析&创建XML
<shopping> <item name="bread" quantity="3" price="2.50"/> <item name="milk" quantity="2" price="3.50"/> </shopping>
-include_lib("xmerl/include/xmerl.hrl"). -export([get_total/1]). get_total(ShoppingList) -> {XmlElt, _} = xmerl_scan:string(ShoppingList), Items = xmerl_xpath:string("/shopping/item", XmlElt), Total = lists:foldl(fun(Item, Tot) -> [#xmlAttribute{value = PriceString}] = xmerl_xpath:string("/item/@price", Item), {Price, _} = string:to_float(PriceString), [#xmlAttribute{value = QuantityString}] = xmerl_xpath:string("/item/@quantity", Item), {Quantity, _} = string:to_integer(QuantityString), Tot + Price*Quantity end, 0, Items), io:format("$~.2f~n", [Total]).
运行上面的代码得到结果:$14.50
动态创建XML
下面我们从CSV文件数据源动态创建一个XML,CSV内容如下:
bread,3,2.50
milk,2,3.50
要创建的XML如下,其实就是上面的购物清单:
<shopping> <item name="bread" quantity="3" price="2.50"/> <item name="milk" quantity="2" price="3.50"/> </shopping>
实现代码:
to_xml(ShoppingList) -> Items = lists:map(fun(L) -> [Name, Quantity, Price] = string:tokens(L, ","), {item, [{name, Name}, {quantity, Quantity}, {price, Price}], []} end, string:tokens(ShoppingList, "\n")), xmerl:export_simple([{shopping, [], Items}], xmerl_xml).
erlsom
erlsom 项目地址:http://sourceforge.net/projects/erlsom/ erlsom支持三种使用模型:
- as a SAX parser. 备注: SAX即Simple API for XML(简称SAX)是个循序存取XML的解析器API.
- As a simple sort of DOM parser. 备注: DOM(Document Object Model)是W3C组织推荐的处理可扩展置标语言的标准编程接口.
- As a ‘data binder’ 直接解析成为Erlang的Record,类似于一个强类型DataSet的概念
下面我们实际操练一下这三种模式,我们使用下面的xml,文件名test2.xml,目标还是计算购物清单的中金额
<?xml version="1.0"?> <shopping> <item name="bread" quantity="3" price="2.50"/> <item name="milk" quantity="2" price="3.50"/> </shopping>
2> {ok, Xml} = file:read_file("test.xml"). {ok,<<"<shopping> \r\n <item name=\"bread\" quantity=\"3\" price=\"2.50\"/> \r\ n <item name=\"milk\" quantity=\"2\" price=\"3.50"...>>} 3> erlsom:parse_sax(Xml, [], fun(Event, Acc) -> io:format("~p~n", [Event]), Acc end). startDocument {startElement,[],"shopping",[],[]} {ignorableWhitespace," \r\n "} {startElement,[],"item",[], [{attribute,"price",[],[],"2.50"}, {attribute,"quantity",[],[],"3"}, {attribute,"name",[],[],"bread"}]} {endElement,[],"item",[]} {ignorableWhitespace," \r\n "} {startElement,[],"item",[], [{attribute,"price",[],[],"3.50"}, {attribute,"quantity",[],[],"2"}, {attribute,"name",[],[],"milk"}]} {endElement,[],"item",[]} {ignorableWhitespace," \r\n"} {endElement,[],"shopping",[]} endDocument {ok,[]," "} 4> Sum = fun(Event, Acc) -> case Event of {startElement, _, "item", _, [{_,_,_,_,P},{_,_,_,_,C},_]} -> Acc + list_to_float(P)*list_to_integer(C); _ -> Acc end end. #Fun<erl_eval.12.82930912> 5> erlsom:parse_sax(Xml, 0, Sum). {ok,14.5," "} 6>
9> erlsom:simple_form(Xml). {ok,{"shopping",[], [{"item", [{"price","2.50"},{"quantity","3"},{"name","bread"}], []}, {"item", [{"price","3.50"},{"quantity","2"},{"name","milk"}], []}]}, " "} 10>
首先设计XML的XSD,然后使用XSD打通数据模型使用的各个环节,比如生成C#代码,直接获得强类型的对象,这个方法在.net里面很常用;erlsom提供的Data binder的模式,其实就是实现了这种设计方法;起点还是设计XSD文件,好吧,我们为上面的test2.xml设计一个XSD,如下:
<xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <xsd:element name="shopping" type="shoppingType"/> <xsd:complexType name="shoppingType"> <xsd:sequence> <xsd:element name="item" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <xsd:complexType> <xsd:attribute name="name" type="xsd:string" use="required"/> <xsd:attribute name="quantity" type="xsd:positiveInteger" use="required"/> <xsd:attribute name="price" type="xsd:decimal" use="required"/> </xsd:complexType> </xsd:element> </xsd:sequence> </xsd:complexType > </xsd:schema>
28> erlsom:write_xsd_hrl_file("test.xsd","test.hrl"). ok
%% HRL file generated by ERLSOM
%%
%% It is possible to change the name of the record fields.
%%
%% It is possible to add default values, but be aware that these will
%% only be used when *writing* an xml document.
-record('shoppingType', {anyAttribs, 'item'}).
-record('shoppingType/item', {anyAttribs, 'name', 'quantity', 'price'}).
为了能在Erlang Shell中完成所有的测试,后面需要使用record的时候我们使用rd()命令,在shell中建立record的定义.
下面就是解析并映射为record了:
Eshell V5.9.1 (abort with ^G)
1> {ok, X} = erlsom:compile_xsd_file("test.xsd").
=ERROR REPORT==== 20-Jul-2012::06:53:09 ===
Call to tuple fun {erlsom_parse,xml2StructCallback}.
Tuple funs are deprecated and will be removed in R16. Use "fun M:F/A" instead, f
or example "fun erlsom_parse:xml2StructCallback/2".
(This warning will only be shown the first time a tuple fun is called.)
{ok,{model,[{type,'_document',sequence,
[{el,[{alt,shopping,shoppingType,[],1,1,true,undefined}],
1,1,1}],
[],undefined,undefined,1,1,1,false,undefined},
{type,shoppingType,sequence,
[{el,[{alt,item,'shoppingType/item',[],1,1,true,undefined}],
0,unbound,1}],
[],undefined,undefined,2,1,1,undefined,undefined},
{type,'shoppingType/item',sequence,[],
[{att,name,1,false,char},
{att,quantity,2,false,char},
{att,price,3,false,char}],
undefined,undefined,4,1,1,undefined,undefined}],
[{ns,"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema","xsd"}],
undefined,[]}}
2> {ok, Xml} = file:read_file("test2.xml").
{ok,<<"锘??xml version=\"1.0\"?>\r\n<shopping> \r\n <item name=\"bread\" quanti
ty=\"3\" price=\"2.50\"/> \r\n <item name=\"milk"...>>}
3> {ok, Result, _} = erlsom:scan(Xml, X).
{ok,{shoppingType,[],
[{'shoppingType/item',[],"bread","3","2.50"},
{'shoppingType/item',[],"milk","2","3.50"}]},
" "}
4>
5> rd('shoppingType', {anyAttribs, 'item'}). shoppingType 6> rd('shoppingType/item', {anyAttribs, 'name', 'quantity', 'price'}). 'shoppingType/item' 7> R4#shoppingType.'item'. [#'shoppingType/item'{anyAttribs = [],name = "bread", quantity = "3",price = "2.50"}, #'shoppingType/item'{anyAttribs = [],name = "milk", quantity = "2",price = "3.50"}] 8> hd(R4#shoppingType.'item'). #'shoppingType/item'{anyAttribs = [],name = "bread", quantity = "3",price = "2.50"} 9> #'shoppingType/item'.quantity. 4
其它可选方案
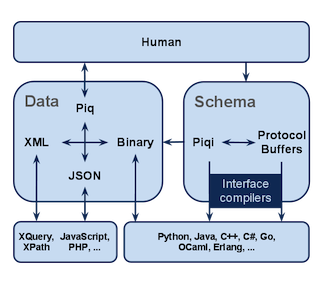
[1] JSON 作为轻量级的数据交换格式,JSON有着巨大的优势,erlang相关解决方案也有很多比如ejson mochiweb也有相关模块
[2] Google的Protocol Buffers 以及Facebook的Thrift为代表的解决方法
[3] Piqi includes a data serialization system for Erlang. It can be used for serializing Erlang values in 4 different formats: Google Protocol Buffers, JSON, XML and Piq. http://piqi.org/#usecasesandlimitations
[4]ASN.1 ASN.1本身只定义了表示信息的抽象句法,但是没有限定其编码的方法。各种ASN.1编码规则提供了由ASN.1描述其抽象句法的数据的值的传送语法(具体表达)。标准的ASN.1编码规则有基本编码规则(BER,Basic Encoding Rules)、规范编码规则(CER,Canonical Encoding Rules)、唯一编码规则(DER,Distinguished Encoding Rules)、压缩编码规则(PER,Packed Encoding Rules)和XML编码规则(XER,XML Encoding Rules)。为了使ASN.1能够描述一些原先没有使用ASN.1定义,因此不适用上述任一编码规则的数据传输和表示的应用和协议,另外制订了ECN来扩展ASN.1的编码形式。ECN可以提供非常灵活的表明方法,但还没有得到普遍应用。
ASN.1与特定的ASN.1编码规则一起通过使用独立于计算机架构和编程语言的方法来描述数据结构,为结构化数据的交互提供了手段,特别是在网络环境的应用程序。
Erlang对ASN.1支持:
The Asn1 application provides:
• An ASN.1 compiler for Erlang, which generates encode and decode functions to be used by Erlang programs
sending and receiving ASN.1 specified data.
• Run-time functions used by the generated code.
• The supported encoding rules are:
• Basic Encoding Rules (BER)
• Distinguished Encoding Rules (DER), a specialized form of BER that is used in security-conscious
applications.
• Packed Encoding Rules (PER) both the aligned and unaligned variant.
相关:
[墙内] Processing XML in Erlang http://www.cnblogs.com/me-sa/articles/2673940.html
record to xml http://www.cnblogs.com/me-sa/articles/2673945.html
http://userprimary.net/posts/2011/02/16/Generating-XML-in-Erlang-Using-xmerl/
http://www.erlang.org/doc/apps/xmerl/xmerl_xs_examples.html
http://www.sics.se/~joe/ericsson/xml/xml.html
http://sourceforge.net/scm/?type=cvs&group_id=157642
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3517914/erlang-xml-to-tuples-and-lists
晚安!
最后送上一张96星河版<笑傲江湖>的截图,这个版本让我欣喜不已,
83版射雕,94版射雕,95版神雕,96版笑傲,97版天龙八部,百看不厌






