C#选择排序
1:原理
选择排序是从冒泡排序演化而来的,每一轮比较得出最小的那个值,然后依次和每轮比较的第一个值进行交换。
目的:按从小到大排序。
方法:假设存在数组:72, 54, 59, 30, 31, 78, 2, 77, 82, 72
第一轮依次比较相邻两个元素,将最小的一个元素的索引和值记录下来,然后和第一个元素进行交换。
如上面的数组中,首先比较的是72,54,记录比较小的索引是54的索引1。接着比较54和59,比较小的索引还是1。直到最后得到最小的索引是2的索引6,然后索引6和0互相交换。
第二轮比较的时候是最小的一个元素和索引1进行交换。第三轮、第四轮以此类推。
2:代码
class Program
{
static List<int> list = new List<int>() { 72, 54, 59, 30, 31, 78, 2, 77, 82, 72 };
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Choice();
PrintList();
}
static void Choice()
{
int temp = 0;
int minIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
minIndex = i;
for (int j = i; j < list.Count; j++)
{
//注意这里比较的是list[minIndex]
if (list[j] < list[minIndex])
{
minIndex = j;
}
}
temp = list[minIndex];
list[minIndex] = list[i];
list[i] = temp;
PrintList();
}
}
private static void PrintList()
{
foreach (var item in list)
{
Console.Write(string.Format("{0} ", item));
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
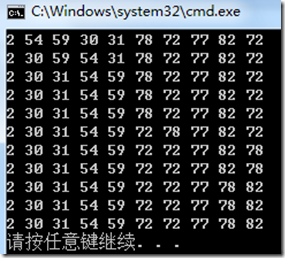
3:输出
4:时间复杂度
O(n^2)