【Netty】Netty传输
一、前言
在简单学习了Netty中的组件后,接着学习Netty中数据的传输细节。
二、传输
2.1 传输示例
Netty中的数据传输都是使用的字节类型,下面通过一个实例进行说明,该实例中服务器接受请求,然后向客户端发送一个Hi,最后关闭连接。下面是不同方式的实现。
1. OIO方式
OIO与NIO对应,使用阻塞式的IO处理,其服务端代码如下

package com.hust.grid.leesf.chapter4; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.nio.charset.Charset; public class PlainOioServer { public void serve(int port) throws IOException { final ServerSocket socket = new ServerSocket(port); try { for (;;) { final Socket clientSocket = socket.accept(); System.out.println("Accepted connection from: " + clientSocket); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { OutputStream out; try { out = clientSocket.getOutputStream(); out.write("Hi!\r\n".getBytes(Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); out.flush(); clientSocket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); try { clientSocket.close(); } catch (IOException ex) { // ignore on close } } } }).start(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
说明:其中,在for循环中会不断的去监听是否有新请求到达,当有请求到达后,初始化一个新的线程去处理,完成向客户端发送Hi字符串,最后关闭连接。使用OIO方式的性能较差,扩展性也不好,需要使用异步方式处理。
2. NIO方式

package com.hust.grid.leesf.chapter4; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; public class PlainNioServer { public void serve(int port) throws IOException { ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); serverChannel.configureBlocking(false); ServerSocket ss = serverChannel.socket(); InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(port); ss.bind(address); Selector selector = Selector.open(); serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); final ByteBuffer msg = ByteBuffer.wrap("Hi!\r\n".getBytes()); for (;;) { try { selector.select(); } catch (IOException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); // handle exception break; } Set<SelectionKey> readyKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); //5 Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = readyKeys.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = iterator.next(); iterator.remove(); try { if (key.isAcceptable()) { //6 ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel)key.channel(); SocketChannel client = server.accept(); client.configureBlocking(false); client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE | SelectionKey.OP_READ, msg.duplicate()); //7 System.out.println( "Accepted connection from " + client); } if (key.isWritable()) { //8 SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel)key.channel(); ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer)key.attachment(); while (buffer.hasRemaining()) { if (client.write(buffer) == 0) { //9 break; } } client.close(); //10 } } catch (IOException ex) { key.cancel(); try { key.channel().close(); } catch (IOException cex) { // ignore on close } } } } } }
说明:NIO方法使用了Selector和Channel等组件,使用Selector来处理多个Channel,其代码与OIO代码几乎是完全不相同。
3. Netty的OIO方式
当使用Netty框架处理时,并且采用OIO的方式,其代码如下

package com.hust.grid.leesf.chapter4; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.oio.OioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.oio.OioServerSocketChannel; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.charset.Charset; public class NettyOioServer { public void server(int port) throws Exception { final ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.unreleasableBuffer( Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hi!\r\n", Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); EventLoopGroup group = new OioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.group(group) .channel(OioServerSocketChannel.class) .localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port)) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { ctx.writeAndFlush(buf.duplicate()).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } }); } }); ChannelFuture f = b.bind().sync(); f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully().sync(); } } }
可以看到上述代码很多都是和之前示例中使用的代码相同,再来看看在Netty框架下使用NIO时的处理方式。
4. Netty的NIO方式

package com.hust.grid.leesf.chapter4; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.charset.Charset; public class NettyNioServer { public void server(int port) throws Exception { final ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.unreleasableBuffer( Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hi!\r\n", Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(), new NioEventLoopGroup()) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port)) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { ctx.writeAndFlush(buf.duplicate()).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } }); } }); ChannelFuture f = b.bind().sync(); f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully().sync(); } } }
可以看到Netty框架下的NIO和OIO的代码基本相同。
2.2 传输细节
传输的核心是Channel接口,其继承结构图如下所示
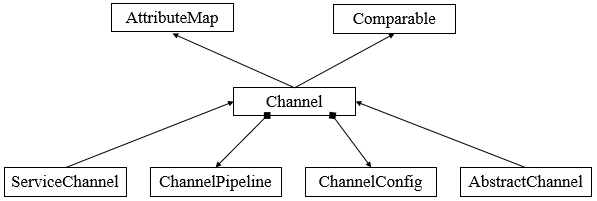
其中,Channel继承了AttributeMap和Comparable接口,其包含ChannelPipeline和ChannelConfig两个实例,ChannelConfig包含了所有的配置信息,ChannelPipeline包含了所有的ChannelHandler实例,其中用于存放用户的处理逻辑。典型的ChannelHandler用法如下
· 将数据类型进行转化
· 提供异常通知
· 提供Channel变为活动或非活动的通知
· 提供当Channel在EventLoopGroup中注册或者注销时的通知
· 提供用户定义事件的通知
Netty中的Channel实现是线程安全的,所以在多线程环境中可安全使用。
2.3 传输方案
Netty提供了多种传输方案,你可根据应用的不同选择合适的传输方案。
1. NIO-非阻塞型I/O
NIO提供了完全异步的IO实现,其使用基于选择器的API,选择器的核心概念是将其作为注册表,当通道的状态变化时会接受到通知,可能有的变化状态如下
· 一个新通道被接受并已准备好
· 一个通道的连接已经完成
· 一个通道已经有准备好读取的数据
· 一个通道可以写入数据
当应用程序对状态的变化做出反应后,会重置选择器并重复处理,根据不同的状态给出不同的响应,选择操作有如下四种类型OP_ACCEPT 、OP_CONNECT、OP_READ 、OP_WRITE,其中选择器的处理流程如下图所示

2. Epoll-Linux的本机非阻塞传输
Netty可在任何系统上运行,但对于不同的系统会有不同的折中,Linux系统中的epoll具有高可扩展的I/O的事件通知,Linux上的JDK的NIO则是基于epoll,当使用epoll取代NIO时,可以使用Netty中的EpollEventLoopGroup取代NioEventLoopGroup,使用EpollServerSocketChannel.class取代NioServerSocketChannel.class。
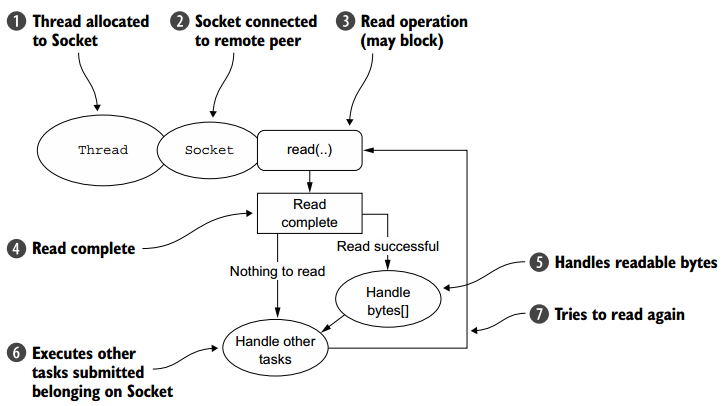
3. OIO-阻塞型I/O
Netty的OIO是一种妥协方案,其使用JAVA中原生态的旧的API,其是同步阻塞的。在java.net的API中,通常使用一个线程接受来自指定端口的请求,当创建一个套接字时,就会创建一个新的线程来进行处理,其处理流程图如下图所示
4. 在JVM内进行通信的本地传输
Netty提供了在同一个JVM中的客户端与服务端之间的异步通信,在此传输中,与服务器通道相关联的SocketAddress不绑定到物理网络地址,相反,当服务器运行时,其存储在注册表中,关闭时取消注册。因为传输不能接受真正的网络流量,所以它不能与其他传输实现互操作。
5. 嵌入式传输
Netty还提供了一个额外的传输,其可以将ChannelHandler作为帮助类嵌入其他的ChannelHandler中,以这种方式,你无需修改其内部代码便能扩展ChannelHandler的功能。
2.4 传输示例
并非所有的传输都支持所有的传输协议,下表是传输方式与传输协议之间的关系

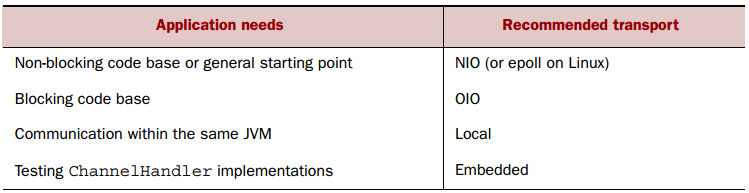
而对于不同的应用,可根据下表选择合适的传输方式
三、总结
本篇博文讲解了Netty中的传输细节,了解了多种不同的传输方式,以及其和不同传输协议之间的关系,也谢谢各位园友的观看~
PS:如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮,您的“推荐”,将会是我不竭的动力!
作者:leesf 掌控之中,才会成功;掌控之外,注定失败。
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
如果觉得本文对您有帮助,您可以请我喝杯咖啡!






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号