爬山法、随机重启爬山法、模拟退火算法对八皇后问题和八数码问题的性能测试
代码地址:https://github.com/laiy/AI/tree/master/awesome-search
一些前提:
1. 首先要明确这些算法并不是用于解决传统的搜索问题的(环境是可观察的,确定的,已知的,问题解是一个行动序列),这些算法适用于哪些关注解状态而不是路径代价的问题,我们讨论的搜索算法往往和现实世界的一些问题更加的契合。
2. 为了便于测试我们选择了八皇后和八数码问题,不考虑它的一些特殊性质来作为一个搜索问题。(因为这两个问题本身就可以用经典搜索策略来解决,这里只是忽略掉问题的一些性质来模拟一个不可用经典搜索解决的问题)
首先对八皇后问题和八数码问题做个简单的介绍:
八皇后问题:
The eight queens puzzle is the problem of placing eight chess queens on an 8×8 chessboard so that no two queens threaten each other. Thus, a solution requires that no two queens share the same row, column, or diagonal.
八数码问题:
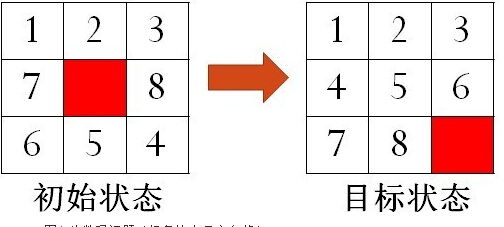
对给的任意一个初始状态,找到回到目标状态的步骤。
这两个问题都是经典的搜索问题,用DFS或BFS都可以找到解,这里我们探讨的是爬山法,随机重启爬山法和模拟退火算法对这两个问题的求解性能和能力。
首先,编写测例生成器,我选择生成100k个初始状态的测例,生成思想:
八皇后:生成八个1-8的随机数作为一个八皇后的初始状态,数字表示在每一列皇后的位置,例如4 6 8 2 7 1 3 5对应如下状态

八数码:终点位置开始随机移动10k步达到一个有解初始状态
测例生成器代码如下:
1 /* 2 * this program is used for generate the majority of 8 digits problems and 8 queens problems 3 */ 4 5 #include <cstdio> 6 #include <cstdlib> 7 8 #define TESRCASE 100000 9 #define STEP 10000 10 #define UP 0 11 #define DOWN 1 12 #define LEFT 2 13 #define RIGHT 3 14 15 inline void swap(int *a, int *b) { 16 *a ^= *b ^= *a ^= *b; 17 } 18 19 void generate_8_digits_problem() { 20 FILE *fp = fopen("testcase_8_digits_problem", "w"); 21 int testcase = TESRCASE, direction, position, steps; 22 while (testcase--) { 23 int state[9] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 0}; 24 steps = STEP; 25 position = 9; 26 while (steps--) { 27 direction = rand() % 4; 28 switch (direction) { 29 case UP: 30 if (position <= 3) 31 break; 32 else { 33 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position - 4]), position -= 3; 34 break; 35 } 36 case DOWN: 37 if (position >= 7) 38 break; 39 else { 40 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position + 2]), position += 3; 41 break; 42 } 43 case LEFT: 44 if (position % 3 == 1) 45 break; 46 else { 47 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position - 2]), position--; 48 break; 49 } 50 case RIGHT: 51 if (position % 3 == 0) 52 break; 53 else { 54 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position]), position++; 55 break; 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 fprintf(fp, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d\n", state[0], state[1], state[2], state[3], state[4], state[5], state[6], state[7], state[8]); 60 } 61 fclose(fp); 62 } 63 64 void generate_8_queens_problem() { 65 FILE *fp = fopen("testcase_8_queens_problem", "w"); 66 int testcase = TESRCASE, state[8], position, i; 67 while (testcase--) { 68 for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) 69 position = rand() % 8 + 1, state[i] = position; 70 fprintf(fp, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d\n", state[0], state[1], state[2], state[3], state[4], state[5], state[6], state[7]); 71 } 72 fclose(fp); 73 } 74 75 int main() { 76 generate_8_digits_problem(); 77 generate_8_queens_problem(); 78 return 0; 79 }
好,现在我们就得到了八皇后问题和八数码问题各100k个初始状态的测例了,分别保存在testcase_8_digits_problem和testcase_8_queens_problem中,每个测例占用1行。
首先测试爬山法,我们约定用成功的测例的平均时间作为性能指标,用测例的解决率作为能力指标。
爬山法的思想:对每一个状态,永远像最理想的状态前进(贪心)。
对八皇后问题来说,我们用相互碰撞的皇后对作为状态的权重(weight),那么爬山法的做法就是对每一个后继状态计算weight,记录下最小weight的状态,前进。
对八数码问题来说,我们用移动后曼哈顿距离作为状态权重(weight),最小weight的下一状态作为前进状态。
如果周围的所有状态都不能达到“爬山”的效果,则算法达到一个山脊(极大值),如果未找到解则认为算法失败。
爬山法测试代码如下:
1 # ifndef CLK_TCK 2 # define CLK_TCK CLOCKS_PER_SEC 3 # endif 4 5 #include <cstdio> 6 #include <ctime> 7 #include <cmath> 8 #include <cstdlib> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <algorithm> 11 12 #define TESRCASE 100000 13 #define UP 0 14 #define DOWN 1 15 #define LEFT 2 16 #define RIGHT 3 17 18 struct State { 19 int direction, diff_manhattan; 20 State(int i, int dis) { 21 this->direction = i; 22 this->diff_manhattan = dis; 23 } 24 bool operator<(const State &s) const { 25 return diff_manhattan > s.diff_manhattan; 26 } 27 }; 28 29 double eight_digits_problem_time; 30 double eight_queens_problem_time; 31 int eight_digits_problem_failed_times; 32 int eight_queens_problem_failed_times; 33 int diff_manhattan_distance; 34 35 inline void swap(int *a, int *b) { 36 *a ^= *b ^= *a ^= *b; 37 } 38 39 inline bool solved(int *state) { 40 for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) 41 if (state[i] != i + 1) 42 return false; 43 return true; 44 } 45 46 inline int manhattan_distance(int num, int position) { 47 int dest_x = ceil(num / 3), dest_y = (num - 1) % 3 + 1, position_x = ceil(position / 3), position_y = (position - 1) % 3 + 1; 48 return abs(dest_x - position_x) + abs(dest_y - position_y); 49 } 50 51 bool eight_digits_better(int *state, int position, int direction) { 52 switch (direction) { 53 case UP: 54 if (position <= 3) 55 return false; 56 else { 57 diff_manhattan_distance = manhattan_distance(state[position - 4], position - 3) - manhattan_distance(state[position - 4], position); 58 return manhattan_distance(state[position - 4], position - 3) > manhattan_distance(state[position - 4], position); 59 } 60 case DOWN: 61 if (position >= 7) 62 return false; 63 else { 64 diff_manhattan_distance = manhattan_distance(state[position + 2], position + 3) - manhattan_distance(state[position + 2], position); 65 return manhattan_distance(state[position + 2], position + 3) > manhattan_distance(state[position + 2], position); 66 } 67 case LEFT: 68 if (position % 3 == 1) 69 return false; 70 else { 71 diff_manhattan_distance = manhattan_distance(state[position - 2], position - 1) - manhattan_distance(state[position - 2], position); 72 return manhattan_distance(state[position - 2], position - 1) > manhattan_distance(state[position - 2], position); 73 } 74 case RIGHT: 75 if (position % 3 == 0) 76 return false; 77 else { 78 diff_manhattan_distance = manhattan_distance(state[position], position + 1) - manhattan_distance(state[position], position); 79 return manhattan_distance(state[position], position + 1) > manhattan_distance(state[position], position); 80 } 81 } 82 return false; 83 } 84 85 void solve_one_case_of_8_digits_problem(int *state) { 86 clock_t start_time = clock(); 87 int position, i; 88 bool found; 89 for (i = 0; i < 9; i++) 90 if (state[i] == 0) { 91 position = i + 1; 92 break; 93 } 94 while (!solved(state)) { 95 found = false; 96 std::vector<State> v; 97 for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 98 if (eight_digits_better(state, position, i)) { 99 found = true; 100 v.push_back(State(i, diff_manhattan_distance)); 101 } 102 if (i == 3 && found) { 103 std::sort(v.begin(), v.end()); 104 switch (v[0].direction) { 105 case UP: 106 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position - 4]), position -= 3; 107 break; 108 case DOWN: 109 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position + 2]), position += 3; 110 break; 111 case LEFT: 112 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position - 2]), position--; 113 break; 114 case RIGHT: 115 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position]), position++; 116 break; 117 } 118 } 119 } 120 if (!found) { 121 eight_digits_problem_failed_times++; 122 return; 123 } 124 } 125 eight_digits_problem_time += (double)(clock() - start_time) / CLK_TCK; 126 } 127 128 void solve_8_digits_problem() { 129 FILE *fp = fopen("testcase_8_digits_problem", "r"); 130 int original_state[9]; 131 while (fscanf(fp, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d", original_state, original_state + 1, original_state + 2, original_state + 3, original_state + 4, original_state + 5, original_state + 6, original_state + 7, original_state + 8) != EOF) 132 solve_one_case_of_8_digits_problem(original_state); 133 fclose(fp); 134 } 135 136 int peers_of_attacking_queens(int *state) { 137 int peers = 0, i, j, k; 138 for (i = 0; i < 7; i++) { 139 for (j = i + 1; j < 8; j++) 140 if (state[j] == state[i]) 141 peers++; 142 for (j = i + 1, k = state[i] + 1; j < 8 && k <= 8; j++, k++) 143 if (state[j] == k) 144 peers++; 145 for (j = i + 1, k = state[i] - 1; j < 8 && k >= 1; j++, k--) 146 if (state[j] == k) 147 peers++; 148 } 149 return peers; 150 } 151 152 void solve_one_case_of_8_queens_problem(int *state) { 153 clock_t start_time = clock(); 154 int h = peers_of_attacking_queens(state), i, j, best_i, best_j, temp, record; 155 while (h != 0) { 156 best_i = -1; 157 for (i = 1; i <= 8; i++) { 158 record = state[i - 1]; 159 for (j = 1; j <= 8; j++) { 160 if (j != record) { 161 state[i - 1] = j; 162 temp = peers_of_attacking_queens(state); 163 if (temp < h) 164 h = temp, best_i = i, best_j = j; 165 } 166 } 167 state[i - 1] = record; 168 } 169 if (best_i == -1) { 170 eight_queens_problem_failed_times++; 171 return; 172 } 173 state[best_i - 1] = best_j; 174 } 175 eight_queens_problem_time += (double)(clock() - start_time) / CLK_TCK; 176 } 177 178 void solve_8_queens_problem() { 179 FILE *fp = fopen("testcase_8_queens_problem", "r"); 180 int original_state[8]; 181 while (fscanf(fp, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d", original_state, original_state + 1, original_state + 2, original_state + 3, original_state + 4, original_state + 5, original_state + 6, original_state + 7) != EOF) 182 solve_one_case_of_8_queens_problem(original_state); 183 fclose(fp); 184 } 185 186 void print_result() { 187 printf("eight digits problem average solved times: %lf\n", eight_digits_problem_time / (double)(TESRCASE - eight_digits_problem_failed_times)); 188 printf("eight digits problem solved rate: %lf\n", 1 - double(eight_digits_problem_failed_times) / TESRCASE); 189 printf("eight queens problem average solved times: %lf\n", eight_queens_problem_time / (double)(TESRCASE - eight_queens_problem_failed_times)); 190 printf("eight queens problem solved rate: %lf\n", 1 - double(eight_queens_problem_failed_times) / TESRCASE); 191 } 192 193 int main() { 194 eight_digits_problem_time = 0; 195 eight_queens_problem_time = 0; 196 eight_digits_problem_failed_times = 0; 197 eight_queens_problem_failed_times = 0; 198 solve_8_digits_problem(); 199 solve_8_queens_problem(); 200 print_result(); 201 return 0; 202 }
测试结果如下:

我们可以看到,用爬山法来解决八数码问题解决率是非常非常低的,99.9%+的测例用爬山法是无法得到解的。
而对于八皇后问题,爬山法解决率也不是很理想,14.6%的测例是可以找到解的。
优点是平均解决时间短,因为贪心并不需要回溯,找到底就结束了,可以理解为不回溯的启发式DFS。
然后是随机重启爬山法
随机重启爬山法的思想是,对于给定的初始状态如果不能找到解,自己随机生成一个初始状态重启求解直到找到最终的解为止。
这个作为对于八皇后问题来说是合情合理的作为,对于八数码问题可能有人会认为是不妥当的,因为八数码问题的目标就是给定初始状态,找到到达最终状态的路线,初始状态是不能随意改变的。
而八皇后问题不一样,八皇后问题目标就是找到最终状态,所有初始状态随机改变是可以允许的。
提出这个问题的读者可以回到本文最开始理解一些我描述的前提。
代码如下:
1 # ifndef CLK_TCK 2 # define CLK_TCK CLOCKS_PER_SEC 3 # endif 4 5 #include <cstdio> 6 #include <ctime> 7 #include <cmath> 8 #include <cstdlib> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <algorithm> 11 12 #define TESRCASE 100000 13 #define STEP 100 14 #define UP 0 15 #define DOWN 1 16 #define LEFT 2 17 #define RIGHT 3 18 19 struct State { 20 int direction, diff_manhattan; 21 State(int i, int dis) { 22 this->direction = i; 23 this->diff_manhattan = dis; 24 } 25 bool operator<(const State &s) const { 26 return diff_manhattan > s.diff_manhattan; 27 } 28 }; 29 30 double eight_digits_problem_time; 31 double eight_queens_problem_time; 32 int eight_digits_problem_failed_times; 33 int eight_queens_problem_failed_times; 34 int diff_manhattan_distance; 35 36 inline void swap(int *a, int *b) { 37 *a ^= *b ^= *a ^= *b; 38 } 39 40 inline bool solved(int *state) { 41 for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) 42 if (state[i] != i + 1) 43 return false; 44 return true; 45 } 46 47 inline int manhattan_distance(int num, int position) { 48 int dest_x = ceil(num / 3), dest_y = (num - 1) % 3 + 1, position_x = ceil(position / 3), position_y = (position - 1) % 3 + 1; 49 return abs(dest_x - position_x) + abs(dest_y - position_y); 50 } 51 52 bool eight_digits_better(int *state, int position, int direction) { 53 switch (direction) { 54 case UP: 55 if (position <= 3) 56 return false; 57 else { 58 diff_manhattan_distance = manhattan_distance(state[position - 4], position - 3) - manhattan_distance(state[position - 4], position); 59 return manhattan_distance(state[position - 4], position - 3) > manhattan_distance(state[position - 4], position); 60 } 61 case DOWN: 62 if (position >= 7) 63 return false; 64 else { 65 diff_manhattan_distance = manhattan_distance(state[position + 2], position + 3) - manhattan_distance(state[position + 2], position); 66 return manhattan_distance(state[position + 2], position + 3) > manhattan_distance(state[position + 2], position); 67 } 68 case LEFT: 69 if (position % 3 == 1) 70 return false; 71 else { 72 diff_manhattan_distance = manhattan_distance(state[position - 2], position - 1) - manhattan_distance(state[position - 2], position); 73 return manhattan_distance(state[position - 2], position - 1) > manhattan_distance(state[position - 2], position); 74 } 75 case RIGHT: 76 if (position % 3 == 0) 77 return false; 78 else { 79 diff_manhattan_distance = manhattan_distance(state[position], position + 1) - manhattan_distance(state[position], position); 80 return manhattan_distance(state[position], position + 1) > manhattan_distance(state[position], position); 81 } 82 } 83 return false; 84 } 85 86 void eight_digits_random_state(int *s) { 87 int state[9] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 0}, steps, position, direction; 88 steps = STEP; 89 position = 9; 90 while (steps--) { 91 direction = rand() % 4; 92 switch (direction) { 93 case UP: 94 if (position <= 3) 95 break; 96 else { 97 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position - 4]), position -= 3; 98 break; 99 } 100 case DOWN: 101 if (position >= 7) 102 break; 103 else { 104 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position + 2]), position += 3; 105 break; 106 } 107 case LEFT: 108 if (position % 3 == 1) 109 break; 110 else { 111 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position - 2]), position--; 112 break; 113 } 114 case RIGHT: 115 if (position % 3 == 0) 116 break; 117 else { 118 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position]), position++; 119 break; 120 } 121 } 122 } 123 for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) 124 s[i] = state[i]; 125 } 126 127 void solve_one_case_of_8_digits_problem(int *state) { 128 clock_t start_time = clock(); 129 int position, i; 130 bool found; 131 for (i = 0; i < 9; i++) 132 if (state[i] == 0) { 133 position = i + 1; 134 break; 135 } 136 while (!solved(state)) { 137 found = false; 138 std::vector<State> v; 139 for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 140 if (eight_digits_better(state, position, i)) { 141 found = true; 142 v.push_back(State(i, diff_manhattan_distance)); 143 } 144 if (i == 3 && found) { 145 std::sort(v.begin(), v.end()); 146 switch (v[0].direction) { 147 case UP: 148 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position - 4]), position -= 3; 149 break; 150 case DOWN: 151 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position + 2]), position += 3; 152 break; 153 case LEFT: 154 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position - 2]), position--; 155 break; 156 case RIGHT: 157 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position]), position++; 158 break; 159 } 160 } 161 } 162 if (!found) 163 eight_digits_random_state(state); 164 } 165 eight_digits_problem_time += (double)(clock() - start_time) / CLK_TCK; 166 } 167 168 void solve_8_digits_problem() { 169 FILE *fp = fopen("testcase_8_digits_problem", "r"); 170 int original_state[9]; 171 while (fscanf(fp, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d", original_state, original_state + 1, original_state + 2, original_state + 3, original_state + 4, original_state + 5, original_state + 6, original_state + 7, original_state + 8) != EOF) 172 solve_one_case_of_8_digits_problem(original_state); 173 fclose(fp); 174 } 175 176 int peers_of_attacking_queens(int *state) { 177 int peers = 0, i, j, k; 178 for (i = 0; i < 7; i++) { 179 for (j = i + 1; j < 8; j++) 180 if (state[j] == state[i]) 181 peers++; 182 for (j = i + 1, k = state[i] + 1; j < 8 && k <= 8; j++, k++) 183 if (state[j] == k) 184 peers++; 185 for (j = i + 1, k = state[i] - 1; j < 8 && k >= 1; j++, k--) 186 if (state[j] == k) 187 peers++; 188 } 189 return peers; 190 } 191 192 inline void eight_queens_random_state(int *state) { 193 for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) 194 state[i] = rand() % 8 + 1; 195 } 196 197 void solve_one_case_of_8_queens_problem(int *state) { 198 clock_t start_time = clock(); 199 int h = peers_of_attacking_queens(state), i, j, best_i, best_j, temp, record; 200 while (h != 0) { 201 best_i = -1; 202 for (i = 1; i <= 8; i++) { 203 record = state[i - 1]; 204 for (j = 1; j <= 8; j++) { 205 if (j != record) { 206 state[i - 1] = j; 207 temp = peers_of_attacking_queens(state); 208 if (temp < h) 209 h = temp, best_i = i, best_j = j; 210 } 211 } 212 state[i - 1] = record; 213 } 214 if (best_i == -1) 215 eight_queens_random_state(state), h = peers_of_attacking_queens(state); 216 else 217 state[best_i - 1] = best_j; 218 } 219 eight_queens_problem_time += (double)(clock() - start_time) / CLK_TCK; 220 } 221 222 void solve_8_queens_problem() { 223 FILE *fp = fopen("testcase_8_queens_problem", "r"); 224 int original_state[8]; 225 while (fscanf(fp, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d", original_state, original_state + 1, original_state + 2, original_state + 3, original_state + 4, original_state + 5, original_state + 6, original_state + 7) != EOF) 226 solve_one_case_of_8_queens_problem(original_state); 227 fclose(fp); 228 } 229 230 void print_result() { 231 printf("eight digits problem average solved times: %lf\n", eight_digits_problem_time / (double)(TESRCASE - eight_digits_problem_failed_times)); 232 printf("eight digits problem solved rate: %lf\n", 1 - double(eight_digits_problem_failed_times) / TESRCASE); 233 printf("eight queens problem average solved times: %lf\n", eight_queens_problem_time / (double)(TESRCASE - eight_queens_problem_failed_times)); 234 printf("eight queens problem solved rate: %lf\n", 1 - double(eight_queens_problem_failed_times) / TESRCASE); 235 } 236 237 int main() { 238 eight_digits_problem_time = 0; 239 eight_queens_problem_time = 0; 240 eight_digits_problem_failed_times = 0; 241 eight_queens_problem_failed_times = 0; 242 solve_8_digits_problem(); 243 solve_8_queens_problem(); 244 print_result(); 245 return 0; 246 }
测试结果如下:

我们可以看到随机重启爬山法的解决率是接近1的(不能说是1,因为确实存在无论怎么重启都找不到解的可能性)
但是在每个测例解决的时间消耗上面就大打折扣了,对八数码问题,是爬山法单个测例解决时间的600倍,对八皇后问题单个测例平均解决时间大概是7倍。
这个时间效率和爬山法的问题解决率有关系,解决率越大时间差距越小。
现在测试最后一个算法:模拟退火算法
模拟退火算法的思想:模拟炼金退火的步骤,温度随时间下降,在温度高的时候,分子是活跃的,有较大可能性随机运动。
对应到具体问题上就是:对每一个后继状态,如果找到的状态不能使weight更好,也有exp(weight/temperature)的可能性去走这个状态,然后随着温度下降,这个概率越来越小,达到模拟退火的效果。
我选择温度下降为比例下降,系数为0.8,每一个温度最多可以持续300次迭代,终止温度为0.000000001,八数码问题起始温度为10,八皇后问题起始温度为50。
代码如下:
1 # ifndef CLK_TCK 2 # define CLK_TCK CLOCKS_PER_SEC 3 # endif 4 5 #include <cstdio> 6 #include <ctime> 7 #include <cmath> 8 #include <cstdlib> 9 #include <vector> 10 #include <algorithm> 11 12 #define TESRCASE 100000 13 #define UP 0 14 #define DOWN 1 15 #define LEFT 2 16 #define RIGHT 3 17 #define EIGHT_DIGITS_ORIGINAL_TEMPERATURE 10 18 #define EIGHT_QUEENS_ORIGINAL_TEMPERATURE 50 19 #define MAX_TRIES_IN_ONE_TEMPERATURE 300 20 #define STOP_TEMPERATURE 0.000000001 21 #define COLD_DOWN_RATE 0.8 22 23 double eight_digits_problem_time; 24 double eight_queens_problem_time; 25 int eight_digits_problem_failed_times; 26 int eight_queens_problem_failed_times; 27 double temperature; 28 29 inline void swap(int *a, int *b) { 30 *a ^= *b ^= *a ^= *b; 31 } 32 33 inline bool solved(int *state) { 34 for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) 35 if (state[i] != i + 1) 36 return false; 37 return true; 38 } 39 40 inline int manhattan_distance(int num, int position) { 41 int dest_x = ceil(num / 3), dest_y = (num - 1) % 3 + 1, position_x = ceil(position / 3), position_y = (position - 1) % 3 + 1; 42 return abs(dest_x - position_x) + abs(dest_y - position_y); 43 } 44 45 bool eight_digits_better(int *state, int position, int direction) { 46 int dis; 47 switch (direction) { 48 case UP: 49 if (position <= 3) 50 return false; 51 else { 52 dis = manhattan_distance(state[position - 4], position - 3) - manhattan_distance(state[position - 4], position); 53 return (dis > 0) ? true : ((double)(rand() % 1000) / 1000) < exp(dis / temperature); 54 } 55 case DOWN: 56 if (position >= 7) 57 return false; 58 else { 59 dis = manhattan_distance(state[position + 2], position + 3) - manhattan_distance(state[position + 2], position); 60 return (dis > 0) ? true : ((double)(rand() % 1000) / 1000) < exp(dis / temperature); 61 } 62 case LEFT: 63 if (position % 3 == 1) 64 return false; 65 else { 66 dis = manhattan_distance(state[position - 2], position - 1) - manhattan_distance(state[position - 2], position); 67 return (dis > 0) ? true : ((double)(rand() % 1000) / 1000) < exp(dis / temperature); 68 } 69 case RIGHT: 70 if (position % 3 == 0) 71 return false; 72 else { 73 dis = manhattan_distance(state[position], position + 1) - manhattan_distance(state[position], position); 74 return (dis > 0) ? true : ((double)(rand() % 1000) / 1000) < exp(dis / temperature); 75 } 76 } 77 return false; 78 } 79 80 void solve_one_case_of_8_digits_problem(int *state) { 81 clock_t start_time = clock(); 82 int position, i, tries_count; 83 bool found; 84 for (i = 0; i < 9; i++) 85 if (state[i] == 0) { 86 position = i + 1; 87 break; 88 } 89 temperature = EIGHT_DIGITS_ORIGINAL_TEMPERATURE; 90 tries_count = MAX_TRIES_IN_ONE_TEMPERATURE; 91 while (!solved(state)) { 92 found = false; 93 for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) 94 if (eight_digits_better(state, position, i)) { 95 found = true; 96 switch (i) { 97 case UP: 98 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position - 4]), position -= 3; 99 break; 100 case DOWN: 101 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position + 2]), position += 3; 102 break; 103 case LEFT: 104 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position - 2]), position--; 105 break; 106 case RIGHT: 107 swap(&state[position - 1], &state[position]), position++; 108 break; 109 } 110 break; 111 } 112 if (--tries_count == 0) 113 tries_count = MAX_TRIES_IN_ONE_TEMPERATURE, temperature *= COLD_DOWN_RATE; 114 if (!found || temperature < STOP_TEMPERATURE) { 115 eight_digits_problem_failed_times++; 116 return; 117 } 118 } 119 eight_digits_problem_time += (double)(clock() - start_time) / CLK_TCK; 120 } 121 122 void solve_8_digits_problem() { 123 FILE *fp = fopen("testcase_8_digits_problem", "r"); 124 int original_state[9]; 125 while (fscanf(fp, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d", original_state, original_state + 1, original_state + 2, original_state + 3, original_state + 4, original_state + 5, original_state + 6, original_state + 7, original_state + 8) != EOF) 126 solve_one_case_of_8_digits_problem(original_state); 127 fclose(fp); 128 } 129 130 int peers_of_attacking_queens(int *state) { 131 int peers = 0, i, j, k; 132 for (i = 0; i < 7; i++) { 133 for (j = i + 1; j < 8; j++) 134 if (state[j] == state[i]) 135 peers++; 136 for (j = i + 1, k = state[i] + 1; j < 8 && k <= 8; j++, k++) 137 if (state[j] == k) 138 peers++; 139 for (j = i + 1, k = state[i] - 1; j < 8 && k >= 1; j++, k--) 140 if (state[j] == k) 141 peers++; 142 } 143 return peers; 144 } 145 146 void solve_one_case_of_8_queens_problem(int *state) { 147 clock_t start_time = clock(); 148 int h = peers_of_attacking_queens(state), i, j, best_i, best_j, temp, record, tries_count, temp_h; 149 temperature = EIGHT_QUEENS_ORIGINAL_TEMPERATURE; 150 tries_count = MAX_TRIES_IN_ONE_TEMPERATURE; 151 while (h != 0) { 152 temp_h = 28; 153 for (i = 1; i <= 8; i++) { 154 record = state[i - 1]; 155 for (j = 1; j <= 8; j++) { 156 if (j != record) { 157 state[i - 1] = j; 158 temp = peers_of_attacking_queens(state); 159 if (temp < temp_h) 160 temp_h = temp, best_i = i, best_j = j; 161 } 162 } 163 state[i - 1] = record; 164 } 165 if (--tries_count == 0) 166 tries_count = MAX_TRIES_IN_ONE_TEMPERATURE, temperature *= COLD_DOWN_RATE; 167 if (!(temperature < STOP_TEMPERATURE) && (temp_h < h || ((double)(rand() % 1000) / 1000) < exp(temp_h / temperature))) 168 state[best_i - 1] = best_j, h = temp_h; 169 else { 170 eight_queens_problem_failed_times++; 171 return; 172 } 173 } 174 eight_queens_problem_time += (double)(clock() - start_time) / CLK_TCK; 175 } 176 177 void solve_8_queens_problem() { 178 FILE *fp = fopen("testcase_8_queens_problem", "r"); 179 int original_state[8]; 180 while (fscanf(fp, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d", original_state, original_state + 1, original_state + 2, original_state + 3, original_state + 4, original_state + 5, original_state + 6, original_state + 7) != EOF) 181 solve_one_case_of_8_queens_problem(original_state); 182 fclose(fp); 183 } 184 185 void print_result() { 186 printf("eight digits problem average solved times: %lf\n", eight_digits_problem_time / (double)(TESRCASE - eight_digits_problem_failed_times)); 187 printf("eight digits problem solved rate: %lf\n", 1 - double(eight_digits_problem_failed_times) / TESRCASE); 188 printf("eight queens problem average solved times: %lf\n", eight_queens_problem_time / (double)(TESRCASE - eight_queens_problem_failed_times)); 189 printf("eight queens problem solved rate: %lf\n", 1 - double(eight_queens_problem_failed_times) / TESRCASE); 190 } 191 192 int main() { 193 eight_digits_problem_time = 0; 194 eight_queens_problem_time = 0; 195 eight_digits_problem_failed_times = 0; 196 eight_queens_problem_failed_times = 0; 197 solve_8_digits_problem(); 198 solve_8_queens_problem(); 199 print_result(); 200 return 0; 201 }
这个测试时间比较久,题主跑了6个小时才跑出来,测试结果如下:

可以看到,模拟退火算法的性能是比较优秀的,和爬山法的解决效率只相差0-1个数量级。
而且解决率相比爬山法也大幅度提升,对于八数码问题问题解决率提升了10倍左右,对于八皇后问题解决率也提升了2倍多。
结论:
1. 解决NP问题用模拟退火算法在性能上和解决率上都有出色的表现。
2. 随机重启爬山法来达到很高的解决率,但是时间效率非常低下。
3. 爬山法有最高性能,但是问题解决率不堪入目。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号