[RN] 02 - Overview: React Native Practice of 50 lectures
观看笔记:零基础 React Native 实战开发视频 50讲
本篇效果:RN入门,整体认识
基本原理 # 1

React到RN # 2
一个简单的例子
/** * Sample React Native App * https://github.com/facebook/react-native */ 'use strict'; import React, { AppRegistry, Component, StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native'; # 引入组件
class DongFang extends Component { render() { return ( <View style={styles.container}> <Text style={styles.welcome}> Welcome to React Native!东方耀的第5课 </Text> <Text style={styles.instructions}> To get started, edit index.android.js </Text> <Text style={styles.instructions}> Shake or press menu button for dev menu </Text> </View> ); } }
# 样式表 系统api const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { # 可伸缩的表 flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center', backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF', }, welcome: { fontSize: 20, textAlign: 'center', margin: 10, }, instructions: { textAlign: 'center', color: '#333333', marginBottom: 5, }, }); AppRegistry.registerComponent('DongFang', () => DongFang);
flexbox布局 # 3,4,5
UI利器:弹性盒子布局,主流浏览器都支持。
讲义:http://www.cnblogs.com/dfy888/p/5374329.html
参考:阮一峰: Flex 布局教程:语法篇
参考:阮一峰: Flex 布局教程:实例篇
JSX入门 # 6
jsx是个语法糖;
(1) 转换 解析器 html --> js,然后在浏览器运行。

(2) 执行js表达式。html with js --> js
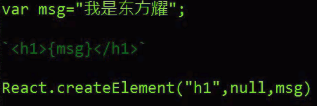
(3) 执行js表达式。属性 --> js
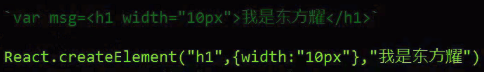
(4) 执行js表达式。延展属性 --> js,使用ES6语法。

(5) 以字符串的形式完整显示HTML,借助_html属性

(6) 样式style的使用,比如颜色,字体大小。

(7) 事件绑定 - button
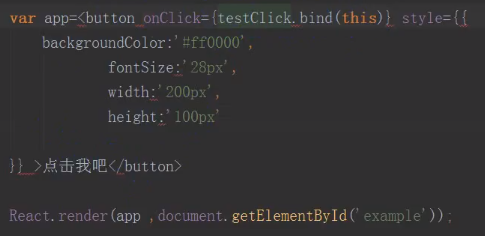
ReactJS代码结构 # 7
React.createClass: 创建组件类的方法。
React.render: 将制定组件渲染到制定的DOM节点。【会被ReactDOM.render替代】
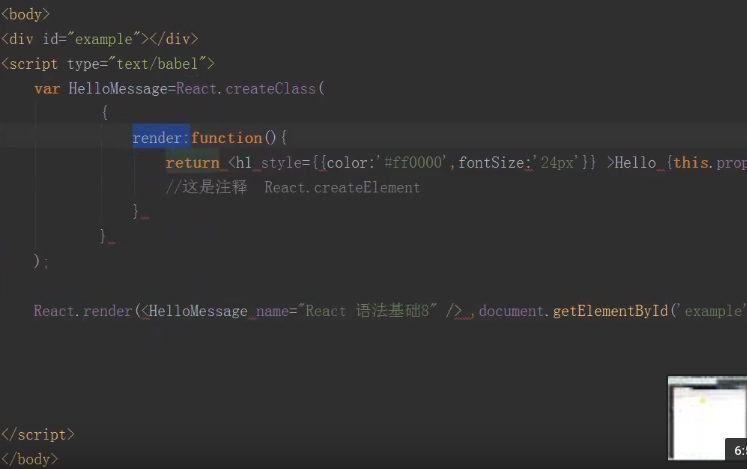
ReactJS组件生命周期 # 8
Ref: React Native Component Lifecycle【简洁,清晰】
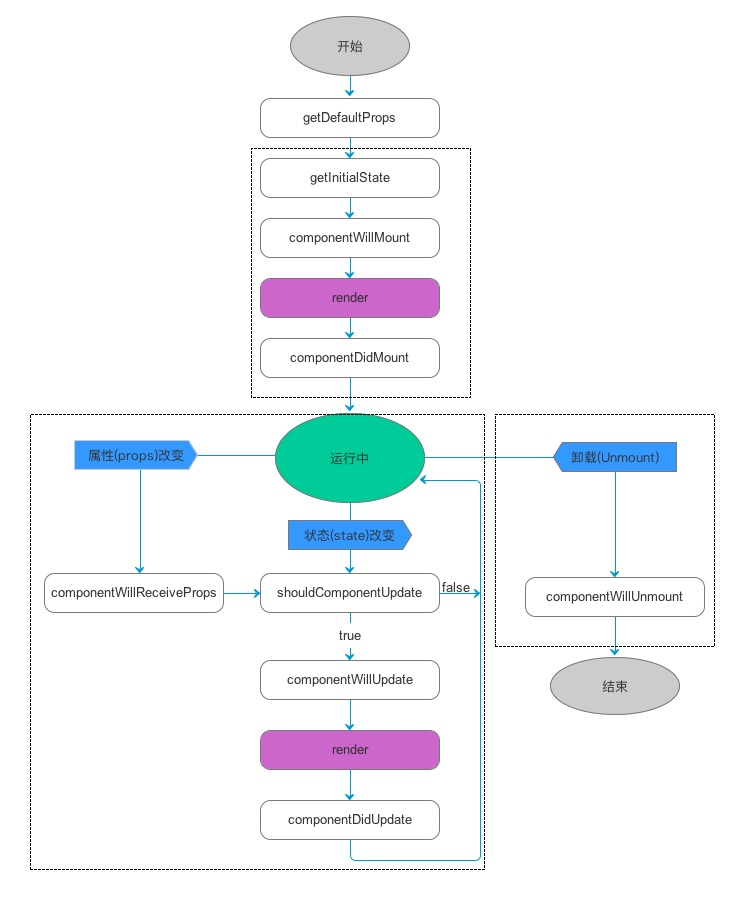
如图,可以把组件生命周期大致分为三个阶段:
-
- 第一阶段:是组件第一次绘制阶段,如图中的上面虚线框内,在这里完成了组件的加载和初始化;
- 第二阶段:是组件在运行和交互阶段,如图中左下角虚线框,这个阶段组件可以处理用户交互,或者接收事件更新界面;
- 第三阶段:是组件卸载消亡的阶段,如图中右下角的虚线框中,这里做一些组件的清理工作。
| 生命周期 | 调用次数 | 能否使用 setSate() |
|---|---|---|
| 创建阶段,处理props的默认值 | ||
| getDefaultProps | 1(全局调用一次) | 否 |
|
实例化阶段,React.render(<HelloMessage 启动之后 State:ReactJS内部监听state属性的变化,一旦发生变化,主动触发组件的render方法更新虚拟DOM结构, which is 真实的DOM结构映射成一个json数据结构。 |
||
| getInitialState | 1 | 否 |
| componentWillMount | 1 | 是 |
| render | >=1 | 否 |
| componentDidMount | 1 | 是 |
| 更新阶段,根据用户操作行为进行相应的页面结构的调整。 | ||
| componentWillReceiveProps | >=0 | 是 |
| shouldComponentUpdate | >=0 | 否 |
| componentWillUpdate | >=0 | 否 |
| componentDidUpdate | >=0 | 否 |
| 销毁阶段,取消事件绑定、移除虚拟DOM等。 | ||
| componentWillUnmount | 1 | 否 |
ReactJS组件通信 # 9
父子组件之间的通信方式?
Ref: http://blog.csdn.net/p106786860/article/details/52408875 【代码实例】
var Parent=React.craeteClass({
click:function() {
this.refs.child.getDOMNode().stype.color="red";
},
render:function() {
return (
<div onClick={this.click} >Parent is :
<Child name={this.props.name} ref="child"></Child>
</div> ); #子组件 调用 父组件
}
});
var Child=React.craeteClass({
render:function() {
return <span> {this.props.name} </span>
}
});
ReactDOM.render(<Parent name="React语法基础" />, document.getElementById('example'));
Ref: react native 之子组件和父组件之间的通信
*** 父组件 --> 子组件 ***
/** * Sample React Native App * https://github.com/facebook/react-native * 父组件传递给子组件 * 父组件把值或者navigator传给子组件,然后在子组件里面实现push和显示 */ import React, { Component } from 'react'; import ChildOne from './ChildOne' import { AppRegistry, StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native'; export default class HomeOne extends Component { render() { return (
// 类似:调用函数,将参数传入子函数,将参数看作一种通信方式 <ChildOne navigatorPush = {this.props.navigator} passValue = '我是一个父组件传给子组件的值'/> ); } } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center', backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF', }, welcome: { fontSize: 20, textAlign: 'center', margin: 10, }, instructions: { textAlign: 'center', color: '#333333', marginBottom: 5, }, });
子组件,childOne的代码:通过 this.props.属性名 使用传过来的值。
/** * Sample React Native App * https://github.com/facebook/react-native * 父组件传递给子组件 */ import React, { Component } from 'react'; import { AppRegistry, StyleSheet, Text, View, navigator, } from 'react-native';
import OneDetails from './OneDetails'
export default class ChildOne extends Component { render() { return ( <View style={styles.container}> <Text style={styles.welcome} onPress={()=>this.pushOneDetails()}> 我是子组件ONE </Text> <Text> {this.props.passValue} # 直接获取 </Text> </View> ); } pushOneDetails = ()=>{ this.props.navigatorPush.push({ component: OneDetails }) } } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center', backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF', }, welcome: { fontSize: 20, textAlign: 'center', margin: 10, }, instructions: { textAlign: 'center', color: '#333333', marginBottom: 5, }, });
*** 父组件 --> 子组件 ***
子组件通过定义一个属性直接把事件传递给主组件。
/** * Sample React Native App * https://github.com/facebook/react-native * 子组件传递给父组件 */ import React, { Component } from 'react'; import { AppRegistry, StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native'; export default class ChildTwo extends Component { static defaultProps = { two: '我是子组件传给主组件的值' }; render() { return ( <Text style={styles.welcome} onPress={()=>this.passMenthod()}> 我是子组件TWO </Text> ); } passMenthod = () =>{ this.props.pushDetails() } } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center', backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF', }, welcome: { fontSize: 20, textAlign: 'center', margin: 10, }, instructions: { textAlign: 'center', color: '#333333', marginBottom: 5, }, });
父组件这边直接通过子组件的属性来接受事件,从而在主组件这边push和pop。
/** * Sample React Native App * https://github.com/facebook/react-native * 子组件传递给父组件 * 子组件把事件或值传递给父组件,然后在父组件push和显示 */ import React, { Component } from 'react'; import { AppRegistry, StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native'; import ChildTwo from './ChildTwo' import TwoDetails from './TwoDetails'
export default class HomeTwo extends Component { // 构造 constructor(props) { super(props); // 初始状态 this.state = { value:'' }; } render() { return ( <View style={styles.container}> <ChildTwo pushDetails = {()=>this.pushDetails()} /> <Text> {ChildTwo.defaultProps.two} </Text> </View> ); } pushDetails = ()=>{ this.props.navigator.push({ component:TwoDetails }) } } const styles = StyleSheet.create({ container: { flex: 1, justifyContent: 'center', alignItems: 'center', backgroundColor: '#F5FCFF', }, welcome: { fontSize: 20, textAlign: 'center', margin: 10, }, instructions: { textAlign: 'center', color: '#333333', marginBottom: 5, }, });
总体感觉,需要一个系统的文章来学习,以上关于通信这块,还是很零碎,需要看书上的相关章节来系统地加强认识。
状态、属性、样式
继续细细分析【props】和【state】in: [RN] Try a little bit of React Native
我们使用两种数据来控制一个组件:props和state。
- props: 在父组件中指定,而且一经指定,在被指定的组件的生命周期中则不再改变。
- state: 对于需要改变的数据,我们需要使用state。
-
关于属性:props
/** * Sample React Native App * https://github.com/facebook/react-native * @flow */ import React, { Component } from 'react'; import { Platform, StyleSheet, Text, View, Image } from 'react-native'; export default class App extends Component { render() {
let pic = { uri: 'https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/de/Bananavarieties.jpg' }; // 如下:pic 被一个<Image/>控件所引用 return ( <Image source={pic} style={{width: 193, height: 110}}/> );
} }
{pic} 括号把JSX语句嵌入其中,括号里可能是表达式也可以是js变量,所以,这一切 都可以是 动态的。
例如下面这代码:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { AppRegistry, Text, View } from 'react-native';
// 创建了一个 Greeting 对象
class Greeting extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Text>Hello {this.props.name}!</Text>
);
}
}
class LotsOfGreetings extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={ {alignItems: 'center'} }>
<Greeting name='Rexxar' />
<Greeting name='Jaina' />
<Greeting name='Valeera' />
</View>
);
}
}
AppRegistry.registerComponent('LotsOfGreetings', () => LotsOfGreetings);
-
关于状态:state
1 .props是在父组件中指定,一经指定,在被指定的生命周期中则不再改变
2 .对于需要改变的数据,我们需要使用state
3 .需要在constructor中初始化state,然后在需要修改时调用setState方法。
/** * Sample React Native App * https://github.com/facebook/react-native * @flow 此代码可直接运行 */ import React, { Component } from 'react'; import { Platform, StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native'; class Blink extends Component {
constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { showText: true };
// 调用计时器方法 // 每1000毫秒对showText状态做一次取反操作 setInterval(() => { this.setState({ showText: !this.state.showText }); }, 1000); }
render() { // 根据当前showText的值决定是否显示text内容 let display = this.state.showText ? this.props.text : ' '; return ( <Text>{display}</Text> ); }
}
// main export default class App extends Component<Props> { render() { return ( <View> <Blink text='I love to blink' /> <Blink text='Yes blinking is so great' /> <Blink text='Why did they ever take this out of HTML' /> <Blink text='Look at me look at me look at me' /> </View> ); } }
-
关于样式:style
一个View可以有多个样式属性,他们以数组形势共存,
当然如果多个样式出现重复,排在右边的会覆盖之前的,具体情况我们看一例子:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { AppRegistry, StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native';
class LotsOfStyles extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View>
<Text style={styles.red}>just red</Text>
<Text style={styles.bigblue}>just bigblue</Text>
<Text style={[styles.bigblue, styles.red]}>bigblue, then red</Text>
<Text style={[styles.red, styles.bigblue]}>red, then bigblue</Text>
</View>
);
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
bigblue: {
color: 'blue',
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: 30,
},
red: {
color: 'red',
},
});
AppRegistry.registerComponent('LotsOfStyles', () => LotsOfStyles);
JSX实战 # 10,11
- 调试五步骤
(1). 启动js服务器。
(2). 确定手机连接可靠。
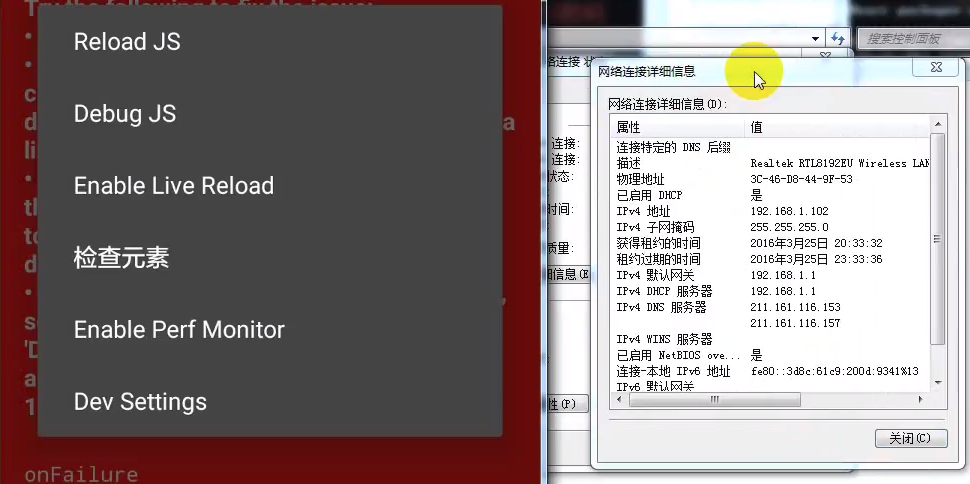
(3). 加载代码。

(4). 设置为与本地同一网段:Dev Settings。
(5). 点击Debug server host & port for device,设置ip地址。

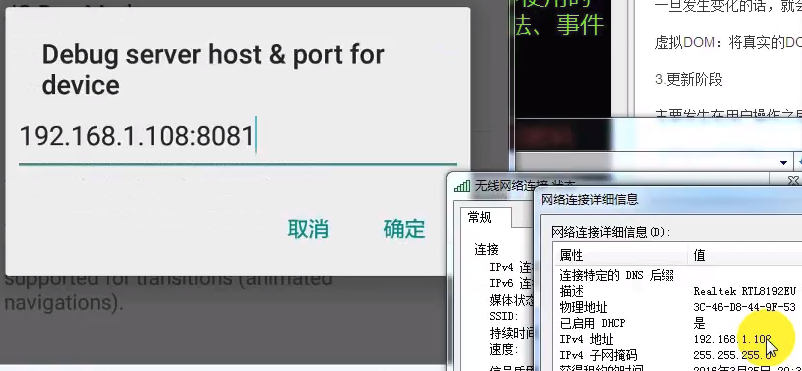
Reload JS:手动刷新
Debug JS:远端调试工具,需要chrome。
Enable Live Reload:自动刷新
检查元素
Enable Perf Monitor
Dev Settings
原理:包服务器,手机端调试依赖这个bundle,也涉及到热更新。

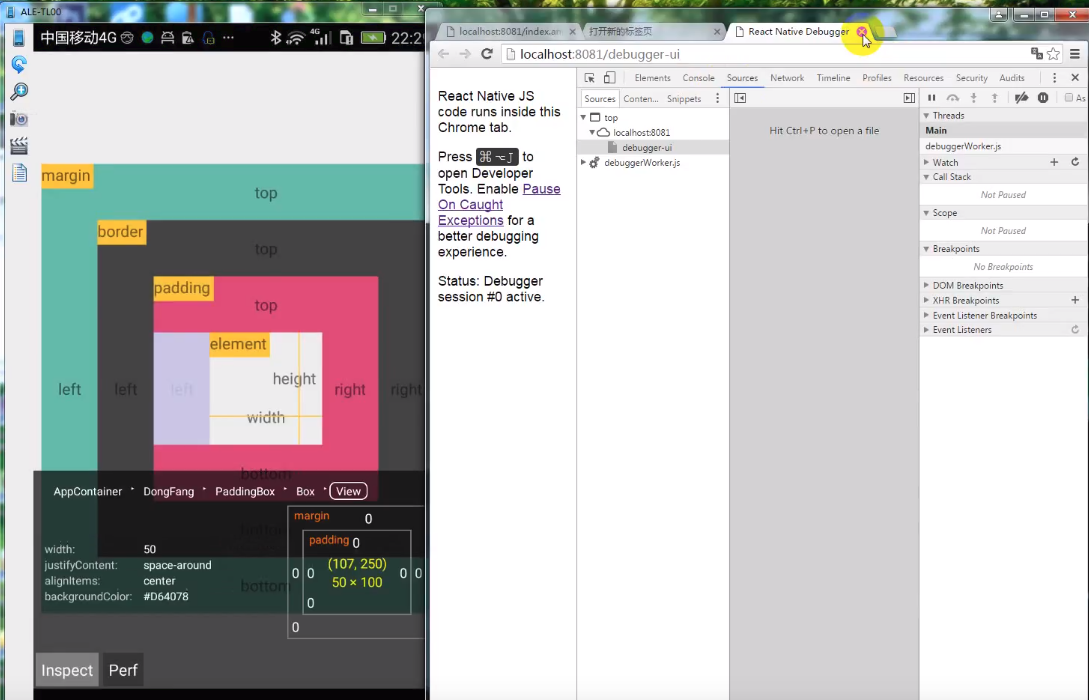
F12进入开发者模式,然后通过浏览器调试,这是Google的牛逼之处。【Debug JS】
当然,Facebook的RN也提供了在线手机上的简单版本的frond-end调试。【检查元素】
发布六步骤
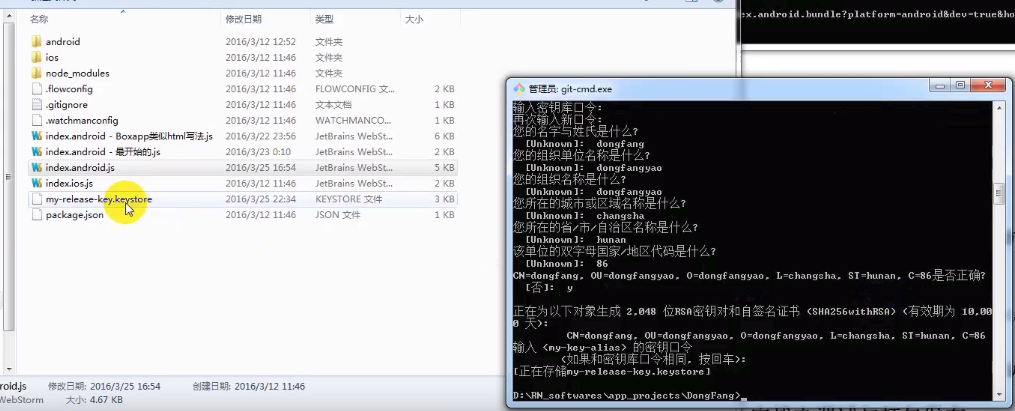
(1). 创建密钥
keytool -genkey -v -keystore my-release-key.keystore -alias my-key-alias -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -validity 10000
生成了用于应用发布的秘钥: my-release-key.keystore
(2). bundle文件
在工程目录下将index.android.bundle下载并保存到assets资源文件中。
首先,创建文件夹:./android/app/src/main/assets;然后,执行命令:
curl -k "http://localhost:8081/index.android.bundle" > android/app/src/main/assets/index.android.bundle
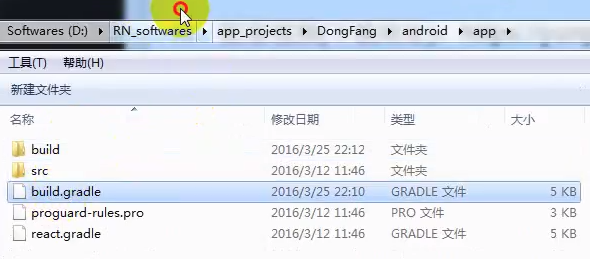
(3). 配置gradle中的签名
(4). 在build.gradle中设置密钥的属性
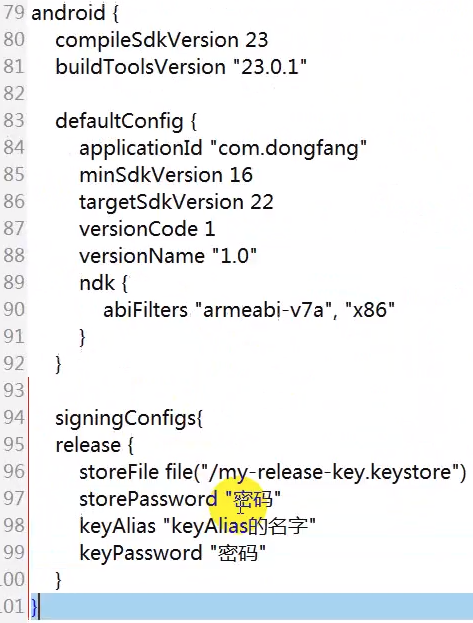
接下来,使签名生效:添加一行,如下:

(5). 为减小发布包的大小,修改如下属性为true

如果是涉及到第三方库,会修改app/proguard-rules.pro。在此,先保持默认配置。
(6). gradle打包并发布
在android目录下执行,便自动编译打包。
gradle assembleRelease
执行成功后在下面的目录中会生成对应的release的两个版本。
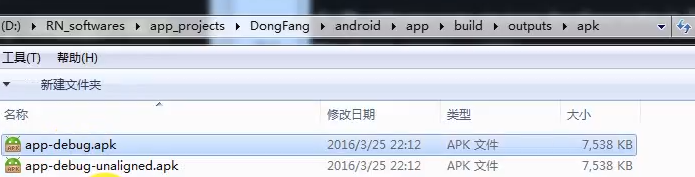
RN主目录:
keytool -genkey -v -keystore my-release-key.keystore -alias my-key-alias -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -validity 10000 [注:在产生的时候需要提供密钥和存储密码,后续会用到] mv my-release-key.keystore android/app/
Step 2:
android/gradle.properties文件: MYAPP_RELEASE_STORE_FILE = my-release-key.keystore // 签名文件
MYAPP_RELEASE_KEY_ALIAS = my-key-alias
MYAPP_RELEASE_STORE_PASSWORD = xx
MYAPP_RELEASE_KEY_PASSWORD = xx
[注意替换xx为你自己设置的密钥和存储密码]
Step 3:
android/app/build.gradle文件: ... android { ... defaultConfig { ... }
signingConfigs { release { storeFile file(MYAPP_RELEASE_STORE_FILE) storePassword MYAPP_RELEASE_STORE_PASSWORD keyAlias MYAPP_RELEASE_KEY_ALIAS keyPassword MYAPP_RELEASE_KEY_PASSWORD } }
buildTypes { release { ... signingConfig signingConfigs.release } } }
cd android/
./gradlew assembleRelease






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号