设计模式系列6-----C++实现状态模式(State Pattern)
什么是状态模式?
Definition: Allow an object to alter its behavior when its internal state changes. The object will appear to change its class.
当对象有几种状态时,不同状态时有不同的表现,为了避免复杂的ifelse逻辑,将每个状态的逻辑单独封装在自己的实现中,容易写出逻辑清晰的代码。
类图结构:

其实上图和策略模式的类图基本一致,那他们的差别在哪里呢?其实主要是应用的目的不一样:策略模式主要针对对象的某一种behavior有多种可能实现,而状态模式是当对象的状态有多种,每种状态下有不同表现,基本上状态模式封装的是一组behavior。
Example:
例子模拟游戏中的一种坦克,有两种状态:坦克状态(Tank),能移动,攻击为20;架起状态(Siege),无法移动,攻击力增强为100。
state.h如下:
class SiegeTank;
class ISiegeTankState
{
public:
virtual void move(int x, int y) = 0;
virtual void attack() = 0;
};
class SiegeState : public ISiegeTankState
{
public:
SiegeState(SiegeTank* pTank);
virtual void move(int x, int y);
virtual void attack();
private:
SiegeTank* m_pTank;
};
class TankState : public ISiegeTankState
{
public:
TankState(SiegeTank* pTank);
virtual void move(int x, int y);
virtual void attack();
private:
SiegeTank* m_pTank;
};
state.cpp如下:
#include "tank.h"
#include "state.h"
#include <iostream>
SiegeState::SiegeState( SiegeTank* pTank ) : m_pTank(pTank)
{
}
void SiegeState::move( int x, int y )
{
std::cout << "Can't move in siege mode." << std::endl;
}
void SiegeState::attack()
{
std::cout << "Attacking for 100" << std::endl;
}
TankState::TankState( SiegeTank* pTank ) : m_pTank(pTank)
{
}
void TankState::move( int x, int y )
{
std::cout << "Move to (" << x << ", " << y << ")" << std::endl;
}
void TankState::attack()
{
std::cout << "Attacking for 20" << std::endl;
}
tank.h如下:
#ifndef __TANK_H__
#define __TANK_H__
class TankState;
class SiegeState;
class ISiegeTankState;
class SiegeTank
{
public:
SiegeTank();
void enterTankMode();
void enterSiegeMode();
public:
void attack();
void move(int x, int y);
private:
void setState(ISiegeTankState* pSiegeTankMode);
private:
TankState* m_pTankState;
SiegeState* m_pSiegeState;
ISiegeTankState* m_pSiegeTankState;
};
#endif
tank.cpp如下:
#include "tank.h"
#include "state.h"
#include <iostream>
SiegeTank::SiegeTank()
{
m_pTankState = new TankState(this);
m_pSiegeState = new SiegeState(this);
m_pSiegeTankState = m_pTankState;
}
void SiegeTank::setState( ISiegeTankState* pSiegeTankMode )
{
m_pSiegeTankState = pSiegeTankMode;
}
void SiegeTank::move( int x, int y )
{
m_pSiegeTankState->move(x, y);
}
void SiegeTank::attack()
{
m_pSiegeTankState->attack();
}
void SiegeTank::enterTankMode()
{
m_pSiegeTankState = m_pTankState;
std::cout << "Switch to tank mode" << std::endl;
}
void SiegeTank::enterSiegeMode()
{
m_pSiegeTankState = m_pSiegeState;
std::cout << "Switch to siege mode" << std::endl;
}
测试代码main.cpp如下:
#include "tank.h"
#include "state.h"
int main()
{
SiegeTank tank;
tank.enterTankMode();
tank.attack();
tank.move(1, 1);
tank.enterSiegeMode();
tank.attack();
tank.move(2, 2);
tank.enterTankMode();
tank.attack();
tank.move(3, 3);
return 0;
}
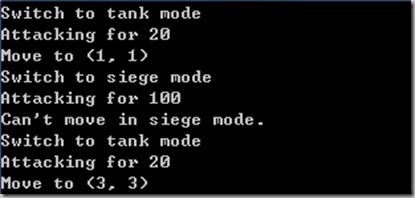
运行结果如下:
posted on 2011-12-09 19:52 GraphicsMe 阅读(1186) 评论(0) 收藏 举报





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号