Java入门——(3)面对对象(下)
class A{}
class B extends A{}
class A{}
class B{}
class C extends A,B{} //C类不可以同时继承A类和B类
①子类覆盖父类,必须保证权限要大于或等于父类的权限。
②静态覆盖静态。
③写法上必须一模一样,函数的返回值类型 函数名 参数列表都要一样。
3、super关键字
①如果子类的构造函数第一行写了this调用了背离其他构造函数,那么super调用父类的语句是没有的,因为this()或者super(),只能在构造函数的第一行,因为初始化动作要先执行。
②父类构造函数中是否有隐式的super呢?也是有的,只要是构造函数默认第一行都是super();
②只要使用父类的指定初始化动作,就在子类中通过super(参数列表)格式进行调用。
①使用super关键字调用父类的成员变量和成员方法。具体格式:
②使用super关键字调用父类的构造方法,具体格式:
①final修饰的类是一个最终类,该类将不能被继承,不能派生子类。
③final修饰的变量是一个常量,只能被赋值一个。
如:final int num = 2;
①抽象类和抽象方法都需要被abstract修饰。(抽象方法一定要定义在抽象类中)。
//定义抽象类Animal
abstract class Animal{
//定义抽象方法shuot()
abstract int shout ();
}
②抽象类不可以创建实例,原因:调用抽象方法没有方法体。
③只要覆盖了抽象类中所有的抽象方法后,其子类才可以实例化。否则该子类还是一个抽象类。
1 interface Animal{
2 int ID = 1; //定义全局变量
3 void breathe(); //定义抽象方法
4 void run ();
5 } // Animal 即为一个接口,接口中定义的的方法和变量都包含一些默认修饰符“public abstract”(抽象方法)“public static final”(全局变量)。
①接口可以创建对象;
②子类必须覆盖掉接口中所有的抽象方法后,子类才可以实例化。否则子类是一个抽象类。
③实现多接口示例:
interface Run{
程序代码…..
}
interface Fly{
程序代码…..
}
class Bird implements Run,Fly{
程序代码…….
}
class Dog extends Canidae implements Animal{ //先继承,再实现
程序代码……
}
1 //定义接口Animal
2 interface Animal{
3 void shout();
4 }
5 //定义Cat类实现Animal接口
6 class Cat implements Animal{
7 //实现shout()方法
8 public void shout(){
9 System.out.println("喵喵...");
10 }
11 }
12 //定义Dog类型实现Animal接口
13 class Dog implements Animal{
14 public void shout(){
15 System.out.println("汪汪");
16 }
17 }
18 //定义测试类
19 public class Example13 {
20 public static void main(String[] args) {
21 Animal an1 =new Cat();//创建Cat对象,使用Animal类型的变量an1引用
22 Animal an2 =new Dog();//创建Dog对象,使用Animal类型的变量an2引用
23 animalShout(an1); //调用animalShout()方法,将an1作为参数传入
24 animalShout(an2); //调用animalShout()方法,将an2作为参数传入
25 }
26 public static void animalShout(Animal an) {
27 an.shout();
28 }
29 }
运行结果
喵喵…
汪汪
Animal a = new Dog();
a.eat();
Dog d = (Dog)a; //将a转型为Dog 类型。向下转型。
d.lookHome();
if(a instanceof Cat){ //a指向的对象的类型是Cat类型。
//将a转型Cat 类型。
Cat c = (Cat)a;
c.catchMouse();
}else if(a instanceof Dog){
Dog d = (Dog) a;
d.lookHome();
}
1 interface Animal{
2 void shout();//定义抽象方法shout()
3 }
4 //定义Cat类实现Animal接口
5 class Cat implements Animal{
6 //实现抽象方法shout()
7 public void shout(){
8 System.out.println("喵喵...");
9 }
10 //定义sleep()方法
11 public void sleep(){
12 System.out.println("猫在睡觉.....");
13 }
14 }
15 //定义Dog类实现Animal接口
16 class Dog implements Animal{
17 //实现抽象方法shout()
18 public void shout(){
19 System.out.println("汪汪...");
20 }
21 }
22 //定义测试类
23 public class Example14 {
24 public static void main(String[] args) {
25 Animal dog = new Dog(); //创建Dog类的实例对象
26 animalShout(dog); //调用animalShout()方法,将dog作为参数传入
27 }
28 public static void animalShout(Animal animal) {
29 if (animal instanceof Cat) {
30 Cat cat = (Cat) animal;//将animal对象强制装换为Cat类型
31 cat.shout(); //调用cat的shout()方法
32 cat.sleep(); //调用cat的sleep()方法
33 }else{
34 System.out.println("this animal is not a cat!");
35 }
36 }
37 }
运行结果:
this animal is not a cat!
①什么时候向上转型?
②什么时候向下转型?
new 父类(参数列表)或父接口(){
// 匿名内部类实现部分
}
示例
1 interface Animal{
2 void shout();
3 }
4 public class Example18 {
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6 animalShout(new Animal(){
7 public void shout() {
8 System.out.println("喵喵...");
9 }
10 });
11 }
12 public static void animalShout(Animal an) {
13 an.shout();
14 }
15 }
运行结果
喵喵...
1 class Animal{
2 /*//定义动物叫的方法
3 void shout(){
4 System.out.println("动物叫");
5 }*/
6 //重写Object类中的toString()方法
7
8 @Override
9 public String toString() {
10 return "I am an animal!";
11 }
12 }
13 //定义测试类
14 public class Example16 {
15 public static void main(String[] args) {
16 Animal animal = new Animal(); //创建Animal类对象
17 System.out.println(animal.toString()); //调用toString()方法并打印
18 }
19 }
五、异常
1、Throwable类的继承体系
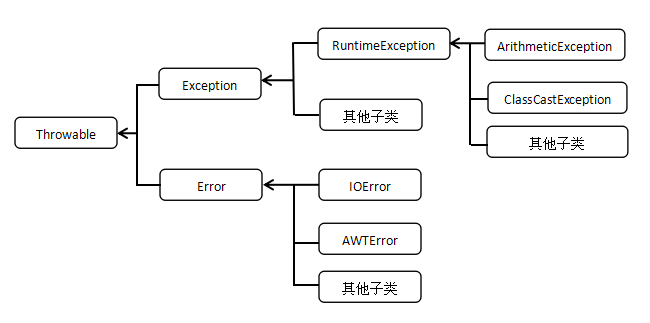
运行时异常:RuntimeException类即其子类都是运行时异常,编译器不会检测的异常,不需要声明。
| Throwable常用方法 | |
| 方法声明 | 功能描述 |
| String getMessage() | 返回此throwable的详细消息字符串 |
| void printStackTrace() | 将此throwable及其追踪输出至标准错误流 |
| void printStackTrace(PrintStream s) | 将此throwable及其追踪输出至指定的输出流 |
try{
//需要被检测的语句
}catch(ExceptionType(Exception类及其子类) e) {
//ExceptionType的处理
}
finally{
//一定会被执行的语句
}
示例
1 public class Example20 {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 // 下面的代码定义了一个try...catch语句用于捕捉异常
4 try {
5 int result = divide(4,0); //调用divide()方法
6 System.out.println(result);
7 } catch (Exception e) { //对异常进行处理
8 System.out.println("捕捉的异常信息为" + e.getMessage());
9 return; //用于结束当前语句
10 }finally {
11 System.out.println("进入finally代码块”);
12 }
13 System.out.println("程序继续向下执行...");
14 }
15 //下面的方法实现了两个整数相除
16 public static int divide(int x,int y) {
17 int result = x/y; //定义一个变量result记录两个整数相除的结果
18 return result; //将结果返回
19 }
20 }
运行结果
捕获的异常信息是:/by zero
进入代码块
在程序设计时,经常会在try...catch后使用finally代码块来完成必须做的事情,例如释放系统资源。需注意,当try...catch中执行了System.exit(0)语句,则退出Java虚拟机,任何代码都不能继续执行。
①try catch :对代码进行异常检测,并对检测的异常传递给catch处理。
Void show ()throws {//不需要throws
try{
throw new Exception();
}finally{
}
}
②try finally:对代码进行异常检测,检测到异常后因为没有catch,所以一样会被默认jvm抛出。
Void show () {//需要throws
try{
throw new Exception();
}finally{
}
}
③try catch finally
④try catch1 catch2 catch3………
void show ()throws Exception{
throw new Exception();
}
1 class DivideByMinusException extends Exception{
2 public DivideByMinusException(){
3 super();//调用Exception无参的构造方法
4 }
5 public DivideByMinusException(String message){
6 super(message);//调用Exception无参的构造方法
7 }
8 }
9 public class Example26 {
10 public static void main(String[] args) {
11 try{
12 int result = divide(4,-2);
13 System.out.println(result);
14 }catch (DivideByMinusException e){
15 System.out.println(e.getMessage());
16 }
17 }
18 public static int divide(int x,int y)throws DivideByMinusException{
19 if(y<0){
20 throw new DivideByMinusException("被除数是负数");
21 }
22 int result = x/y ;
23 return result;
24 }
25 }
import 包名.类名;
|
访问控制级别 |
||||
|
同一类中 |
同一包下 (有无关系均可) |
不同包下(子类) |
不同包下 (没有关系) |
|
|
private |
Y |
|||
|
default(默认) |
Y |
Y |
||
|
protected |
Y |
Y |
Y |
|
|
public |
Y |
Y |
Y |
Y |







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号