委托的异步编程和同步编程的使用( Invoke 和BeginInvoke)
一,区别:
使用Invoke完成一个委托方法的封送,就类似于使用SendMessage方法来给界面线程发送消息,是一个同步方法。也就是说在Invoke封送的方法被执行完毕前,Invoke方法不会返回,从而调用者线程将被阻塞。
使用BeginInvoke方法封送一个委托方法,类似于使用PostMessage进行通信,这是一个异步方法。也就是该方法封送完毕后马上返回,不会等待委托方法的执行结束,调用者线程将不会被阻塞。但是调用者也可以使用EndInvoke方法或者其它类似WaitHandle机制等待异步操作的完成。
二,使用ASPX页面和浏览器测试页面响应速度
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; using System.Web.UI; using System.Web.UI.WebControls; namespace WebApplication1 { public partial class WebForm1 : System.Web.UI.Page { protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { Test t = new Test(); Action<string> action = new Action<string>(t.Say); action.BeginInvoke("Demoyibu", null, null); //这个是异步的方法 //action.Invoke("Demotongbu"); //这个是同步的方法 Label1.Text = "显示结果:"; if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(t.T)) { Label2.Text = "Demoyibu"; } else { Label2.Text = t.T; } } } public class Test { public string T { get; set; } public void Say(string a) { int j = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) { j = i; } this.T = a; } } }
页面
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="WebForm1.aspx.cs" Inherits="WebApplication1.WebForm1" %> <!DOCTYPE html> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head runat="server"> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8" /> <title></title> </head> <body> <form id="form1" action="#"> <div> <asp:Label ID="Label1" runat="server"></asp:Label> <asp:Label ID="Label2" runat="server"></asp:Label> </div> </form> </body> </html>
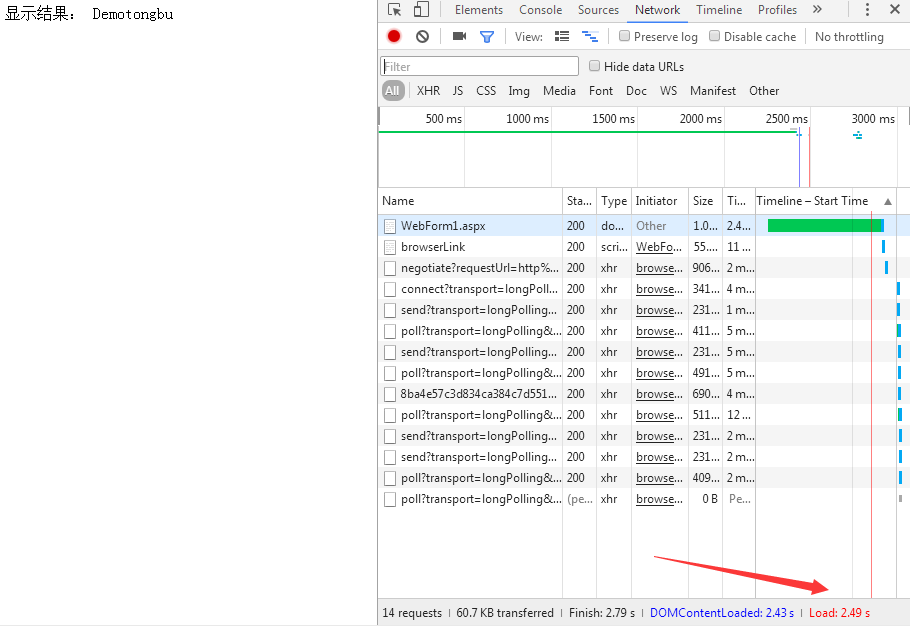
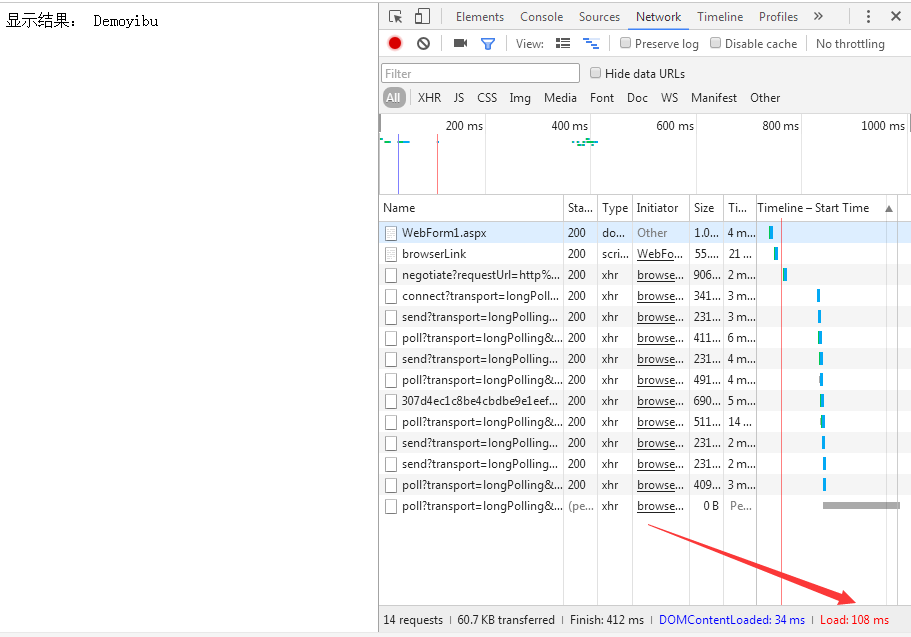
三,查看结果
异步使用:在异步使用,循环耗时在异步执行,耗时只是页面加载
同步使用:由于页面返回要加载以上代码的同步循环,所以耗时比较多