面向对象程序设计(C++)_实验4_类的继承、派生和多态(1)
一、实验结论
1.车辆信息管理
源代码:
battery.h:
#ifndef BATTERY_H
#define BATTERY_H
class Battery {
public:
Battery(int sz = 70) :batterySize(sz) {}
int getSize() const;
private:
int batterySize;
};
#endif
car.h:
#ifndef CAR_H
#define CAR_H
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Car {
public:
Car(string mak, string mod, int y) :maker(mak), model(mod), year(y), odometer(0) {}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Car& c);
void updateOdometer(int);
private:
string maker;
string model;
int year;
int odometer;
};
#endif
electricCar.h:
#ifndef ELECTRICCAR_H
#define ELECTRICCAR_H
#include "car.h"
#include "battery.h"
class ElectricCar :public Car {
public:
ElectricCar(string mak, string mod, int y) :Car(mak, mod, y) {}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const ElectricCar& ec);
private:
Battery battery;
};
#endif
battery.cpp:
#include "battery.h"
int Battery::getSize() const{
return batterySize;
}
car.cpp:
#include "car.h"
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Car& c) {
out << "maker: " << c.maker << endl;
out << "moder: " << c.model << endl;
out << "year: " << c.year << endl;
out << "odometer: " << c.odometer;
return out;
}
void Car::updateOdometer(int meter) {
if (meter < odometer) {
cout << "Illegal!" << endl;
return;
}
odometer = meter;
}
electricCar.h:
#include "electricCar.h"
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const ElectricCar& ec) {
Car tmp = ec;
out << tmp << endl;
out << "batterySize: " << (ec.battery).getSize()<<"-kWh";
return out;
}
main.cpp:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "car.h"
#include "electricCar.h"
int main() {
// 测试Car类
Car oldcar("Audi", "a4", 2016);
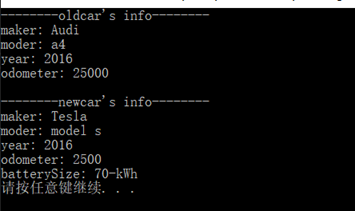
cout << "--------oldcar's info--------" << endl;
oldcar.updateOdometer(25000);
cout << oldcar << endl;
// 测试ElectricCar类
ElectricCar newcar("Tesla", "model s", 2016);
newcar.updateOdometer(2500);
cout << "\n--------newcar's info--------\n";
cout << newcar << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1.重载运算符[]为一维动态整形数组类ArrayInt的成员函数
源代码:
arrayInt.h:
#ifndef ARRAY_INT_H
#define ARRAY_INT_H
class ArrayInt {
public:
ArrayInt(int n, int value = 0);
~ArrayInt();
// 补足:将运算符[]重载为成员函数的声明
// ×××
int &operator[](int);
void print();
private:
int* p;
int size;
};
#endif
arrayInt.cpp:
#include "arrayInt.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
ArrayInt::ArrayInt(int n, int value) : size(n) {
p = new int[size];
if (p == nullptr) {
cout << "fail to mallocate memory" << endl;
exit(0);
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
p[i] = value;
}
ArrayInt::~ArrayInt() {
delete[] p;
}
void ArrayInt::print() {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << p[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int& ArrayInt::operator[](int idx) {
return p[idx];
}
main.cpp:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "arrayInt.h"
int main() {
// 定义动态整型数组对象a,包含2个元素,初始值为0
ArrayInt a(2);
a.print();
// 定义动态整型数组对象b,包含3个元素,初始值为6
ArrayInt b(3, 6);
b.print();
// 通过对象名和下标方式访问并修改对象元素
b[0] = 2;
cout << b[0] << endl;
b.print();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:

二、实验总结与体会
没收到deadline通知邮件所以完全忘了还有这么个实验,好在还是在截止前发现并完成了。可能是因为太简单吧,实验过程中并没有踩到什么坑。非要说的话,第一题electricCar.cpp第五行和第六行出于简洁起见我原本写的是out<<ec<<endl,因为我想当然的以为这里会调用<<运算符函数以Car类对象为参数的重载形式(可能是当时觉得以派生类作为形参的还没定义完?(lll¬ω¬) ),而由于类型兼容规则存在,ec可以方便地被隐式转换为Car类对象从而直接输出其从基类继承的成员……然而当然不会是这样,事实上这样写只是在递归调用自身,这一点只要查看一下调用栈或是在前面加上一行输出语句就可以很明显地看出:
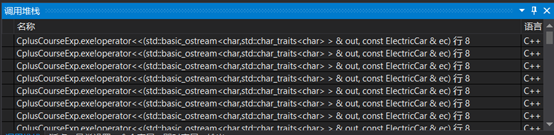

这个愚蠢的错误其实我当时立刻就发现并更正了……所以上面这两张图完全是为了丰富实验总结与体会部分的内容而特意把它重新改回来又运行的……啧啧啧,真是用心良苦_(:з」∠)_
posted on 2019-05-21 17:27 Alexander_Yang 阅读(399) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报

