数值优化 —— CPU版本的共轭梯度法和GPU版本的共轭梯度法,到底哪个快???—— pytorch实现
共轭梯度法,是数值优化算法中才会用到的一个算法,可以说共轭梯度法并不是一个求最优值的算法,但是在数值优化算法中的那些球最优值的算法很多都会用到这个共轭梯度法,于是这个共轭梯度法也就显得蛮有用的。
共轭梯度法本身运算起来还是很消耗运算量的,平时见到的实现版本一般都是CPU版本,由于搞pytorch,突然想到使用GPU版本来实现一个共轭梯度法是不是会更快一些呢?于是就有了本文。
给出编写的代码:
import numpy as np
import time
import torch
n = 100
B = np.random.randn(n, n)
B = (B + B.T) / 2 # 对称化
diag = np.sum(np.abs(B), axis=1) + 1e-5 # 对角线足够大
np.fill_diagonal(B, diag)
M = B # 此时B正定
M_cpu = M
M_gpu = torch.Tensor(M_cpu).to("cuda:0")
def f_cpu(x):
return np.dot(M_cpu, x)
def f_gpu(x):
return M_gpu@x
def conjugate_gradients_gpu(Avp, b, nsteps, residual_tol=1e-10):
x = torch.zeros(b.size()).to("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
r = b.clone()
p = b.clone()
rdotr = torch.dot(r, r)
for i in range(nsteps):
_Avp = Avp(p)
alpha = rdotr / torch.dot(p, _Avp)
x += alpha * p
r -= alpha * _Avp
new_rdotr = torch.dot(r, r)
betta = new_rdotr / rdotr
p = r + betta * p
rdotr = new_rdotr
if rdotr < residual_tol:
break
return x
def conjugate_gradients_cpu(Avp, b, nsteps, residual_tol=1e-10):
x = np.zeros(b.size)
r = np.copy(b)
p = np.copy(b)
rdotr = np.dot(r, r)
for i in range(nsteps):
_Avp = Avp(p)
alpha = rdotr / np.dot(p, _Avp)
x += alpha * p
r -= alpha * _Avp
new_rdotr = np.dot(r, r)
betta = new_rdotr / rdotr
p = r + betta * p
rdotr = new_rdotr
if rdotr < residual_tol:
break
return x
b_cpu = np.random.randn(n)
b_gpu = torch.randn(n).to("cuda:0")
_a = time.time()
conjugate_gradients_cpu(f_cpu, b_cpu, 30)
_b = time.time()
conjugate_gradients_gpu(f_gpu, b_gpu, 30)
_c = time.time()
print("cpu: ",_b - _a)
print("gpu: ", _c - _b)
运行效果:
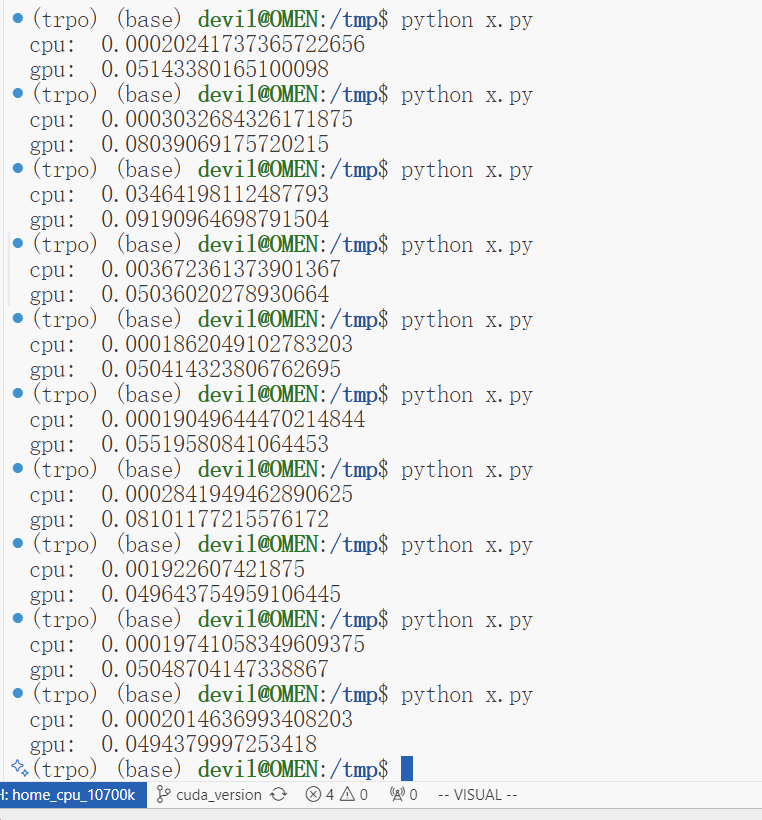
从这个运行效果来看,使用pytorch实现的GPU版本的共轭梯度法是远远没有CPU版本的速度快,其实这个原因也是比较好解释的,因为共轭梯度法很多步骤都是逻辑判断、循环的结构,并且pytorch版本的共轭梯度法的每一个计算步骤都是需要从CPU端发送指令给GPU端的,这本身也是存在较大的设备间切换的时间损耗的,总的来说,共轭梯度法并不是单纯的矩阵计算,其中有大量的不适合GPU端实现的操作,因此使用GPU端实现不能取得CPU端运行的速度。
虽然使用CUDA原语,用C++实现这个代码会进一步的提升GPU版本的运行效率,但是共轭梯度法本身的逻辑结构和判断结构就不是很适合GPU加速器来执行的,因此CPU版本的共轭梯度法会有更好的性能表现。
本博客是博主个人学习时的一些记录,不保证是为原创,个别文章加入了转载的源地址,还有个别文章是汇总网上多份资料所成,在这之中也必有疏漏未加标注处,如有侵权请与博主联系。
如果未特殊标注则为原创,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议。
posted on 2025-03-20 20:39 Angry_Panda 阅读(64) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号