实验6-模板类和文件
task3:
task3.1.cpp
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<fstream> 3 #include<array> 4 #define N 5 5 int main() 6 { 7 using namespace std; 8 array<int ,5> x{97,98,99,100,101}; 9 ofstream out; 10 out.open("data1.dat",ios::binary); 11 if(!out.is_open()) 12 {cout<<"打开失败"; 13 return 1; 14 } 15 out.write(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&x),sizeof(x)); 16 out.close(); 17 }
task3.2.cpp
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<fstream> 3 #include<array> 4 #define N 5 5 int main() 6 { 7 using namespace std; 8 array<int ,5> x{97,98,99,100,101}; 9 ifstream in; 10 in.open("data1.dat",ios::binary); 11 if(!in.is_open()) 12 {cout<<"打开失败"; 13 return 1; 14 } 15 in.read(reinterpret_cast<char *>(&x),sizeof(x)); 16 in.close(); 17 for(auto i=0;i<N;++i) 18 cout<<x[i]<<","; 19 cout<<"\b\b\n"; 20 }
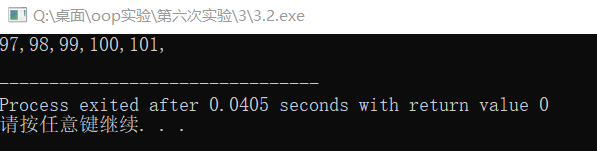
代码改动过后运行结果如下
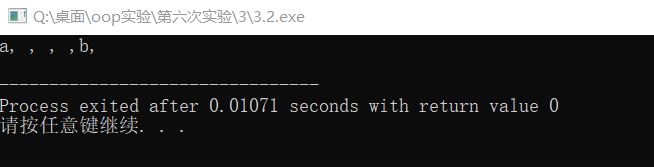
原因分析如图所示:

task4:
task4.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include<iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 template <typename T> 6 class Vector{ 7 public: 8 Vector(int n0); 9 Vector(int n0,T value); 10 Vector(const Vector<T> &v1); 11 ~Vector(); 12 int get_size() const {return n ;} 13 T& at(int i){return *(p+i);} 14 T& operator[](int i){return *(p+i);} 15 template<typename T1> 16 friend void output( Vector<T1> &x); 17 18 private: 19 int n; 20 T *p; 21 }; 22 template <typename T> 23 Vector<T>::Vector(int n0) 24 { 25 n=n0; 26 p=new T[n]; 27 //cout<<"没有初始值的构造函数被调用"; 28 29 } 30 template <typename T> 31 Vector<T>::Vector(int n0,T value) 32 { 33 n=n0; 34 p=new T[n]; 35 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 36 *(p+i)=value; 37 //cout<<"有初始值的构造函数被调用"; 38 } 39 template <typename T> 40 Vector<T>::Vector(const Vector<T>& v1) 41 {n=v1.n; 42 p=new T[n]; 43 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 44 p[i]=v1.p[i]; 45 } 46 template <typename T> 47 Vector<T>::~Vector() 48 { 49 delete [] p; 50 } 51 template<typename T1> 52 void output(Vector<T1>&x) 53 {for(int i=0;i<x.n;i++) 54 cout<<x.at(i)<<","; 55 cout<<endl; 56 }
task4.cpp:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "Vector.hpp" 3 4 void test() { 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int n; 8 cin >> n; 9 10 Vector<double> x1(n); 11 for(auto i = 0; i < n; ++i) 12 x1.at(i) = i * 0.7; 13 14 output(x1); 15 16 Vector<int> x2(n, 42); 17 Vector<int> x3(x2); 18 19 output(x2); 20 output(x3); 21 22 x2.at(0) = 77; 23 output(x2); 24 25 x3[0] = 999; 26 output(x3); 27 } 28 29 int main() { 30 test(); 31 }
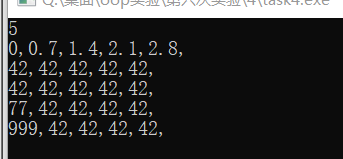
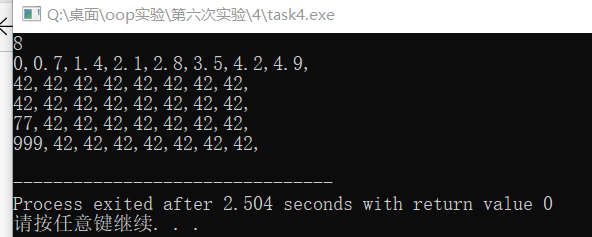
实验当中出现的 问题:
1.注意语法,在类外声明类的成员函数的时候,声明一个就必须要在前面加一个template<typename T>。而在声明类的友元的时候,在类的内部和外部都需要在函数声明前加上template<typename T1>(和成员函数模板元素名子不同)。
2.设计好类的数据成员,要根据场景进行设计,不能类型只是T。
task5:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 #include<fstream> 4 #include<iomanip> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 void output(ostream &out) 8 { 9 10 11 cout<<" "; 12 out<<" "; 13 for( int i=97;i<123;i++) 14 { 15 cout<<char(i)<<" "; 16 out<<char(i)<<" "; 17 } 18 19 cout<<endl; 20 out<<endl; 21 int count=1; 22 for(count=1;count<=26;count++) 23 { 24 cout<<setw(2)<<count<<" "; 25 out<<setw(2)<<count<<" "; 26 for(int i=65+count ,k=1;k<=26;i++,k++) 27 {int temp=(i-65)%26+65; 28 cout<<char(temp)<<" "; 29 out<<char(temp)<<" "; 30 } 31 cout<<endl; 32 out<<endl; 33 } 34 35 36 }


实验5当中的注意事项:
1.函数参数传递中用到了类的继承中类型兼容原则,ofstream这个派生类的对象可以作为基类ostream的对象去使用。
2.创建了ofstream的对象out,并用out打开文件。向文件中写数据的方式有两种。一种如task3中利用write函数(这种一般要知道要往文件里写多少个字节),一种就是task5中直接用对象配合运算符”<<“进行向文件写入。
实验总结:
1.通过这次实验,更进一步的学习了模板的知识以及相关的语法,并在task1,ask4的实践中应用。
2.学会了向文件导入数据的两种方式,在task3和task5中得到了实践。



