实验1类和对象(1)
1. 实验任务1
1.template指的是模板。比如,我们要写一个swap函数来交换两个元素。但这两个元素可能是int也可能使char,如果不用模板的话,我们可能要写多个函数才能完成。但是用模板的话。就可以很轻松的相当与用一个函数完成多项任务、
2.类似v1.begin返回的值是指针类型,因此输出的时候要注意、还要注意begin,end等的返回位置。
2. 实验任务2
#include<iostream> using std::cout; using std::endl; class Point {public : Point (int x0=0,int y0=0); Point(const Point &p); ~Point()=default; int get_x() const {return x;} int get_y() const {return y;} void show() const; private: int x,y; }; //Point 类的实现 //构造函数(带有默认值的形参值) Point::Point(int x0,int y0):x{x0},y{y0} {cout <<"constructor called."<<endl; } Point::Point(const Point &p):x{p.x},y{p.y} {cout <<"constructor called."<<endl; } void Point::show()const{ cout<<"("<<x<<","<<y<<")"<<endl;} int main() { Point p1(4,5);//构造函数被应用 p1.show(); Point p2=p1;// 复制构造函数被应用 p2.show(); Point p3{p2};// 复制构造函数被应用 p3.show(); cout<<p3.get_x()<<endl; }
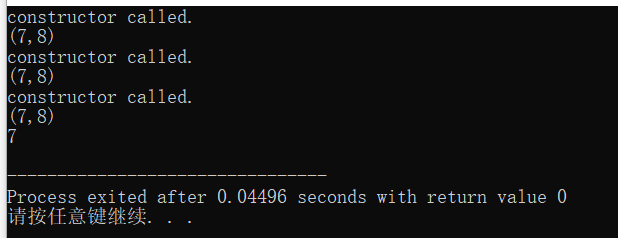
在本次实验中。构造函数被调用是在创建一个对象的时侯。而复制构造函数的调用则是在用该类中的一个对象去初始化该类的另外一个对象的时候被调用。
在 复制构造函数中加 const有效的防止原对象数据被篡改。
3. 实验任务3
#include<iostream> #include<iomanip> using std::cout; using std::endl; class Clock{ public: Clock(int h=0,int m=0,int s=0); Clock(const Clock&t); ~Clock()=default; void set_time(int h,int m=0,int s=0); void show_time() const; private: int hour,minute,second; }; Clock::Clock(int h,int m, int s):hour(h),minute(m),second(s){ cout<<"constructor called"<<endl; } Clock::Clock(const Clock&t):hour{t.hour},minute{t.minute},second{t.second}{ cout <<"copy constructor called"<<endl; } void Clock::set_time(int h,int m,int s) { hour=h; minute=m; second=s; } void Clock::show_time() const{ using std::setw; using std::setfill; cout <<setfill('0')<<setw(2)<<hour<<":" <<setw(2)<<minute<<":" <<setw(2)<<second<<endl; } Clock reset(){ return Clock(0,0,0); } int main() { Clock c1(11,1,5); c1.show_time(); c1=reset();//;理论上复制构造函数被调用 c1.show_time() ; Clock c2(c1); c2.set_time(9); c2.show_time() ; }
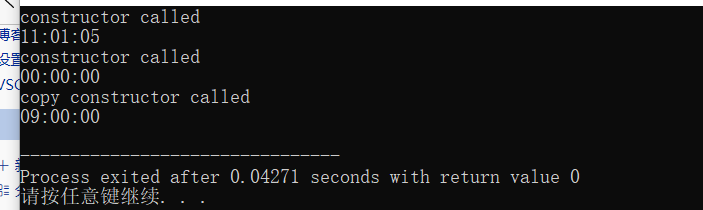
构造函数和复制构造函数同2.但是c1=reset()因为编译器优化理论上调用的复制构造函数可能并没有调用;
4. 实验任务4
#include<iostream> //定义一个简单抽象类 class X{ public: X();// 默认构造函数 ~X();//析构函数 X(int m);//构造函数 X(const X& obj);//复制构造函数 X(X&& obj) noexcept;//移动构造函数 void show() const ;//显示数据 private: int data; }; X::X():data{42} { std::cout <<"default constructor called.\n"; } X::~X(){ std::cout <<"destructor called.\n"; } X::X(int m):data{m}{ std::cout <<"constructor called.\n"; } X::X(const X& obj):data{obj.data} {std::cout <<"copy constructor called.\n"; } X::X( X&&obj)noexcept:data{obj.data}{ std::cout<<"move constructor called.\n";} void X::show() const { std:: cout <<data<<std::endl; } int main() { X x1; x1.show(); X x2{2049}; x2.show(); X x3 {x1}; x3.show(); X x4{std::move (x2)}; x4.show(); }
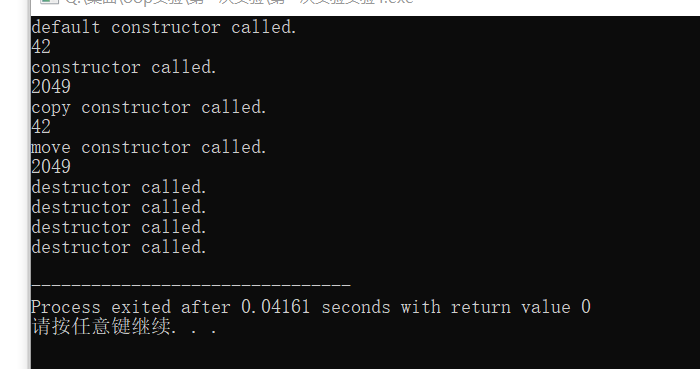
X x1 时是类中对象的定义,且没有形参 调用默认构造函数
X x2也是类中对象的定义,但是有参数,调用构造函数
X x3{x1}是用该类中的一个对象去初始化该类的另外一个对象,这会调用复制构造函数
X x4{std::move (x2)}; 调用了移动构造函数; 乍一看,移动构造函数和复制构造函数完成了相同的任务,但是,其实,移动构造函数是把对象移动到了另外一个对象当中,而复制构造函数,是吧对象拷贝,然后拷贝到另一个对象中,我们可以看出,在某些问题上,移动构造函数更省空间。
根据输出结果我们可以看出,当代码整个执行结束后,析构函数会被调用,销毁和清理了x1 x2 x3 x4占用的资源。并且,要注意,先被定义的最后销毁。
5. 实验任务5
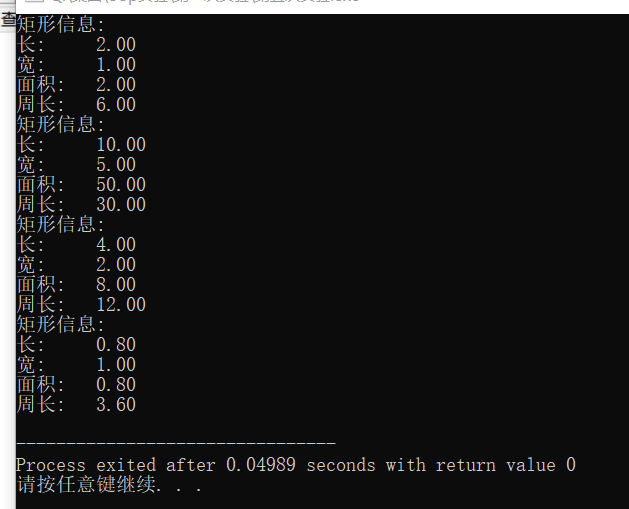
#include <iostream> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; // 矩形类Rectangle的定义和实现 // 补足代码 class Rectangle{ public: Rectangle ();//默认构造函数 Rectangle(double l,double w);//构造函数 Rectangle(const Rectangle &rect);//复制构造函数 ~Rectangle()=default;//析构函数 double len ( ) const{return length;}//多个内联函数 double wide( ) const {return width;} double area()const {return (length*width);} double circumference() const {return((length+width)*2);} void resize(int times); void resize(int l_times, int w_times); void output(const Rectangle &rect) ; private : double length,width; }; Rectangle::Rectangle(){length=2.0;width=1.0;} Rectangle::Rectangle(double l,double w) {length=l;width=w;} Rectangle::Rectangle(const Rectangle&rect): length{rect.length},width{rect.width}{} void Rectangle::resize(int l_times,int w_times) { length=length/l_times; width=width/w_times; } void Rectangle::resize(int times) { length=length*times; width=width*times; } // 普通函数, 用于输出矩形信息 void output(const Rectangle &rect) { using namespace std; cout << "矩形信息: \n"; cout << fixed << setprecision(2);// 控制输出格式:以浮点数形 式输出、小数部分保留两位 // 补足代码:分行输出矩形长、宽、面积、周长 cout <<"长: "<<rect.len()<<endl; cout <<"宽: "<<rect.wide()<<endl; cout <<"面积: "<<rect.area()<<endl; cout <<"周长: "<<rect.circumference()<<endl;} // 主函数,测试Rectangle类 int main() { Rectangle rect1; // 默认构造函数被调用 output(rect1); Rectangle rect2(10, 5); // 带有两个参数的构造函数被调用 output(rect2); Rectangle rect3(rect1); // 复制构造函数被调用 rect3.resize(2); // 矩形rect3的长和宽同时缩放2倍 output(rect3); rect3.resize(5, 2); // 矩形rect3的长缩放5倍, 宽缩放2倍 output(rect3); }
实验总结
实验中涉及到了调用复制构造函数两种情况。还有在函数的形参是类的对象,调用函数时也会调用复制构造函数。



