多维数组
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arrs = {{1,2},{1,2},{1,2}};
printarrs(arrs);
}
public static void printarrs(int[][] arrs){
for (int i = 0; i < arrs.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arrs[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(arrs[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
多维数组的使用
Arrays类
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,4,5,3,6};
//用Arrays类下的toString方法打印数组中的数据,直接打印a只能输出hashChde()
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,4,5,3,6};
//用Arrays类下的toString方法打印数组中的数据,直接打印a只能输出hashChde()
Arrays.sort(a);//sout方法可以排序,升序
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
冒泡排序
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,67,3,45,7,58};
int[] sout = sout(arr);//有返回值类型用变量接收
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sout));
}
public static int[] sout(int[] arr){//定义一个sout方法来存放排序后的数组
int temp = 0;//交换两个容器的值需要借助第三个容器
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) {//用来确定循环次数
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length-1-i; j++) {//进行前后判断
if (arr[j+1]<arr[j]){
temp = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
}
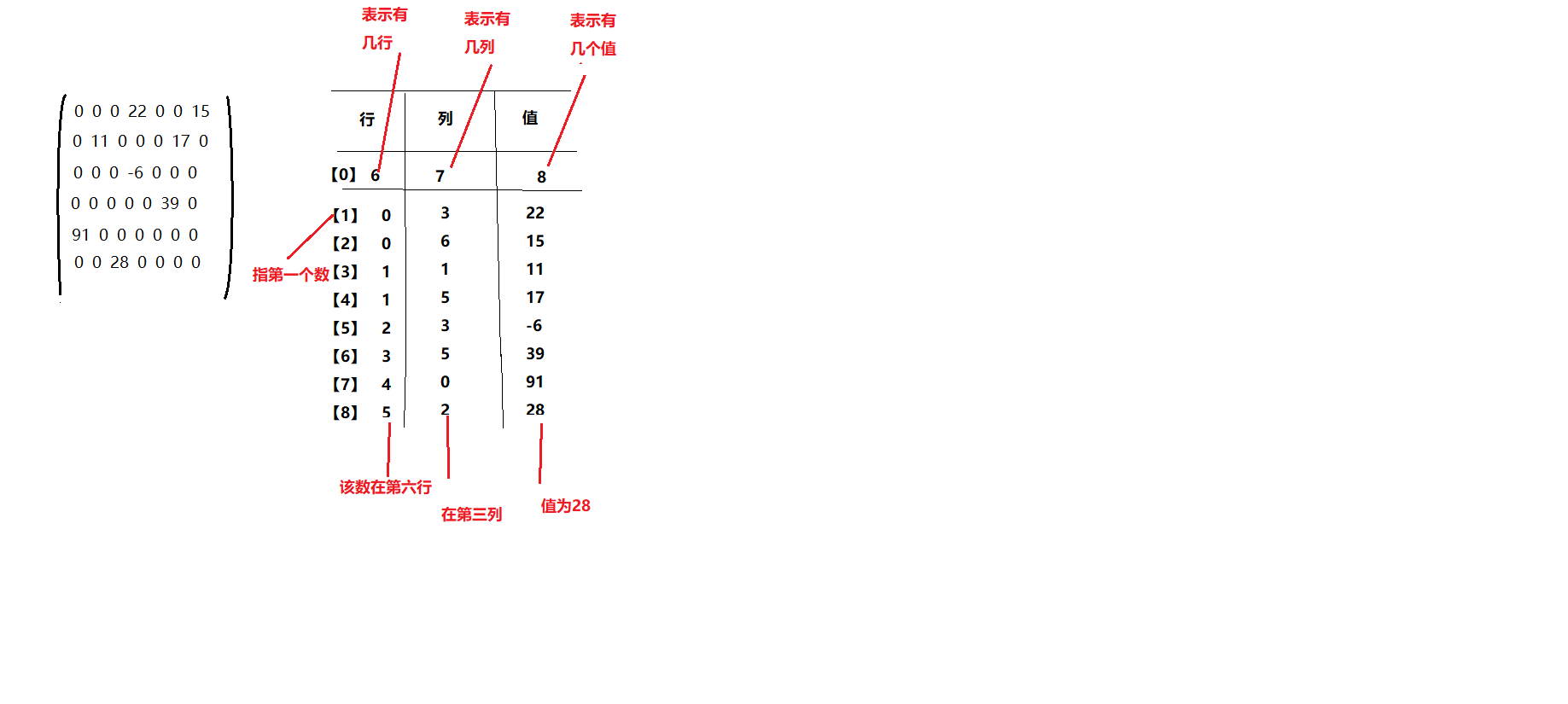
稀疏数组
- 为避免记录很多无异议的数
- 当一个数组中大部分元素为0,或者为同一值得数组时,可使用系数数组来保存该数组
- 记录数组一共有几行几列,有多少个不同值
- 例
![]()
![]()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号