C# 面向对象
C# 面向对象
定义第一个类
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; namespace _22_面向对象 { class Person { public string _name; public int _age; public char _gender; public string IdlePerson() { Console.WriteLine("调用 IdlePerson 方法"); return string.Format("my name is {0}, I'm {1} year old, gender is {2}", this._name, this._age, this._gender); } } }
调用
using System; namespace _22_面向对象 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Person person = new Person(); // 创建对象 person._name = "Irving"; // 字段赋值 person._age = 18; person._gender = '男'; Console.WriteLine(person); Console.WriteLine(person.IdlePerson()); // 调用方法 } } }
属性操作
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; namespace _22_面向对象 { class Person { // public 只能外部也能访问 // private 只能内部访问 默认权限 // public string _name; 加上public外部可以访问的到 private string _name; // 去掉public就变成private权限了 外部就访问不到了,只能内部访问 public string Name // 给字段进行打印和赋值操作时不会走属性方法 { // 当 输出 属性的值的时候会执行 get方法 get { return this._name; } // 当给属性 赋值 的,会先执行 set方法 set { this._name = value; } } private char _gender; public char Gender { get { if (this._gender!='男' || this._gender!='女') { return this._gender = '男'; } return this._gender; } set { this._gender = value; } } private int _age; public int Age { get { return this._age; } set { this._age = 1<value?(value<100?value:100):1; } } public string IdlePerson() { Console.WriteLine("调用 IdlePerson 方法"); return string.Format("my name is {0}, I'm {1} year old, gender is {2}", this.Name, this.Age, this.Gender); } } }
赋值 调用
using System; namespace _22_面向对象 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Person person = new Person(); // 创建对象 person.Name = "Irving"; // 属性赋值 person.Age = -18; // 属性赋值 Console.WriteLine(person); Console.WriteLine(person.IdlePerson()); // 调用方法 Console.WriteLine(person.Name); // 打印属性 Console.ReadKey(); } } }
构造函数
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; namespace _23_静态和非静态的区别 { public class Student { public Student(string name, int age, char gender, int chease, int math, int englist) // 构造函数创建对象的时候执行 new Student() { // 相当于 def __init__ 方法 Console.WriteLine("print Student func"); this.Name = name; this.Age = age; this.Gender = gender; this.Chease = chease; this.Math = math; this.English = englist; }
public Student(string name,int chease, int math, int englist):this(name,0,'男',chease,math,englist)
{
Console.WriteLine("print Student func 2");
}
public Student(string name, int age, char gender) // 构造函数也能重载 { this.Name = name; this.Age = age; this.Gender = gender; } private string _name; public string Name { get => _name; set => _name = value; } private int _age; public int Age { get => _age>100||_age<0?_age=0:_age;set => _age = value; } private char _gender; public char Gender { get => (_gender!='男'&& _gender!='女')? _gender='男':_gender; set => _gender = value; } private int _chease; public int Chease { get => _chease; set => _chease = value; } private int _math; public int Math { get => _math; set => _math = value; } private int _english ; public int English { get => _english; set => _english = value; } public int AvgScore { get => (this.Chease + this.Math + this.English)/3; } public int TotalScore { get => this.Chease + this.Math + this.English; } public void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("I'm {0}, I'm {1} year old, I'm {2}", this.Name, this.Age, this.Gender); } public void ShowScore() { Console.WriteLine("I'm {0}, I total score is {1}, I avg score is {2}", this.Name, this.TotalScore, this.AvgScore); }
~Student() //当程序结束是析构函数才执行, 帮助我们释放资源
{
Console.WriteLine("我是析构函数");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
调用方法
using System; namespace _23_静态和非静态的区别 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Student IrvinSstudent = new Student("文哥", 18,'男', 20, 60, 70); // 构造函数,初始化 //IrvinSstudent.Name = "文哥"; //IrvinSstudent.Age = 18; //IrvinSstudent.Chease = 20; //IrvinSstudent.Math = 60; //IrvinSstudent.English = 70; Console.WriteLine(IrvinSstudent.Name); IrvinSstudent.SayHello(); IrvinSstudent.ShowScore(); Student twoSstudent = new Student("小兰", 16, '女', 70, 50, 60); // 构造函数,初始化 twoSstudent.SayHello(); twoSstudent.ShowScore(); Student IrvinSstudentTwo = new Student("文哥", 18, '男'); // 构造函数,初始化 IrvinSstudentTwo.SayHello(); IrvinSstudentTwo.ShowScore();
Student IrvinSstudentThree = new Student("文文", 20, 60, 70); // 构造函数,this调用this
IrvinSstudentThree.SayHello();
IrvinSstudentThree.ShowScore();
}
}
}
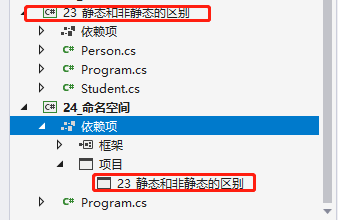
命名空间
先引入项目, 再引入命名空间
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using _23_静态和非静态的区别; namespace _24_命名空间 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<int> list = new List<int>(); Student student = new Student("Irving", 18,'男'); } } }
继承
- 所有的类都是继承的object
- 子类继承的父类的属性和方法,但是并没有继承父类的私有字段
- 子类没有继承父类的构造函数
- 单根性:一个子类只能有一个父类
- 传递性
using System; namespace _26_继承 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); Student student = new Student("Irving", 18, '男', 10); student.SayHello(); Console.WriteLine(student.Name); //Teacher t = new Teacher(); //t.Name = "Irving"; Console.WriteLine(1); } } public class Person { private string _name; private int _age; private char _gender; public string Name { get => _name; set => _name = value; } public int Age { get => _age; set => _age = value; } public char Gender { get => _gender; set => _gender = value; } public void PubPlay() { Console.WriteLine("吃饭,睡觉,打豆豆"); } public void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("大家好"); } public Person(string name, int age, char gender) // 父类构造函数 { this.Name = name; this.Age = age; this.Gender = gender; } } public class Student:Person { private int _id; public int Id { get => _id; set => _id = value; } public Student(string name, int age, char gender, int id): base(name, age, gender) // 子类构造函数 { this.Id = id; } public void Study() { Console.WriteLine("学习"); } public new void SayHello() // new 隐藏父类的方法 { Console.WriteLine("大家好, 我是学生"); } } public class Teacher : Person { private double _salary; public double Salary { get => _salary; set => _salary = value; } public Teacher(string name, int age, char gender, int salary) : base(name, age, gender) { this.Salary = salary; } public void Teach() { Console.WriteLine("教书"); } } public class Drive : Person { private int _driveTime; public int DriveTime { get => _driveTime; set => _driveTime = value; } public Drive(string name, int age, char gender, int driveTime) : base(name, age, gender) { this.DriveTime = driveTime; } public void drive() { Console.WriteLine("开车"); } } }
里氏转换语法
Person p = new Student("Irving", 18, '男', 10); // 子类可以代替父类 Console.WriteLine(p is Student); // 是否可以转换 True || False if (p is Student) { Student ss = (Student)p; // 把父类转成子类 } else { Console.WriteLine("转换失败"); } Teacher t = p as Teacher; // 转换对象,无法转换返回null Console.WriteLine(t);
protected 访问修饰符 可以在当前类和当前子类访问字段
internal 访问修饰符 只能在当前项目中访问
在一个项目里 internal 的权限要大于 protected
但是出了项目 protected 的权限就大于 internal
using System; namespace _27_protected_访问修饰符 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); Person p = new Person(); } } internal class Person { protected string _name; // 可以在当前类和当前类的子类中访问 public int _age; internal char _gender; protected internal int _math; public string Name { get => _name; set => _name = value; } public int Age { get => _age; set => _age = value; } } public class Student:Person { public void Text() { Console.WriteLine(_name); } } internal class Teacher : Person { public void Text() { Console.WriteLine(_name); } } }

多态之虚方法
父类 :virtual
子类 :override
using System; namespace _33_面向对象2 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); Person person = new Person("Irving"); Chease chease = new Chease("wenwen"); Chease chease2 = new Chease("wenwen"); Japanese japanese = new Japanese("Irving"); Korea korea = new Korea("小韩"); American american = new American("小美"); Person[] personArray = { chease, chease2, japanese, korea, american , new English("小英")}; foreach (var item in personArray) { item.SayHello(); } } } public class Person { private string _name; public string Name { get => _name; set => _name = value; } public Person(string name) { this.Name = name; } public virtual void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("I'm Person"); } } public class Chease : Person { public Chease(string name) : base(name) { } public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("I'm Chease"); } } public class Japanese : Person { public Japanese(string name) : base(name) { } public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("I'm Japanese"); } } public class Korea : Person { public Korea(string name) : base(name) { } public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("I'm korea"); } } public class American:Person { public American(string name) : base(name) { } public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("I'm American"); } } public class English : Person { public English(string name) : base(name) { } public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("I'm English"); } } }
抽象类
父类:abstract
子类:override
父类不允许创建对象, 子类必须实现父类的抽象方法
using System; namespace _34_抽象类 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 抽象类不允许创建对象 Animal animal = new Dog(); animal.Bark(); } } public abstract class Animal // 抽象类 // 抽象类不允许创建对象 { public abstract void Bark(); // 抽象方法 } public class Dog : Animal { public override void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("汪汪"); } } public class Cat : Animal { public override void Bark() { Console.WriteLine("喵喵"); } } }
简单工厂设计模式
using System; namespace _35_简单工厂设计模式 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); NoteBook nb = GetNoteBook("dell"); nb.SayHello(); } public static NoteBook GetNoteBook(string brand) { NoteBook nb = null; switch (brand) { case "lenovo": nb = new Lenovo(); break; case "acer": nb = new Acer(); break; case "dell": nb = new Dell(); break; } return nb; } } public abstract class NoteBook { public abstract void SayHello(); } class Acer: NoteBook { public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("Acer note book"); } } class Dell : NoteBook { public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("dell note book"); } } class Lenovo : NoteBook { public override void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("Lenovo note book"); } } }
序列化和反序列化
using System; using System.IO; using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary; namespace _36_序列化和反序列化 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); Person p = new Person(); p.Name = "Irving"; p.Age = 26; p.Gender = '男'; // 序列化 using(FileStream fsWrite = new FileStream(@"F:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\01.Net基础教程\01.Net基础\03-c#高级\03--面向对象多态\02\video\new.txt",FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Write)) { // fsWrite.Write("sadsdfsa"); BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter(); bf.Serialize(fsWrite,p); } // 反序列化 using (FileStream fsRead = new FileStream(@"F:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\01.Net基础教程\01.Net基础\03-c#高级\03--面向对象多态\02\video\new.txt", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read)) { // fsWrite.Write("sadsdfsa"); BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter(); Person p_new = (Person)bf.Deserialize(fsRead); Console.WriteLine(p_new.Name); Console.WriteLine(p_new.Age); Console.WriteLine(p_new.Gender); } } } [Serializable] // 允许被序列化 public class Person { private string _name; private char _gender; private int _age; public string Name { get => _name; set => _name = value; } public char Gender { get => _gender; set => _gender = value; } public int Age { get => _age; set => _age = value; } } }
部分类 partial
using System; namespace _37_部分类 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); Person p = new Person(); p.Name = "Irving"; p.Test(); } } public partial class Person { private string _name; public string Name { get => _name; set => _name = value; } //public void Test() //{ // Console.WriteLine(Name); //} } public partial class Person { public void Test() { Console.WriteLine(Name); } } }
密封类 sealed
密封类不能被其他类继承,但是能继承其他类
using System; namespace _38_密封类 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); } } public sealed class Person:Text { } public class Text { } }
重写父类的方法
using System; namespace _39_从写父类 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); Person p = new Person(); Console.WriteLine(p); // _39_从写父类.Person || 重写的子类方法 Console.WriteLine(p.ToString()); // 重写的子类方法 } } public class Person { public override string ToString() { return "重写的子类方法"; } } }

接口
不允许有 修饰符,默认public
可以有 方法、自动属性
using System; namespace _40_接口 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); Student s = new Student(); s.KouLan(); // 调用自己定义的方法 IKouLanable iables = new Student(); iables.KouLan(); // 调用接口定义的方法 // 接口就是一个规范,能力。 //[public] interface I...able{ // 成员; //} } } public class Person { private string _name; /// <summary> /// 普通属性 /// </summary> public string Name { get => _name; set => _name = value; } /// <summary> /// 自动属性 /// </summary> public int Age { get; set; } public void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("睡觉"); } } public class Student : Person, IKouLanable { public void KouLan() { Console.WriteLine("我的扣篮"); } void IKouLanable.KouLan() // 防止和自己定义的方法重名 { Console.WriteLine("接口的扣篮"); } } public interface IKouLanable { void KouLan(); } public interface M1 { void Test1(); } public interface M2 { void Test2(); } public interface M3 { void Test3(); } /// <summary> /// 接口继承接口 /// </summary> public interface SuperInterface: M1,M2, M3 { } /// <summary> /// 必须实现继承的方法 /// </summary> public class Car: SuperInterface { public void Test1() { } public void Test2() { } public void Test3() { } } }
结构
static void Main(string[] args) { PersonStruct ps = new PersonStruct(); ps.M2(); PersonStruct.M1(); } /// <summary> /// 结构中的构造函数只能给字段赋值 /// 结构中的构造函数只能给全部的字段赋值,不能选择字段赋值 /// </summary> public struct PersonStruct { private string _name; public string Name { get => _name; set => _name = value; } public int Age { get => _age; set => _age = value; } private int _age; public static void M1() { Console.WriteLine("结构中的静态方法"); } public void M2() { Console.WriteLine("结构中的非静态方法"); } public PersonStruct(string name, int age) { //this.Name = name; //this.Age = age; this._name = name; this._age = age; } }
什么时候用 虚方法 实现多态
什么时候用 抽象类 实现多态
什么时候用 接口 实现多态



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号