3.<tag-二叉树和满二叉树, 完全二叉树, 平衡二叉树等树性质>-lt.222. 完全二叉树的节点个数+lt.110. 平衡二叉树 (同剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树)
lt.222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
[案例需求]
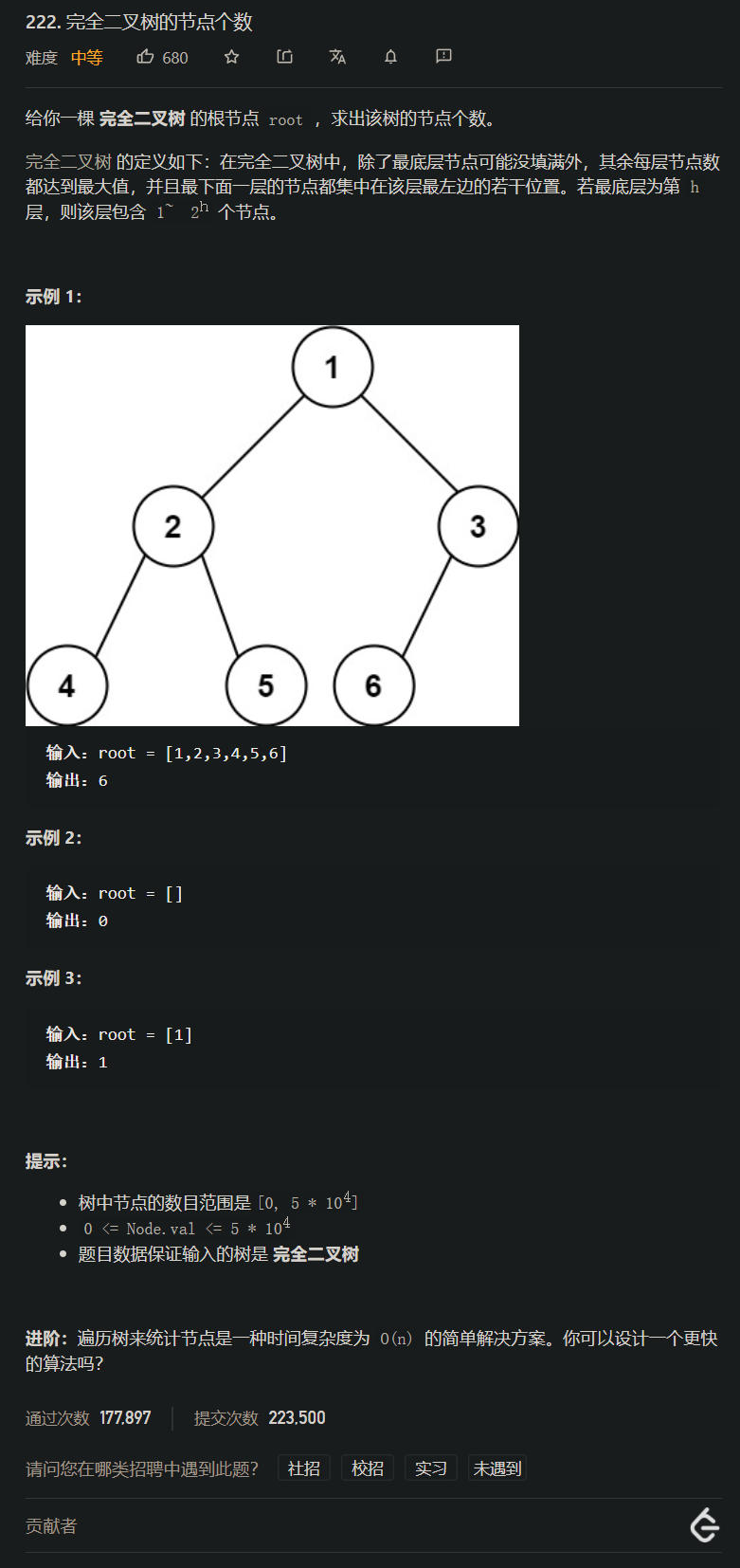
[思路分析一, (DFS)通用递归写法]
这道题目的递归法和求二叉树的深度写法类似, 而迭代法,二叉树:层序遍历的遍历模板 稍稍修改一下,记录遍历的节点数量就可以了。
递归遍历的顺序依然是后序(左右中)。
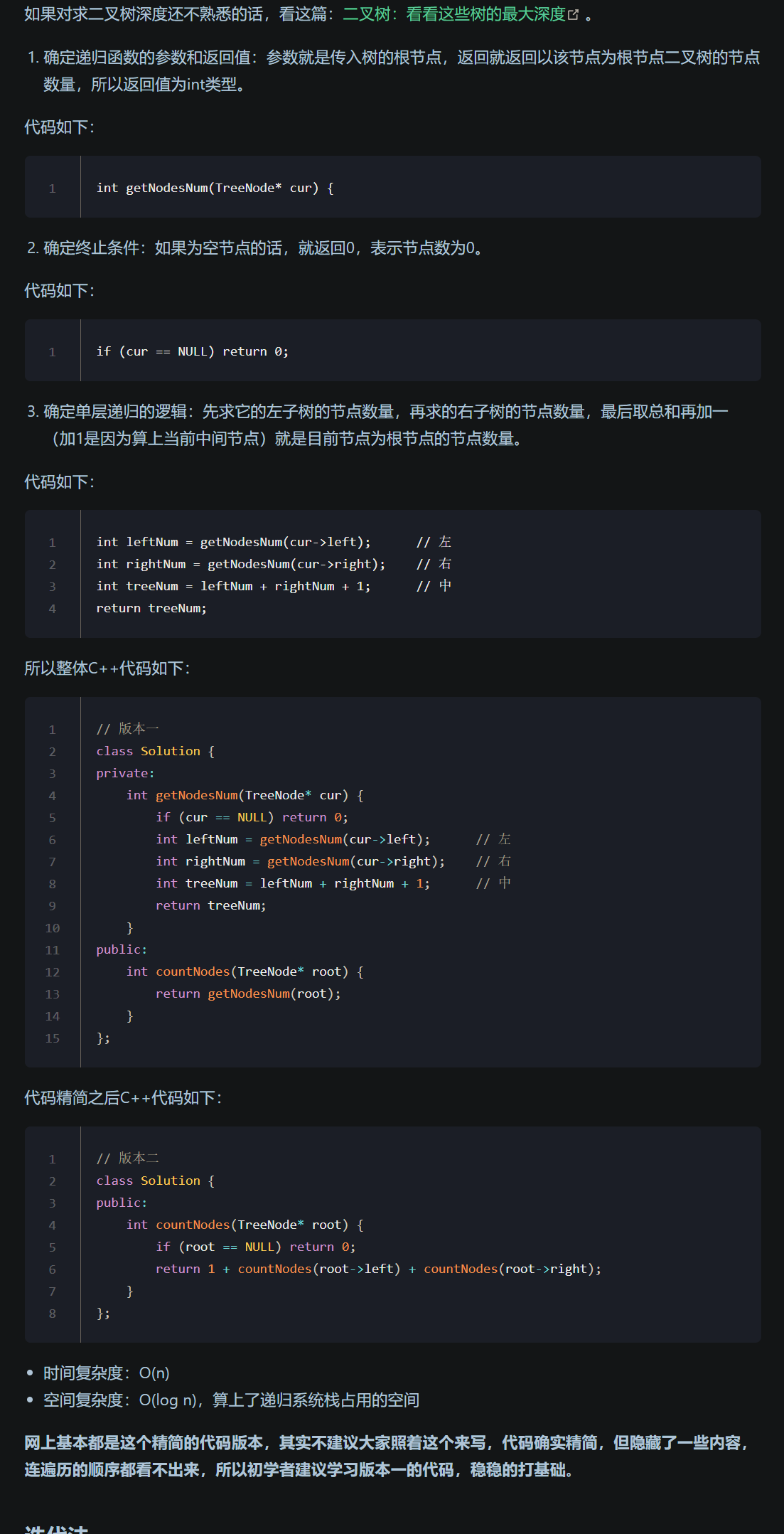
[代码实现]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
//DFS
// 递归出口
if(root == null)return 0;
//单层递归逻辑, 返回值
int leftCount = countNodes(root.left);
int rightCount = countNodes(root.right);
int count = leftCount + rightCount + 1;
return count;
}
}
[思路分析二, (BFS)层寻遍历写法]
[代码实现]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
//层序遍历写法
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null)return 0;
queue.add(root);
int count = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
root = queue.poll();
count++;
if(root.left != null)queue.add(root.left);
if(root.right != null)queue.add(root.right);
}
}
return count;
}
}
[思路分析二, 针对完全二叉树性质的写法]
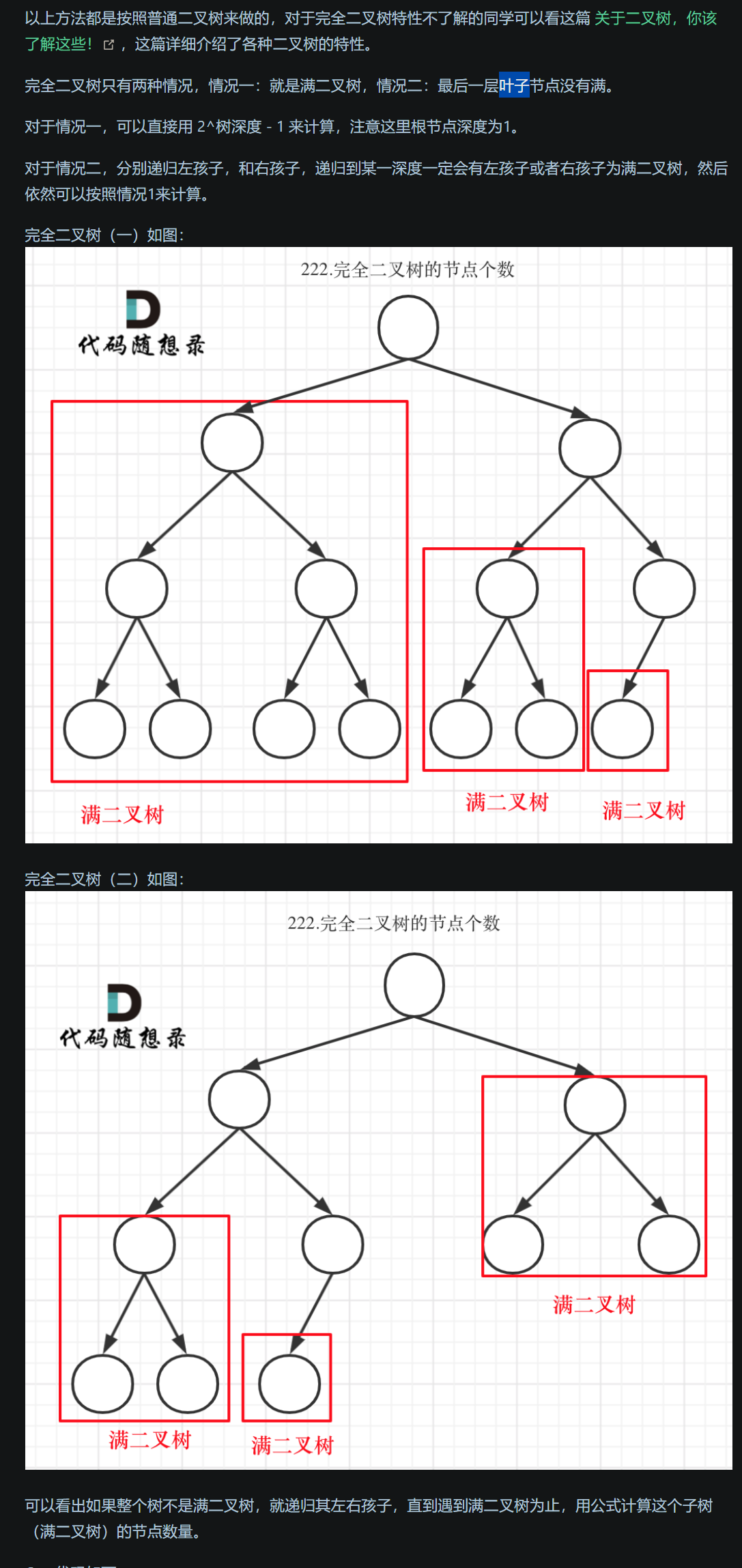
[代码实现]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return getHeight(root) == -1 ? false : true;
}
//求二叉树高度的方法
// 递归参数和返回值, 参数: 当前节点(把它看做根节点),
//返回值: 以当前节点为根节点的树的高度(不平衡时返回-1)
private int getHeight(TreeNode root){
//递归终止条件
if(root == null)return 0;
//单层递归逻辑
//因为平衡二叉树是当前节点的左右子树的高度作比较
//所以, 在单层递归逻辑中(我们可以把当前节点看作是一棵树的根节点,
//对于他的左右子树都要分别求出左子树的高度和右子树的高度,
//然后比较左右子树的高度之差, 如果大于1了则返回-1即可, 不大于1的话说明这个子树是平衡二叉树,
// 我们把以当前节点为根节点的树的高度值直接返回)
int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);
if(leftHeight == -1)return -1;
int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right);
if(rightHeight == -1)return -1;
int result = 0;
if(Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1){
result = -1;
}else{
result = 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
return result;
}
}
lt.110. 平衡二叉树
[案例需求]
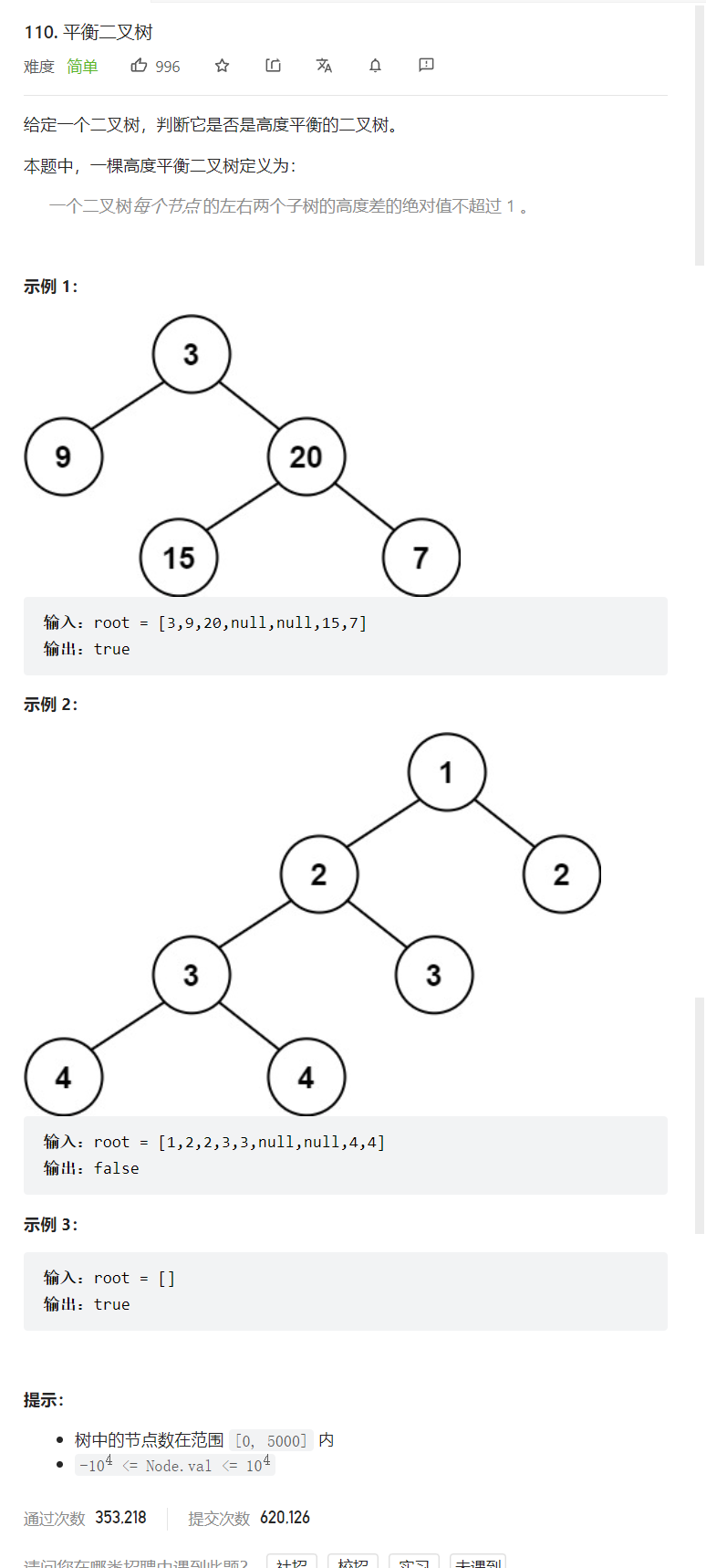
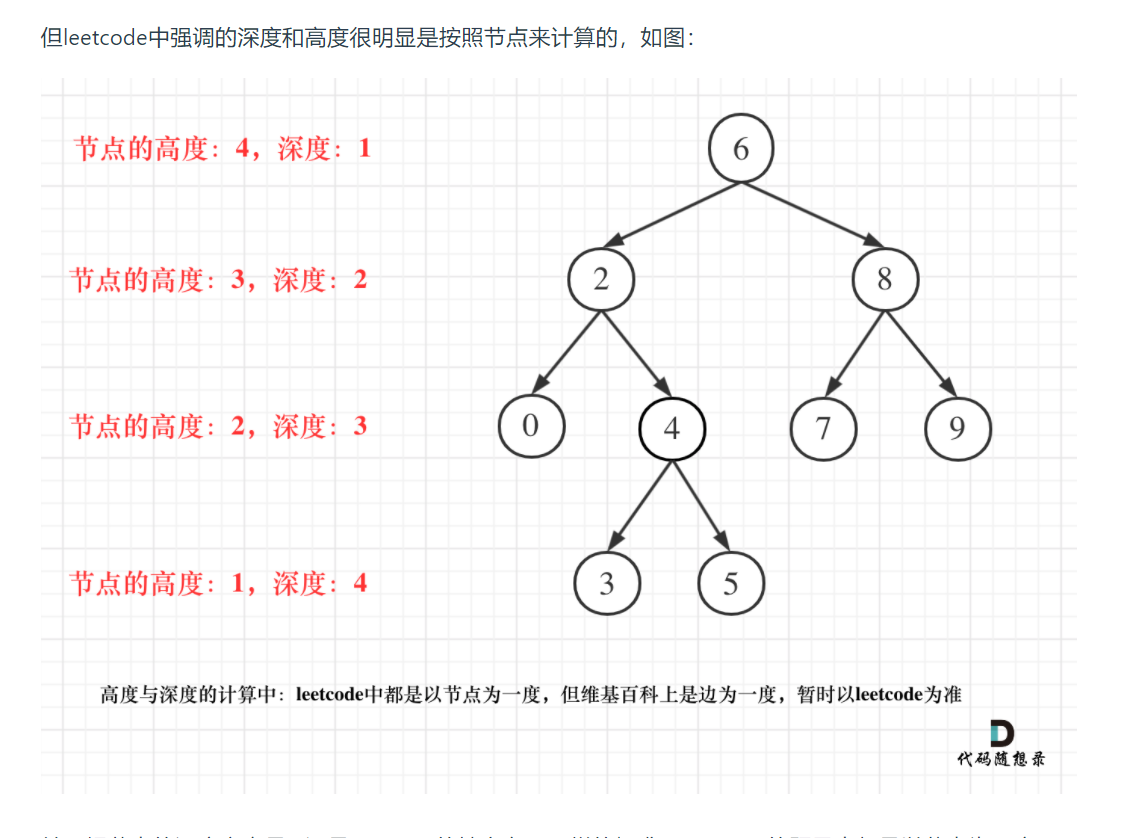
关于二叉树求高度和深度的区别


[思路分析一, 递归法]
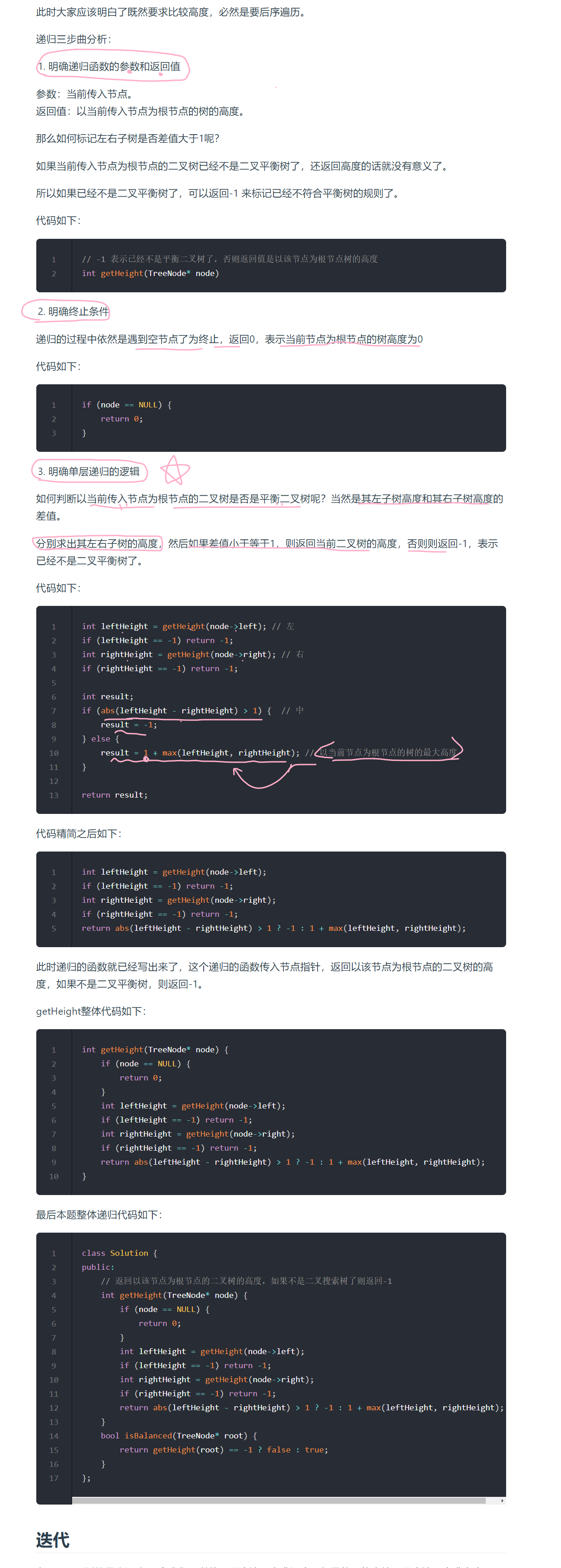
[代码实现]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return getHeight(root) == -1 ? false : true;
}
//求二叉树高度的方法
// 递归参数和返回值, 参数: 当前节点(把它看做根节点),
//返回值: 以当前节点为根节点的数的高度(不平衡时返回-1)
private int getHeight(TreeNode root){
//递归终止条件
if(root == null)return 0;
//单层递归逻辑
int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);
if(leftHeight == -1)return -1;
int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right);
if(rightHeight == -1)return -1;
int result = 0;
if(Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1){
result = -1;
}else{
result = 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
return result;
}
}
[思路分析二, 迭代法]
- 待补充



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号