Vue2 -- 环境搭建
0. 官方文档
https://cn.vuejs.org/guide/quick-start.html
1. Vue概述
1.1 概述
一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式 JavaScript 框架
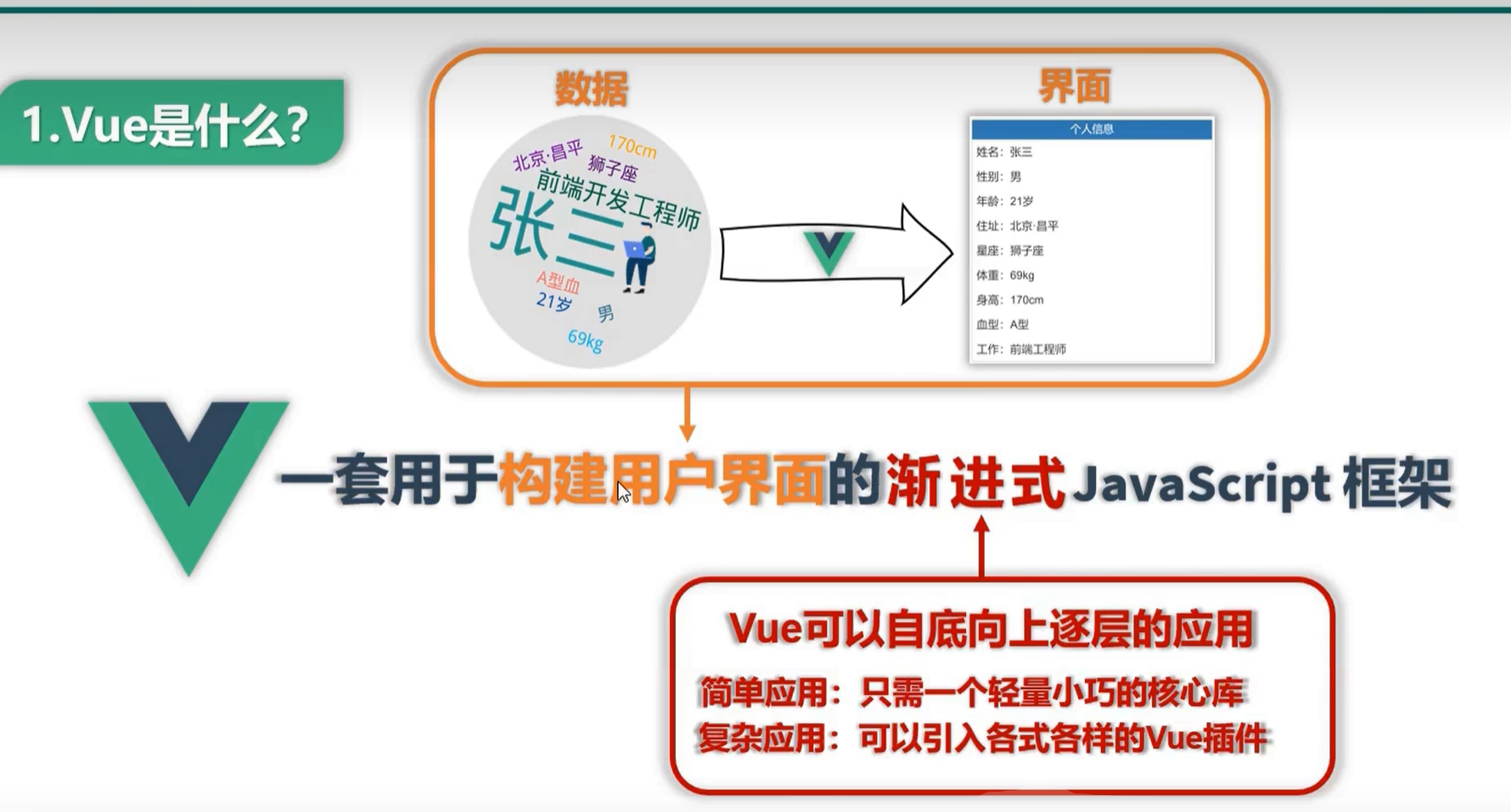
1.2 特点
1. 采用组件化模式,提高代码复用率,且让代码更好维护
2. 声明式编码,让编码人员无需直接操作DOM,提高开发效率
3. 使用虚拟DOM + 优秀的 Diff 算法,尽量复用DOM节点
2. 环境搭建
2.0 开发工具
https://devtools.vuejs.org/guide/installation.html
2.1 Script 标签引入
2.1.1 下载到本地
1. 开发环境
1. 下载地址
https://v2.cn.vuejs.org/js/vue.js
2. 代码中引入
<head>
<!-- 引入Vue.js -->
<script src="./xxx/vue.js"></script>
</head>
2. 生产环境
`1. 下载地址
https://v2.cn.vuejs.org/js/vue.min.js
2. 代码中引入
<head>
<!-- 引入Vue.js -->
<script src="./xxx/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
2.1.2 CDN
1. 开发环境
<head>
<!-- 引入Vue.js -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.16/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
2. 生产环境
<head>
<!-- 引入Vue.js -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.16"></script>
</head>
2.2 NPM
3. 语法
3.1 快速入门
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.7.16/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>Hello {{title}}</h1>
<h2>{{name}}</h2>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false // 阻止 Vue 在启动时生成环境检测提示
// 创建 Vue 实例,Vue实例和容器必须是一对一的关系
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app', // 指定当前Vue实例绑定哪个标签
data: { // 数据存储容器,供前面指定的el区域来使用
title: "World",
name: "你好,世界"
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
3.2 标签绑定
1. 方式一
// 创建 Vue 实例的同时绑定标签
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
title: "World",
name: "你好,世界"
}
})
2. 方式二
// 创建 Vue 实例
const vue = new Vue({
data: {
name: "你好,世界"
}
})
// 手动挂载
v.$mount("#app")
3.3 data声明
1. 方式一
// 创建 Vue 实例的同时声明data
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
name: "你好,世界"
}
})
2. 方式二
// 创建 Vue 实例
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data(){
return{
name:"你好,世界"
}
}
})
3.4 插值语法(变量取值)
<h1> {{title}} </h1>
3.5 数据绑定
3.5.1 v-bind(单向绑定)
<a v-bind:href="url">百度</a>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app', // 指定当前Vue实例绑定哪个标签
data: { // 数据存储容器,供前面指定的el区域来使用
url:"http://www.baidu.com",
}
})
</script>
简写形式
<a :href="url">百度</a>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app', // 指定当前Vue实例绑定哪个标签
data: { // 数据存储容器,供前面指定的el区域来使用
url:"http://www.baidu.com",
}
})
</script>
3.5.2 v-model(双向绑定)
只能用于表单类型元素(有value值的元素),必须有输入或选择框
<div id="app">
<div>
<span>双向绑定:</span><input type="text" v-model:value="data">
</div>
<div>{{data}}</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
data: "1234"
}
})
</script>
简写形式
<div id="app">
<div>
<span>双向绑定:</span><input type="text" v-model="data">
</div>
<div>{{data}}</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
data: "1234"
}
})
</script>
3.5.2 数据代理技术
通过一个对象代理另一个对象中属性的读写操作就是数据代理
1. Object.defineProperty
1. 设置属性
这样设置的属性age,不可被枚举(循环)
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
// 给对象设置属性,如果想要这个属性可被枚举,必须设置 enumerable: true,
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
value: 18,
})
console.log(Object.keys(person))
</script>
2. 设置属性可迭代
如果想要这个属性可被枚举,必须设置 enumerable: true
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
value: 18,
enumerable: true, // 设置属性可迭代
})
console.log(Object.keys(person))
</script>
3. 设置属性可修改
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
value: 18,
writable: true, // 设置属性可修改
})
console.log(Object.keys(person))
</script>
3. 设置属性可删除
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
value: 18,
configurable: true, // 设置属性可删除
})
console.log(Object.keys(person))
</script>
4. get()
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
let number = 18
// 为保证person的age值跟随者number的改变而同时改变,需要用到以下函数
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
get(){ // 当读取person的age属性时,get函数就会被调用,此函数的返回值为age 的值
return number
}
})
console.log(person)
number = 19
console.log(person)
</script>
5. set()
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
let number = 18
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
set(value){ // 当修改person的age属性时,set函数就会被调用,此函数的返回值为age 的值
number = value
}
})
console.log(number)
person.age = 19
console.log(number)
</script>
6. 示例
<script>
let obj = {x:100}
let obj2 = {x:200}
Object.defineProperty(obj2,'x',{
get(){
return obj.x
},
set(value){
obj.x = value
}
})
</script>
2. Vue中对数据代理的应用
Vue将data对象中的每个属性进行代理,并保存到在自身的_data属性中
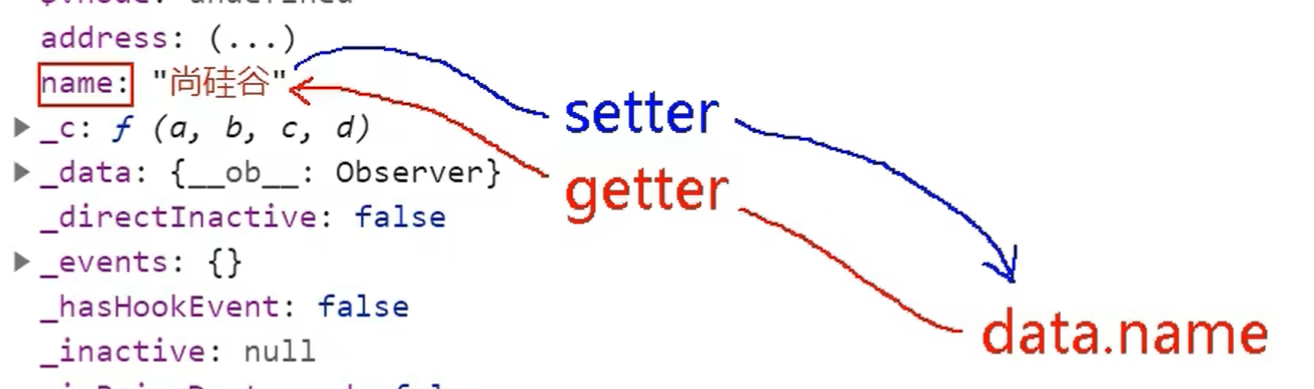
Vue的数据代理

总结
1. Vue中的数据代理:通过vm对象来代理data对象中属性的操作(读/写)
2. Vue中数据代理的好处: 更加方便的操作data中的数据
3. 基本原理:
a. 通过Object.defineProperty()把data对象中所有属性添加到vm上
b. 为每一个添加到vm上的属性,都指定一个getter/setter
c. 在getter/setter内部取操作(读/写) data中对应的属性
3.5.3 _data的数据劫持技术
3.6 事件
3.6.1 v-on
<button v-on:click="changeInfo">修改提示词</button>
简写形式
<button @click="changeInfo">修改提示词</button>
3.6.2 点击事件
1. 绑定点击事件
<div id="app">
<h1>欢迎来到{{name}}</h1>
<button @click="changeInfo">修改提示词</button>
</div>
<body>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
changeInfo(event) {
console.log(event) // 事件对象
console.log(event.target) // 事件标签元素
console.log(event.target.innerText) // 标签元素的内容
this.name = "水上人间" // this为Vue的实例对象
}
// 箭头函数定义的函数是没有自己的this的,会往外层直接找到window
changeInfo2:(event)=>{
this.name // this为Window的实例对象,window对象是没有name属性的,所以此处会报错
}
}
})
</script>
2. 参数传递
<div id="app">
<h1>欢迎来到{{name}}</h1>
<!-- 函数名直接传参,如果想在函数内部调到event,必须传递关键字参数 $event -->
<button @click="changeInfo($event,1)">修改提示词</button>
</div>
<body>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
changeInfo(event,sid) {
console.log(event)
console.log(sid)
}
}
})
</script>
3.6.3 事件修饰符
1. prevent -- 阻止标签默认行为
如,阻止a标签的跳转行为
1. js阻止标签默认行为
<div id="app">
<a href="https://www.baidu.com" @click="changeInfo">弹出信息</a>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
changeInfo(e) {
e.preventDefault() // 阻止a标签的跳转行为
alert(name)
}
}
})
</script>
3. Vue阻止标签默认行为
<div id="app">
<!-- click.prevent 来阻止默认行为 -->
<a href="https://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent="changeInfo">弹出信息</a>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
changeInfo(e) {
alert(name)
}
}
})
</script>
2. stop -- 阻止事件冒泡
1. js阻止事件冒泡
<div id="app">
<!-- 子元素和父元素有相同的点击事件,点击子元素的同时,默认会触发同名事件,这就是事件冒泡,这里点击事件会被执行两次 -->
<div @click="changeInfo">
<!-- 修饰符可以连续写多个 -->
<button @click.stop="changeInfo">弹框</button>
</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
changeInfo(e) {
e.stopPropagation() // 阻止时间冒泡
alert(name)
}
}
})
</script>
3. Vue阻止事件冒泡
<div id="app">
<div @click="changeInfo">
<button @click.stop="changeInfo">弹框</button>
</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
changeInfo(e) {
alert(name)
},
}
})
</script>
3. once -- 事件只触发一次
1. js事件只触发一次
<div id="app">
<!-- 子元素和父元素有相同的点击事件,点击子元素的同时,默认会触发同名事件,这就是事件冒泡,这里点击事件会被执行两次 -->
<div class="demo1" @click="changeInfo">
<button @click="changeInfo">弹出信息</button>
</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
changeInfo(e) {
e.stopPropagation() // 阻止时间冒泡
alert(name)
}
}
})
</script>
3. Vue事件只触发一次
<div id="app">
<button @click.once="changeInfo">弹出信息</button>
</div>
<body>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
changeInfo(e) {
alert(name)
}
}
})
</script>
4. captrue
由于事件是由捕获阶段到冒泡阶段的,此方法是强制事件只使用捕获模式
<div id="app">
<!-- 外层标签加capture -->
<div style="background-color: skyblue;padding: 20px" @click.capture="sendMsg(1)">
div1
<div style="background-color:orange;padding: 20px" @click="sendMsg(2)">
div2
</div>
</div>
</div>
<body>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
changeInfo(e) {
alert(name)
},
sendMsg(msg){
console.log(msg)
}
}
})
</script>
5. self -- 也可以阻止事件冒泡
只有event.target是当前操作的元素才触发事件
<div id="app">
<div @click.self="changeInfo">
<button @click.stop="changeInfo">弹框</button>
</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
changeInfo(e) {
console.log(e.target)
alert(name)
}
}
})
</script>
6. passive
事件的默认行为立即执行,无需等待事件回调执行完毕
鼠标滚轮滚动事件wheel,会先将事件函数执行完毕后,再执行滚动栏的滚动行为,当事件函数需要执行流程很复杂时,会出现鼠标滚轮滚动了,但是滚动栏没动的情况,这里使用passive,则会先执行滚动条滚动,后台默默执行函数
<div id="app">
<ul style="height: 400px;width: 400px;background-color: orange;overflow: auto" @wheel="printMsg">
<li style="height: 200px">1</li>
<li style="height: 200px">2</li>
<li style="height: 200px">3</li>
<li style="height: 200px">4</li>
</ul>
</div>
<body>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
printMsg() {
for (let i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
console.log("@")
}
console.log("执行完毕")
},
}
})
</script>
3.6.4 滚动事件
1. scroll
滚动条绑定滚动事件,如果滚动条到底,则不再会触发
<div id="app">
<ul style="height: 400px;width: 400px;background-color: orange;overflow: auto" @scroll="printMsg">
<li style="height: 200px">1</li>
<li style="height: 200px">2</li>
<li style="height: 200px">3</li>
<li style="height: 200px">4</li>
</ul>
</div>
<body>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
printMsg() {
console.log("@")
},
}
})
</script>
2. wheel
鼠标滚轮绑定滚动事件,滚轮一直动会一直触发,不受制于滚动条是否到底
<div id="app">
<ul style="height: 400px;width: 400px;background-color: orange;overflow: auto" @wheel="printMsg">
<li style="height: 200px">1</li>
<li style="height: 200px">2</li>
<li style="height: 200px">3</li>
<li style="height: 200px">4</li>
</ul>
</div>
<body>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
name: "天上人间"
},
methods: {
printMsg() {
console.log("@")
},
}
})
</script>
3.6.5 键盘事件
1. keyup
键盘抬起时触发的事件
2. keydown
键盘按下时触发的事件
<div id="app">
<input type="text" placeholder="按下回车弹出输入内容" @keyup="printMsg">
</div>
<body>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
},
methods: {
printMsg(e) {
if(e.keyCode !== 13) return
alert(e.target.value)
},
}
})
</script>
3. 按键别名
回车 => enter
删除 => delete (捕获"Delete"和"Backspace"键)
退出 => esc
空格 => space
换行 => tab (必须使用keydown绑定事件,才能正常使用,同时还有ctrl,alt.shift,meta(win键))
上 => up
下 => down
左 => left
右 => right
使用按键别名,监听回车键
<div id="app">
<input type="text" placeholder="按下回车弹出输入内容" @keyup.enter="printMsg">
</div>
<body>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
},
methods: {
printMsg(e) {
alert(e.target.value)
},
}
})
</script>
4. 其他按键
<div id="app">
<input type="text" placeholder="按下回车弹出输入内容" @keyup.caps-lock="printMsg">
</div>
<body>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
},
methods: {
printMsg(e) {
console.log(e.key,e.keyCode) // 键的名字,键的编码,得到键的名字则可以直接调用,但要注意驼峰体的按键是两个单词的拼接,如键盘上切换大小写的键: CapsLock 转换为 caps-lock,其他同理
},
}
})
</script>
5. 特殊按键
1. 换行 => tab (必须使用keydown绑定事件,才能正常使用)
2. 系统修饰键: ctrl,alt.shift,meta(win键)
a. 配合keyup使用时,必须是按下系统修饰键的同时再按下其他键,随后释放其他键,事件才会被触发,@keyup.ctrl.y 就是 ctrl + y
b. 配置keydown使用,正常触发事件
6. 自定义别名
<script>
Vue.config.keyCodes.huiche = 13
</script>
3.7 计算属性
将Vue中定义的属性,重新计算后得到一个新的属性,此为计算属性,底层接住了Object.definepropeerty方法提供的getter和setter
<div id="app">
姓: <input type="text" name="" v-model="firstName"><br>
名: <input type="text" name="" v-model="lastName"><br>
全名: <span>{{fullName}}</span>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: "张",
lastName: "三"
},
computed: {
fullName:{
get(){ // get() 当调用 fullName 时得到计算完成后的属性
// get() 什么时候调用
// 1. 整体模板第一次调用fullName 时,并将结果缓存起来,页面中其他地方读取都是缓存
// 2. fullName 所依赖的数据发生变化时,如firstName 或lastName 发生变化时就会重新执行get()
return this.firstName + "-" + this.lastName
},
// 不是必须定义的,如果很确定这个fullName不会被修改,则无需定义set(),
// fullName 发生变化时会调用set()
set(value){
const arr = value.split("-")
this.firstName = arr[0]
this.lastName = arr[1]
}
}
}
})
</script>
简写形式,确定计算属性只读不改
<div id="app">
姓: <input type="text" name="" v-model="firstName"><br>
名: <input type="text" name="" v-model="lastName"><br>
全名: <span>{{fullName}}</span>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: "张",
lastName: "三"
},
computed: {
fullName(){
return this.firstName + "-" + this.lastName
}
}
})
</script>
3.8 侦听属性(监视属性)
监视数据的变化
1. 定义侦听属性
<div id="app">
<div>今天天气很{{info}}</div>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isHot: true
},
computed: {
info(){
return this.isHot ? "炎热" : "凉爽"
}
},
methods:{
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot
}
},
watch:{ // 监视属性
isHot:{
immediate:true, // 初始化时,调用handler,默认为false
handler(newValue,oldValue){ // 当isHot发生改变时自动执行handler函数,同时保存着之前的值
console.log("改变后的值",newValue,"改变前的值",oldValue)
}
},
info:{ // 也可以监视计算属性
immediate:true, // 初始化时,就先调用一次handler,默认为false
handler(newValue,oldValue){ // 当info发生改变时自动执行handler函数,同时保存着之前的值
console.log("改变后的值",newValue,"改变前的值",oldValue)
}
}
}
})
</script>
方式二
<div id="app">
<div>今天天气很{{info}}</div>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isHot: true
},
computed: {
info(){
return this.isHot ? "炎热" : "凉爽"
}
},
methods:{
changeWeather(){
this.isHot = !this.isHot
}
},
})
vm.$watch('isHot',{
immediate:true,
handler(newValue,oldValue){
console.log("改变后的值",newValue,"改变前的值",oldValue)
}
})
</script>
2. 深度侦听
只监视numbers中的a的改变
<div id="app">
<div>a:{{numbers.a}} b:{{numbers.b}}</div>
<button @click="changeNumber">a+1</button>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
numbers: {
a:1,
b:2
}
},
methods:{
changeNumber(){
this.numbers.a++
}
},
watch:{ // 监视属性
a:{ // a是被包裹在numbers中的,这样写是无法监视到a的
handler(newValue,oldValue){
console.log("改变后的值",newValue,"改变前的值",oldValue)
}
},
'numbers.a':{ // 监视 numbers.a
handler(newValue,oldValue){
console.log("改变后的值",newValue,"改变前的值",oldValue)
}
}
}
})
</script>
监视numbers中的任何项发生改变
<div id="app">
<div>a:{{numbers.a}} b:{{numbers.b}}</div>
<button @click="changeNumber">a+1</button>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
numbers: {
a:1,
b:2
}
},
methods:{
changeNumber(){
this.numbers.a++
}
},
watch:{ // 监视属性
numbers:{
deep:true, // 监视numbers中的任何项发生改变
handler(newValue,oldValue){
console.log("改变后的值",newValue,"改变前的值",oldValue)
}
}
}
})
</script>
3. 侦听属性简写
只监视第一层属性的变化
div id="app">
<div>a:{{a}}</div>
<button @click="changeNumber">a+1</button>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
a:1,
},
methods:{
changeNumber(){
this.a++
}
},
watch:{
a(newValue,oldValue){ // 注意参数
console.log("改变后的值",newValue,"改变前的值",oldValue)
}
}
})
</script>
<div id="app">
<div>a:{{a}}</div>
<button @click="changeNumber">a+1</button>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
a: 1,
},
methods: {
changeNumber() {
this.a++
}
},
})
vue.$watch('a', function (newValue,oldValue) { // 注意参数
console.log("改变后的值", newValue, "改变前的值", oldValue)
})
</script>
4. 侦听属性实现计算属性中的案例
<div id="app">
姓: <input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <br>
姓: <input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <br>
全名: <span>{{fullName}}</span>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: "张",
lastName: "三",
fullName: "张-三"
},
watch: {
firstName(val) {
this.fullName = val + "-" + this.lastName
},
lastName(val) {
this.fullName = this.firstName + "-" + val
}
}
})
</script>
5. 异步任务,只能用侦听属性实现
<div id="app">
姓: <input type="text" v-model="firstName"> <br>
姓: <input type="text" v-model="lastName"> <br>
全名: <span>{{fullName}}</span>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
const vue = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
firstName: "张",
lastName: "三",
fullName: "张-三"
},
watch: {
firstName(val) {
setTimeout(()=>{ // 定时器为异步任务,延迟1秒再修改全名
this.fullName = val + "-" + this.lastName
},1000)
},
lastName(val) {
this.fullName = this.firstName + "-" + val
}
}
})
</script>
3.9 样式绑定
3.9.1 class样式
1. 字符串形式
<style>
.basic {
width: 100%;
height: 400px;
}
.normal {
background-color: skyblue;
}
.happy {
background-color: orange;
}
.sad {
background-color: green;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<!-- 对于不会动态变化的class值 正常定义,对于动态变化的class 值,使用v-bind 管理,适用于样式的类名不确定,需要动态指定-->
<div class="basic" :class="mood" @click="changeMood">test</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
mood: "normal"
},
methods: {
changeMood() {
this.mood = "happy"
}
}
})
</script>
2. 数组形式
<style>
.basic {
width: 100%;
height: 400px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.c1 {
font-size: 100px;
}
.c2 {
border-radius: 90px;
}
.c3 {
color: orange;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<!-- 操作数组中的class类型,来动态修改样式 -->
<div class="basic" :class="classArr" @click="deleteClass">test</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
classArr: ["c1","c2","c3"]
},
methods: {
deleteClass() {
this.classArr.shift()
// this.classArr.push("c1")
}
}
})
</script>
3. 对象形式
<style>
.basic {
width: 100%;
height: 400px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.c1 {
font-size: 100px;
}
.c2 {
border-radius: 90px;
}
</style>
<div id="app">
<!-- 对于不会动态变化的class值 正常定义,对于动态变化的class 值,使用v-bind 管理 -->
<div class="basic" :class="classObj" @click="deleteClass">test</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
classObj: {
c1: false,
c2: false
}
},
methods: {
deleteClass() {
this.classObj.c1 = !this.classObj.c1
this.classObj.c2 = !this.classObj.c2
}
}
})
</script>
3.9.2 style样式
写法一
<div id="app">
<!-- 改为对象形式 font-size 改为 fontSize 并和px拼接-->
<div :style="{fontSize: fSize + 'px'}" @click="changeClass">test</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
fSize:40
},
methods: {
changeClass(){
this.fSize += 10
}
}
})
</script>
写法二
<div id="app">
<!-- font-size 改为 fontSize px拼接-->
<div :style="fontObj" @click="changeClass">test</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
fontObj: {
fontSize: '40px'
}
},
methods: {
changeClass() {
this.fontObj.fontSize = "100px"
}
}
})
</script>
3.10 条件语句
3.10.1 v-show
如果v-show 后面的表达式为false,会将当前标签用display:none隐藏,并不会删除标签,如果节点变化的比较频繁就使用v-show
<div id="app">
<button @click="changeShow">显示test2</button>
<div>test1</div>
<div v-show="isShow">test2</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
isShow: false,
},
methods: {
changeShow() {
this.isShow = !this.isShow
}
}
})
</script>

3.10.1 v-if
v-if
v-if 不满足条件是没有标签节点的
<div id="app">
<button @click="changeShow">显示test2</button>
<div>test1</div>
<div v-if="isShow">test2</div>
<div v-else-if="!isShow">test3</div>
<div v-else>test4</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
isShow: false,
},
methods: {
changeShow() {
this.isShow = !this.isShow
}
}
})
</script>

3.11 循环语句
3.11.1 v-for
1. 遍历数组
<div id="app">
<ul>
<!-- 注意必须要写key值,v为索引值,括号最好写上 -->
<li v-for="(p,v) in persons" :key="p.id">索引{{v}}-{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
persons:[
{id:1,name:'小明',age:18},
{id:2,name:'小红',age:19},
{id:3,name:'小白',age:20},
]
},
})
</script>
2. 遍历对象
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="v,k in persons" :key="k">{{k}}-{{v}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
persons:{id:1,name:'小明',age:18},
},
})
</script>
3. 遍历字符串
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="i,v in persons" :key="i">{{i}}-{{v}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
persons:"jlkajdsf",
},
})
</script>
4. 遍历次数
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="n,v in 5">序号{{n}}-索引{{v}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
})
</script>
5. key 的原理
key是vue在内部使用的并不会在标签上显示
1. 使用index时,且会在数组索引为0的位置安插数据时,破坏了之前数组的顺序,就会出现的标签错乱的bug,同时这样做的效果是很低的,不会复用之前的DOM,在末尾添加数据,并未破坏原本的数据不会出现这个bug,必须要换成后端获取的id字段这种唯一的ID才不会出现这个bug
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in persons" :key="index">
{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}
<input type="text">
</li>
</ul>
<button @click.once="add">添加一个人员</button>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
persons: [
{id: 1, name: "张三", age: 18},
{id: 2, name: "李四", age: 19},
{id: 3, name: "王五", age: 20},
]
},
methods:{
add(){
const onePerson = {id:4,name:"赵六",age:21}
this.persons.unshift(onePerson)
}
}
})
</script>
当所有的input框写入内容后,再点击添加人员时会出现标签结构问题:如下

点击添加人员后

2. key的作用
Index为key时

当循环列表时,会根据初始数据生成虚拟DOM,如上图中,然后再根据虚拟DOM转成真实DOM,用户在Input框中的输入是在操作真实DOM,当有新数据插入在列表的首位时,数据发生了变化,同样根据新数据生成虚拟DOM,然后根据虚拟DOM对比算法来进行比对,比对的根据就是key这个值,如上图,会循环对比两边的虚拟DOM,如:左右两边的key=0的这一行的标签中的文字节点是不一样的,并不能复用,所以当由虚拟DOM转成真实DOM时,会生成老刘-30替换之前的文本节点,而input框在虚拟DOM中对比结果为一致的,则会复用之前携带用户输入数据的节点,以此类推
ID为key时
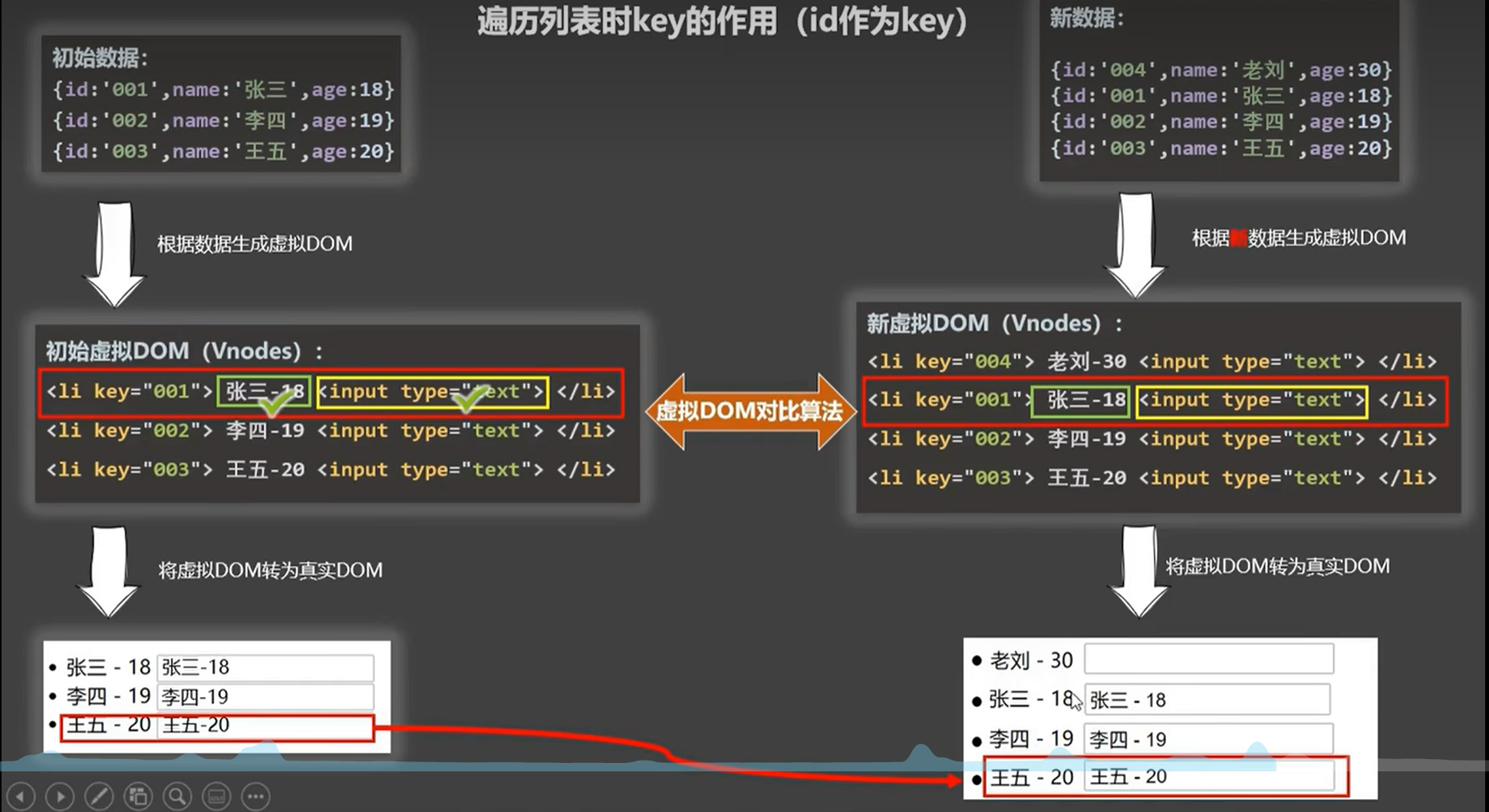
3. 开发中如何选择key
1. 最好使用每条数据的唯一标识作为key,如id,手机号,身份证号,学号等唯一值
2. 如果不存在对数据的逆序添加,逆序删除等破坏顺讯操作,仅用于渲染列表用于展示,使用index作为key是没有问题的
3.12 数组渲染
1. 数组遍历
<div id="app">
<ul>
<!-- 注意必须要写key值,v为索引值,括号最好写上 -->
<li v-for="(p,v) in persons" :key="p.id">索引{{v}}-{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
persons:[
{id:1,name:'小明',age:18},
{id:2,name:'小红',age:19},
{id:3,name:'小白',age:20},
]
},
})
</script>
2. 数组过滤
1. 使用侦听属性实现
<div id="app">
<h1>数组过滤</h1>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入文字" v-model="keyWord">
<ul v-if="filPersons">
<li v-for="(p,index) in filPersons" :key="index">
{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
keyWord: "",
persons: [
{id: 1, name: "张三", age: 18},
{id: 2, name: "李四", age: 19},
{id: 3, name: "王五", age: 20},
],
filPersons: []
},
watch: {
keyWord: {
// immediate:true 初始化时,先调用一次handler
immediate:true, // 由于字符串中都会包含空字符串,当indexOf(空字符串)时,this.filPersons筛选出来的结果为persons数组的每一个元素
handler(val) {
this.filPersons = this.persons.filter((p) => {
return p.name.indexOf(val) !== -1
})
}
}
}
})
</script>
2. 使用计算属性实现
<div id="app">
<h1>数组过滤</h1>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入文字" v-model="keyWord">
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in filPersons" :key="index">
{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
keyWord: "",
persons: [
{id: 1, name: "张三", age: 18},
{id: 2, name: "李四", age: 19},
{id: 3, name: "王五", age: 20},
],
},
computed: {
filPersons(){
return this.filPersons = this.persons.filter((p) => {
return p.name.indexOf(this.keyWord) !== -1
})
}
}
})
</script>
3. 数组过滤后排序
<div id="app">
<h1>数组过滤+排序</h1>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入文字" v-model="keyWord">
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in filPersons" :key="index">
{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}
</li>
</ul>
<button @click="sortType = 2">年龄升序</button>
<button @click="sortType = 1">年龄降序</button>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
keyWord: "",
sortType: 0,
persons: [
{id: 1, name: "马冬梅", age: 18},
{id: 2, name: "周冬雨", age: 19},
{id: 3, name: "周杰伦", age: 40},
{id: 4, name: "王兆伦", age: 25},
],
},
computed: {
filPersons() {
const filteredArr = this.filPersons = this.persons.filter((p) => {
return p.name.indexOf(this.keyWord) !== -1
})
if (this.sortType) {
filteredArr.sort((p1, p2) => {
return this.sortType === 1 ? p2.age - p1.age : p1.age - p2.age
})
}
return filteredArr
}
}
})
</script>
9. 原理
9.1 MVVM模型

1. M: 模型(Model)
对应 Vue data中的数据
2. V: 视图(View)
模版
3. VM: 视图模型(ViewModel)
Vue 实例对象
9.2 数据绑定之数据代理技术
通过一个对象代理另一个对象中属性的读写操作就是数据代理
1. Object.defineProperty
1. 设置属性
这样设置的属性age,不可被枚举(循环)
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
// 给对象设置属性,如果想要这个属性可被枚举,必须设置 enumerable: true,
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
value: 18,
})
console.log(Object.keys(person))
</script>
2. 设置属性可迭代
如果想要这个属性可被枚举,必须设置 enumerable: true
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
value: 18,
enumerable: true, // 设置属性可迭代
})
console.log(Object.keys(person))
</script>
3. 设置属性可修改
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
value: 18,
writable: true, // 设置属性可修改
})
console.log(Object.keys(person))
</script>
3. 设置属性可删除
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
value: 18,
configurable: true, // 设置属性可删除
})
console.log(Object.keys(person))
</script>
4. get()
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
let number = 18
// 为保证person的age值跟随者number的改变而同时改变,需要用到以下函数
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
get(){ // 当读取person的age属性时,get函数就会被调用,此函数的返回值为age 的值
return number
}
})
console.log(person)
number = 19
console.log(person)
</script>
5. set()
<script>
let person = {
name: "张三",
sex: "男",
}
let number = 18
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
set(value){ // 当修改person的age属性时,set函数就会被调用,此函数的返回值为age 的值
number = value
}
})
console.log(number)
person.age = 19
console.log(number)
</script>
6. 示例
<script>
let obj = {x:100}
let obj2 = {x:200}
Object.defineProperty(obj2,'x',{
get(){
return obj.x
},
set(value){
obj.x = value
}
})
</script>
2. Vue中对数据代理的应用
Vue将data对象中的每个属性进行代理,并保存到在自身的_data属性中

Vue的数据代理

总结
1. Vue中的数据代理:通过vm对象来代理data对象中属性的操作(读/写)
2. Vue中数据代理的好处: 更加方便的操作data中的数据
3. 基本原理:
a. 通过Object.defineProperty()把data对象中所有属性添加到vm上
b. 为每一个添加到vm上的属性,都指定一个getter/setter
c. 在getter/setter内部取操作(读/写) data中对应的属性
9.3 数据绑定之_data的数据劫持技术
9.4 数据绑定之数据监视原理
1. 更新时会出现的问题
<div id="app">
<h1>更新时的问题</h1>
<ul>
<li v-for="(p,index) in persons" :key="p.id">
{{p.name}}-{{p.age}}
</li>
</ul>
<button @click="updateMdm2">更新马冬梅的信息</button>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
keyWord: "",
sortType: 0,
persons: [
{id: 1, name: "马冬梅", age: 18},
{id: 2, name: "周冬雨", age: 19},
{id: 3, name: "周杰伦", age: 40},
{id: 4, name: "王兆伦", age: 25},
],
},
methods: {
updateMdm() { // 通过属性修改时Vue是能同时修改页面显示的
this.persons[0].name = "马老师"
this.persons[0].age = 50
},
updateMdm2() { // 直接修改数组中的元素是无法被Vue监测到的,所以代码层面和数据已经改了,但是页面显示并未发生变化
this.persons[0] = {id: 1, name: "马老师", age: 50}
}
}
})
</script>
2. Vue是如何监测对象中的数据变化的
1. 模仿Vue做数据代理
<script>
let data = {
name: "小明"
}
Object.defineProperty(data, "name", { // 如果有人访问data中的name,就会执行get()
get() {
return data.name // 这里同样是在访问data中的name,同样需要执行get(),会造成递归,set()同理
}
set(val) {
data.name = val
}
})
</script>
2. Vue如何解决上述问题的
Vue中写的是对data的递归查找,会找到data中对象中的对象,所有层,这里的示例代码并没有考虑到对象中有对象
<script>
let data = {
name: "小明"
}
// 创建一个监视的实例对象,用于监视data中属性的变化
const obs = new Observer(data)
function Observer(obj) {
// 汇总对象中的所有属性形成一个数组
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
// 遍历
keys.forEach((k) => {
// this 是Observer的实例对象
Object.defineProperty(this,k,{
get(){
return obj[k]
},
set(val){
console.log(`${k} 被改了,接下来,解析模板,生成虚拟DOM......`)
obj[k] = val
}
})
})
}
let vm = {}
// 这里相当于将obs同时复制给Vue中定义的data,和_data
vm._data = data = obs
console.log(vm)
</script>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号