Stream流简单使用
创建流
/**
* 创建流
*/
@Test
public void testOne() {
List<Author> authorList = new ArrayList<>();
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(2).name("小红").address("星光大道").build());
//集合创建流
Stream<Author> stream = authorList.stream();
log.info("stream:{}", stream);
Integer[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
//数组创建流
Stream<Integer> integerStream = Arrays.stream(arr);
log.info("integerStream:{}", integerStream);
//数组创建流
Stream<Integer> integerStream1 = Stream.of(arr);
log.info("integerStream1:{}", integerStream1);
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(16);
map.put("1", 123);
map.put("2", 234);
map.put("3", 345);
map.put("4", 456);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
//map集合创建流
Stream<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entryStream = entrySet.stream();
log.info("entryStream:{}", entryStream);
}
filter过滤使用
List<Author> authorList = new ArrayList<>();
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(2).name("小红").address("星光大道").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(3).name("小绿").address("太古里").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(4).name("小得子").address("三里屯").build());
//集合创建流
Stream<Author> stream = authorList.stream();
//打印id>2的且姓名长度等于3的
stream.filter(new Predicate<Author>() {
@Override
public boolean test(Author author) {
Integer id = author.getId();
int length = author.getName().length();
if (id>2&&length==3){
return true;
}
return false;
}
});
转化为lamda表达式
List<Author> authorList = new ArrayList<>();
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(2).name("小红").address("星光大道").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(3).name("小绿").address("太古里").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(4).name("小得子").address("三里屯").build());
//集合创建流
Stream<Author> stream = authorList.stream();
//打印id>2的且姓名长度等于3的
stream.filter(author -> {
Integer id = author.getId();
int length = author.getName().length();
if (id>2&&length==3){
return true;
}
return false;
}).forEach(new Consumer<Author>() {
@Override
public void accept(Author author) {
log.info(author.toString());
}
});
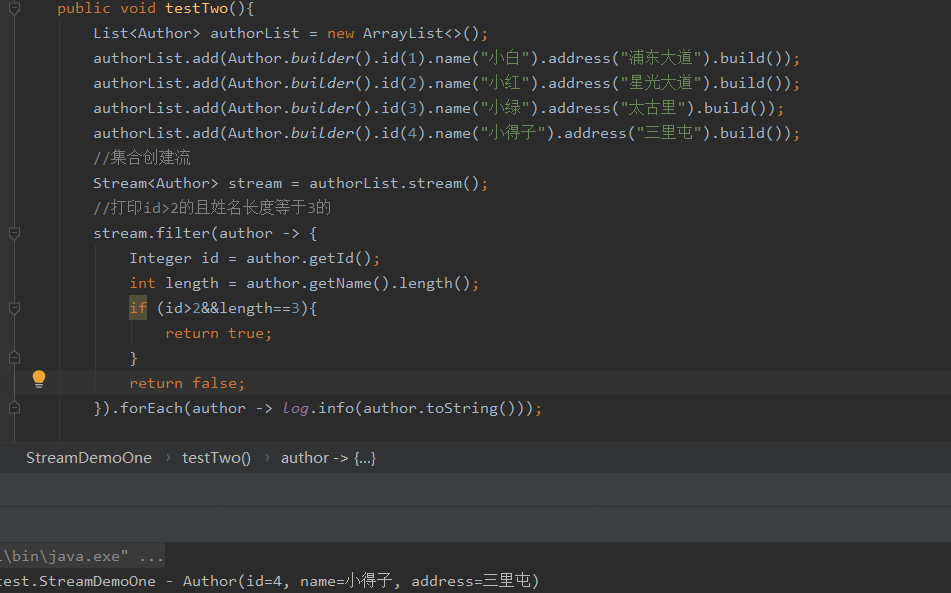
继续简化
List<Author> authorList = new ArrayList<>();
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(2).name("小红").address("星光大道").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(3).name("小绿").address("太古里").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(4).name("小得子").address("三里屯").build());
//集合创建流
Stream<Author> stream = authorList.stream();
//打印id>2的且姓名长度等于3的
stream.filter(author -> {
Integer id = author.getId();
int length = author.getName().length();
if (id>2&&length==3){
return true;
}
return false;
}).forEach(author -> log.info(author.toString()));
Stream中map使用(接受流中的元素,并且将其映射成新的元素)
@Test
public void mapTest(){
List<Author> authorList = new ArrayList<>();
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(2).name("小红").address("星光大道").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(3).name("小绿").address("太古里").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(4).name("小得子").address("三里屯").build());
//集合创建流
Stream<Author> stream = authorList.stream();
stream.map(new Function<Author, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Author author) {
return author.getName();
}
}).forEach(new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
log.info(s);
}
});
}
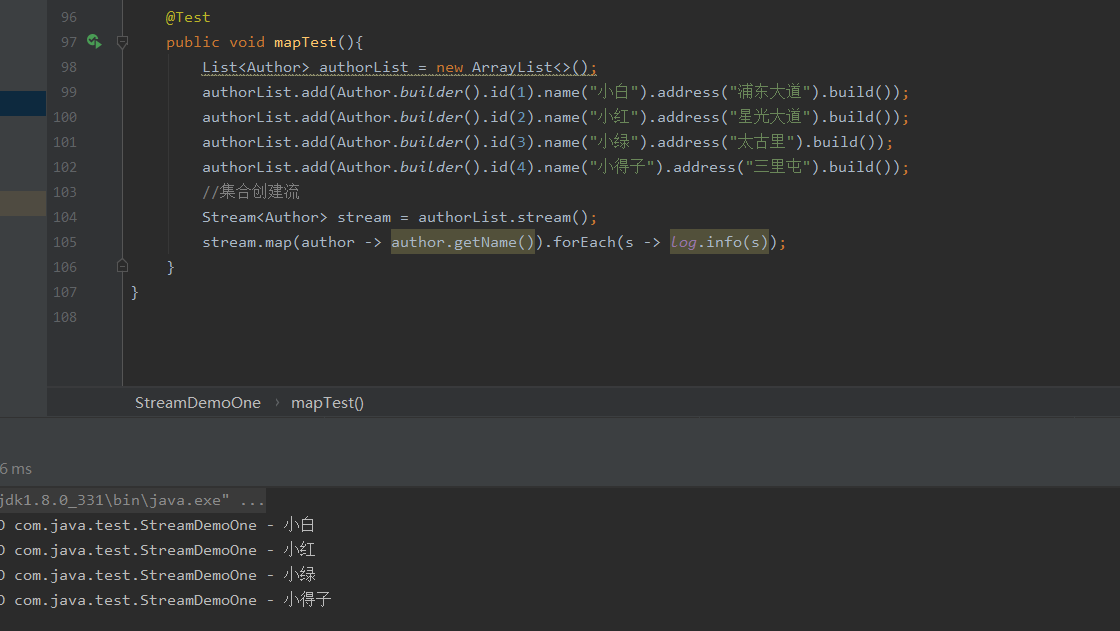
转化为lamada表达式
@Test
public void mapTest(){
List<Author> authorList = new ArrayList<>();
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(2).name("小红").address("星光大道").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(3).name("小绿").address("太古里").build());
authorList.add(Author.builder().id(4).name("小得子").address("三里屯").build());
//集合创建流
Stream<Author> stream = authorList.stream();
stream.map(author -> author.getName()).forEach(s -> log.info(s));
}
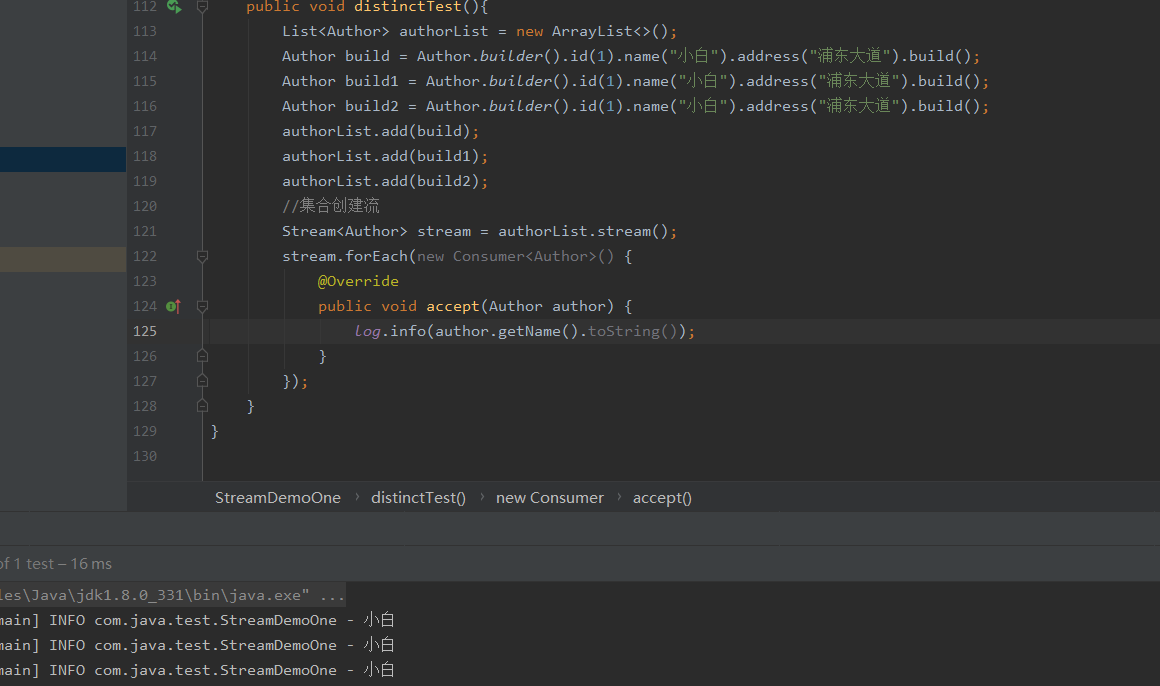
使用distinct去重,其中需要特别注意的是distinct实现的去重功能依赖来自Object的equals方法来判断是否是相同的对象,所以需要重写equals方法
数据准备
package com.java.test.bean;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: Yourheart
* @Create: 2022/10/9 23:40
*/
@Data
@Builder
public class Author extends Object{
private Integer id;
/**
* 作家名称
*/
private String name;
/**
* 作家的居住地址
*/
private String address;
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Author author = (Author) o;
return Objects.equals(id, author.id) &&
Objects.equals(name, author.name) &&
Objects.equals(address, author.address);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name, address);
}
}
去重前
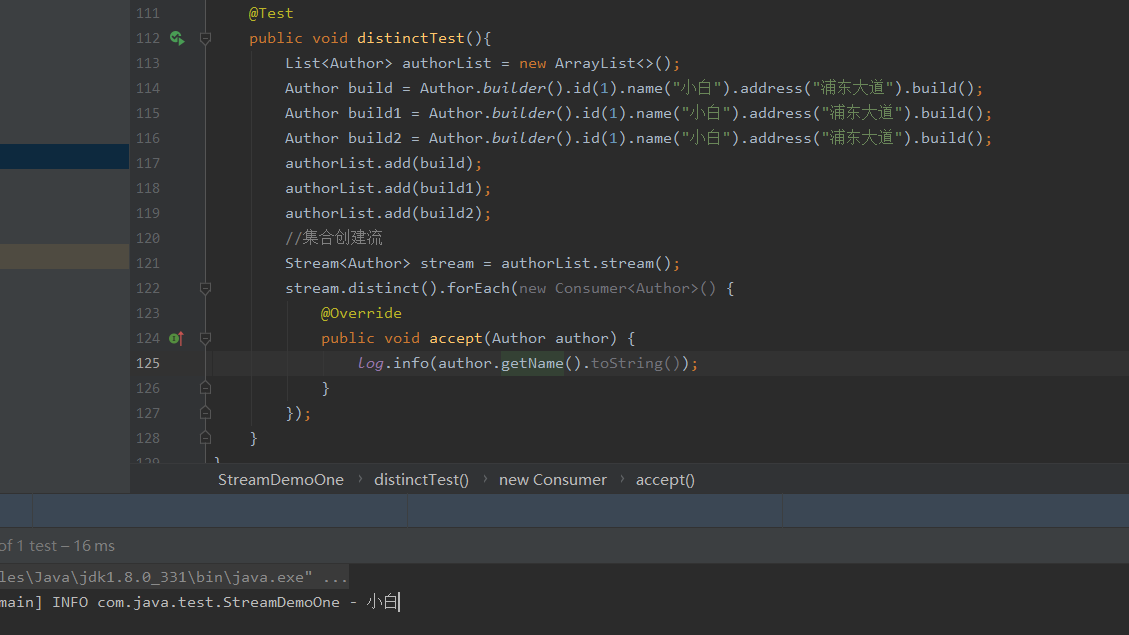
去重后
@Test
public void distinctTest(){
List<Author> authorList = new ArrayList<>();
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").build();
authorList.add(build);
authorList.add(build1);
authorList.add(build2);
//集合创建流
Stream<Author> stream = authorList.stream();
stream.distinct().forEach(new Consumer<Author>() {
@Override
public void accept(Author author) {
log.info(author.getName().toString());
}
});
}
flatMap使用
去重每个作家中,重复的书籍
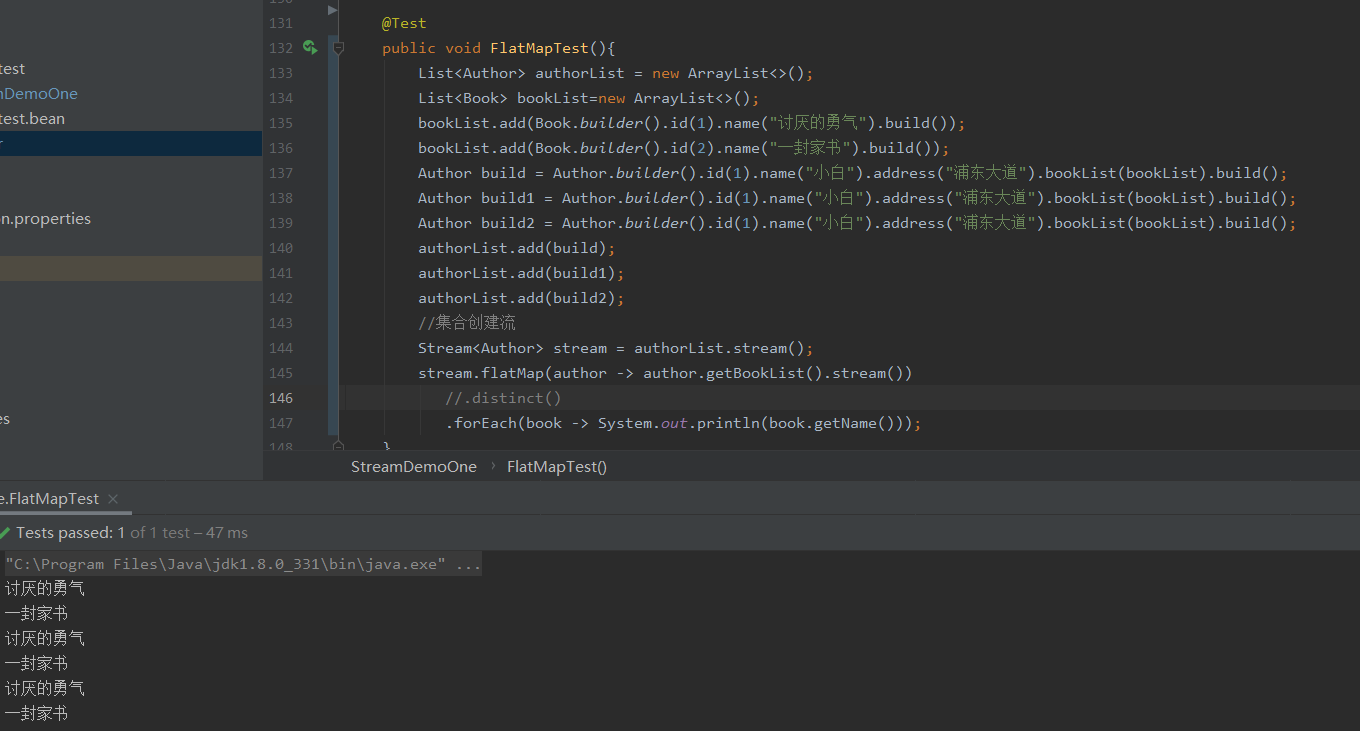
去重后

代码部分
@Test
public void FlatMapTest(){
List<Author> authorList = new ArrayList<>();
List<Book> bookList=new ArrayList<>();
bookList.add(Book.builder().id(1).name("讨厌的勇气").build());
bookList.add(Book.builder().id(2).name("一封家书").build());
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").bookList(bookList).build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").bookList(bookList).build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(1).name("小白").address("浦东大道").bookList(bookList).build();
authorList.add(build);
authorList.add(build1);
authorList.add(build2);
//集合创建流
Stream<Author> stream = authorList.stream();
stream.flatMap(author -> author.getBookList().stream())
.distinct()
.forEach(book -> System.out.println(book.getName()));
}
两个实体类
package com.java.test.bean;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: Yourheart
* @Create: 2022/10/10 7:49
*/
@Data
@Builder
public class Book {
private Integer id;
/**
* 书籍名称
*/
private String name;
}
package com.java.test.bean;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: Yourheart
* @Create: 2022/10/9 23:40
*/
@Data
@Builder
public class Author extends Object{
private Integer id;
/**
* 作家名称
*/
private String name;
/**
* 作家的居住地址
*/
private String address;
private List<Book> bookList;
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Author author = (Author) o;
return Objects.equals(id, author.id) &&
Objects.equals(name, author.name) &&
Objects.equals(address, author.address) &&
Objects.equals(bookList, author.bookList);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name, address, bookList);
}
}
Foreach使用
@Test
public void foreachTest(){
List<Author> authorList = new ArrayList<>();
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(2).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(3).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
authorList.add(build);
authorList.add(build1);
authorList.add(build2);
authorList.stream().forEach(new Consumer<Author>() {
@Override
public void accept(Author author) {
System.out.println(author.toString());
}
});
}
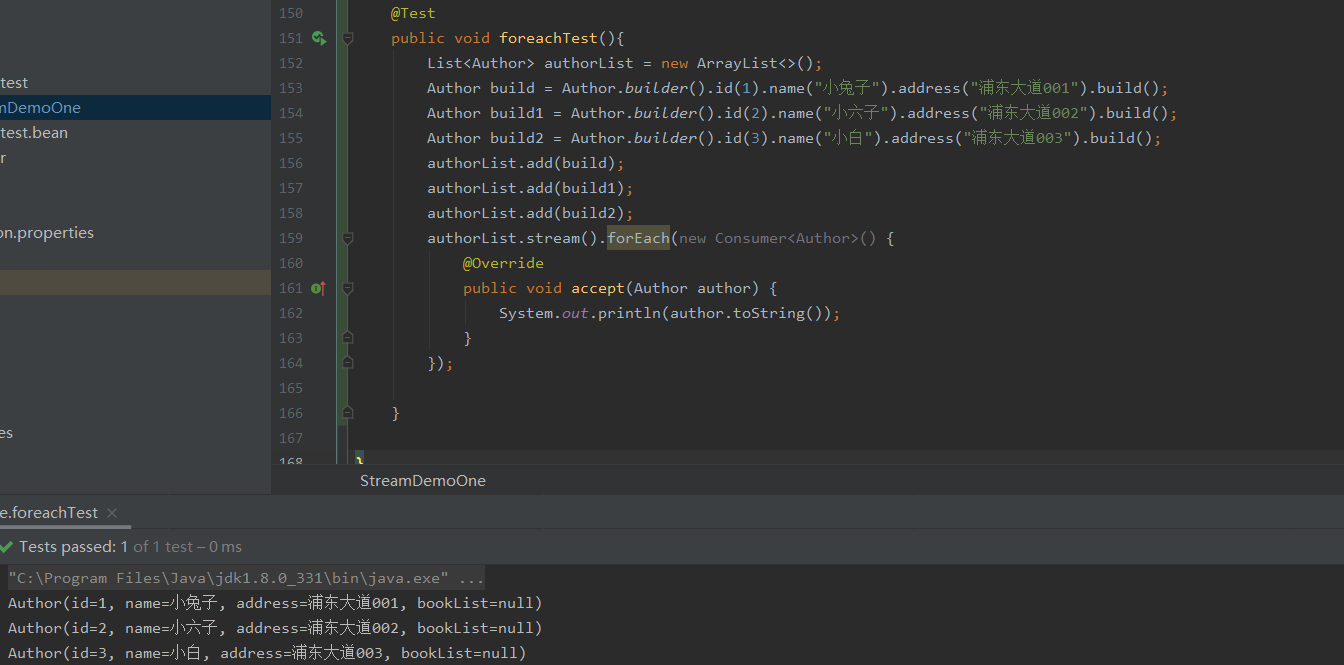
这里插入说点内容
stream收集器
含义就是将流转化为我们想要的集合类型,就是将最终的数据收集成List、Set、Map
转化为set集合
@Test
public void collectTest(){
List<Author> authorList = new ArrayList<>();
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(2).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(3).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(3).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
authorList.add(build);
authorList.add(build1);
authorList.add(build2);
authorList.add(build3);
Set<Author> collect = authorList.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
for (Author author : collect) {
log.info("author:{}",author);
}
}
同时这里还实现了去重功能

将流转化为list集合 Collectors.toList() 将流转化为set集合 Collectors.toSet()
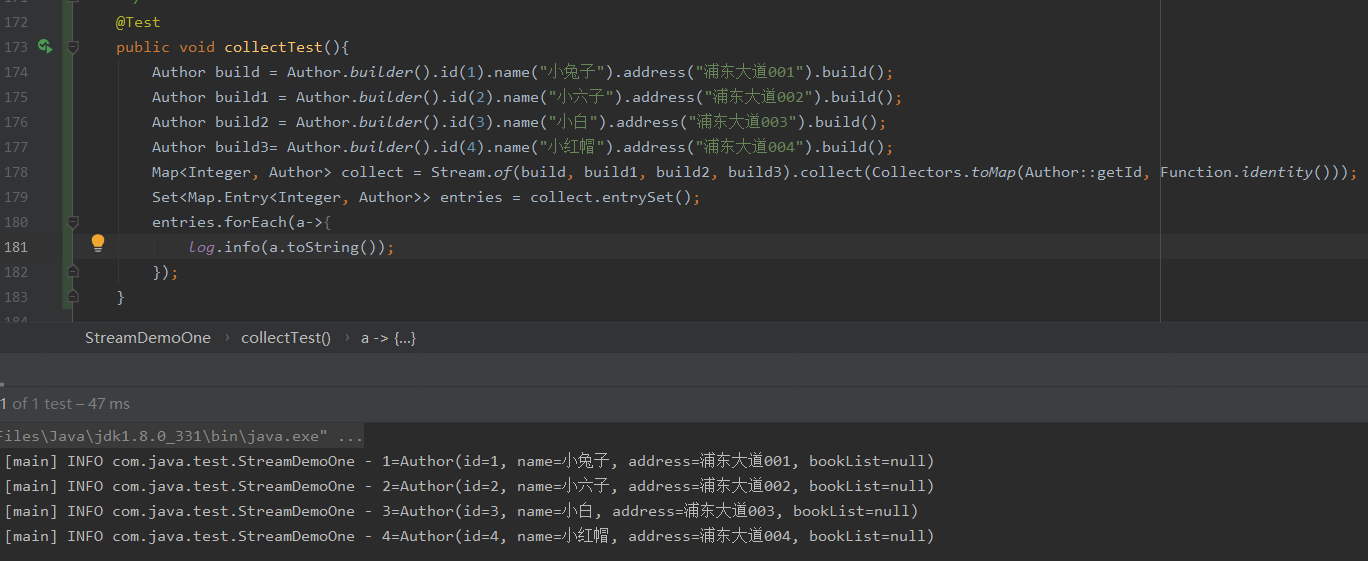
将实体类以key-value形式放置map集合中
@Test
public void collectTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(2).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(3).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(4).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Map<Integer, Author> collect = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3).collect(Collectors.toMap(Author::getId, Function.identity()));
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, Author>> entries = collect.entrySet();
entries.forEach(a->{
log.info(a.toString());
});
}
这里分别使用串行收集和并行收集打印耗时
public void collectTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(21).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(41).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build6 = Author.builder().id(201).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build7 = Author.builder().id(302).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build8= Author.builder().id(403).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build9= Author.builder().id(12).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build10 = Author.builder().id(22).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build11= Author.builder().id(23).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build12= Author.builder().id(24).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
long nanoTime = System.nanoTime();
//串行收集
Map<Integer, Author> collect = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3,build5,build6,build7,build8,build9,build10,build11,build12).collect(Collectors.toMap(Author::getId, Function.identity()));
long nanoTime1 = System.nanoTime();
log.info("串行收集耗时:{} ns",nanoTime1-nanoTime);
long nanoTime2 = System.nanoTime();
//并行收集
Map<Integer, Author> collect1 = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3,build5,build6,build7,build8,build9,build10,build11,build12).collect(Collectors.toMap(Author::getId, Function.identity()));
long nanoTime3 = System.nanoTime();
log.info("并行收集耗时:{} ns",nanoTime3-nanoTime2);
}
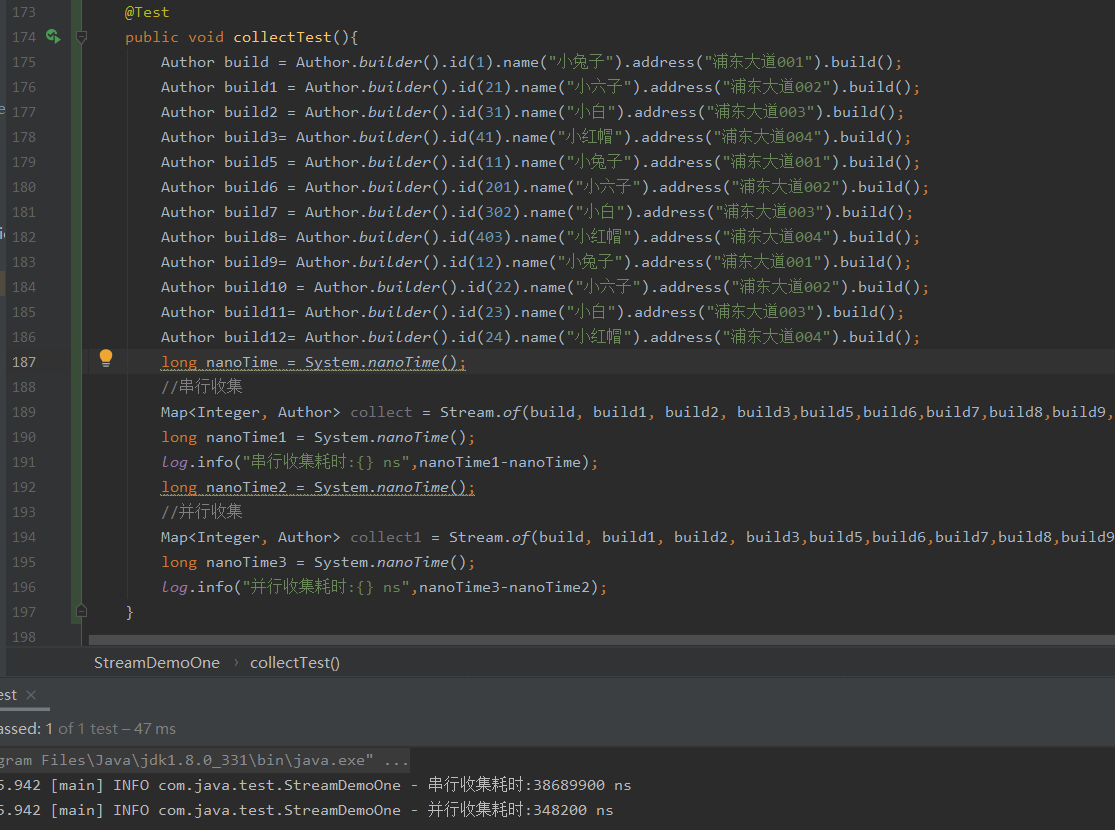
但是需要注意的是并行收集顺序会乱,同时数据如果存在重复的会报错,这点需要注意
前面是转化为id->Author形式
下面转化为id->name的形式
@Test
public void collectTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(21).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(41).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build6 = Author.builder().id(201).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build7 = Author.builder().id(302).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build8= Author.builder().id(403).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build9= Author.builder().id(12).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build10 = Author.builder().id(22).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build11= Author.builder().id(23).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build12= Author.builder().id(24).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Map<Integer, String> collect = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3, build5, build6, build7, build8, build9, build10, build11, build12)
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Author::getId, Author::getName));
collect.entrySet().forEach(a->{
log.info(a.toString());
});
}
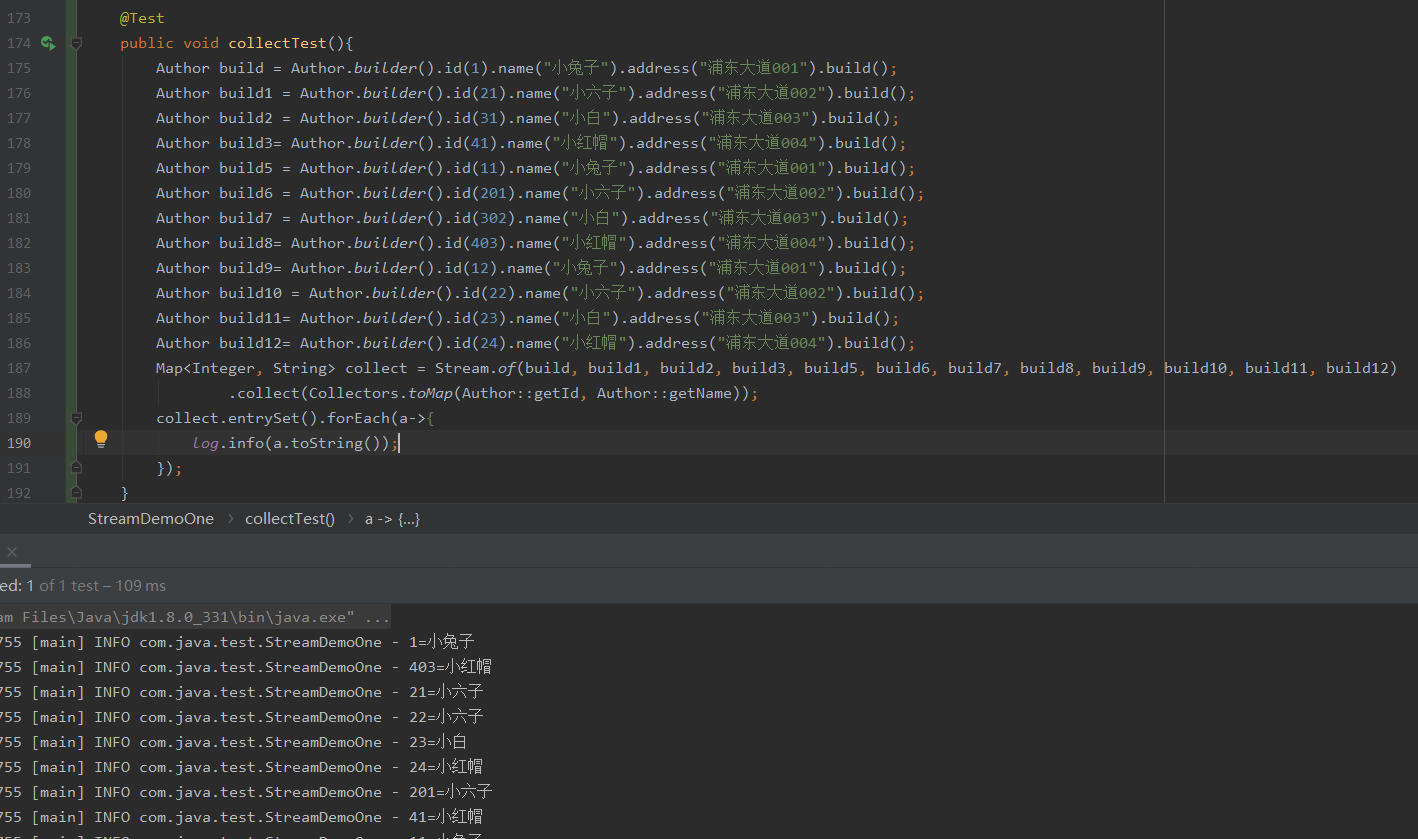
下面继续说收集器中的聚合归约
@Test
public void joinTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(21).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(41).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道005").build();
String collect = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3, build5)
.map(Author::getName)
.collect(Collectors.joining("^_^"));
log.info(collect.toString());
}
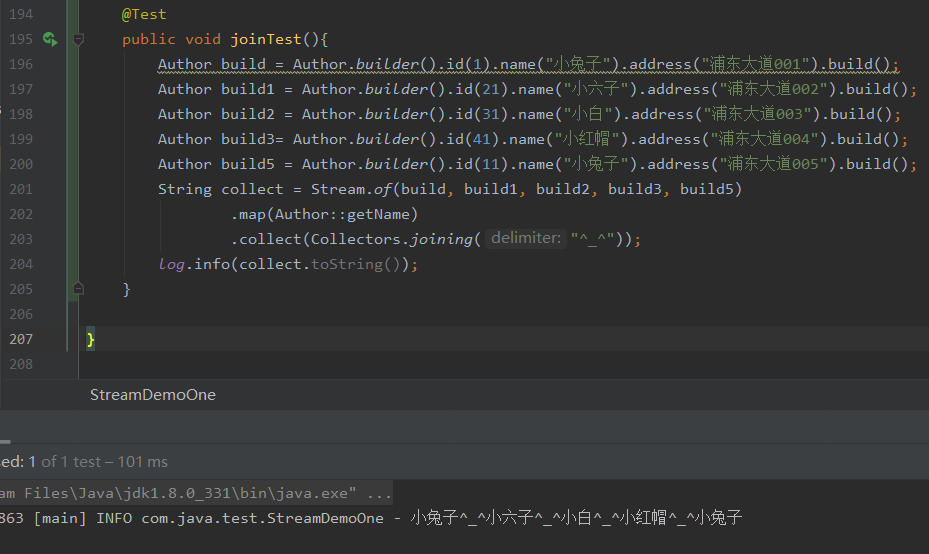
count使用
@Test
public void countTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(21).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(41).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道005").build();
Author build6 = Author.builder().id(12).name("小兔子3").address("浦东大道006").build();
List<Author> collect = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3, build5, build6).collect(Collectors.toList());
long count = collect.stream().count();
log.info("打印数量:{}",count);
}
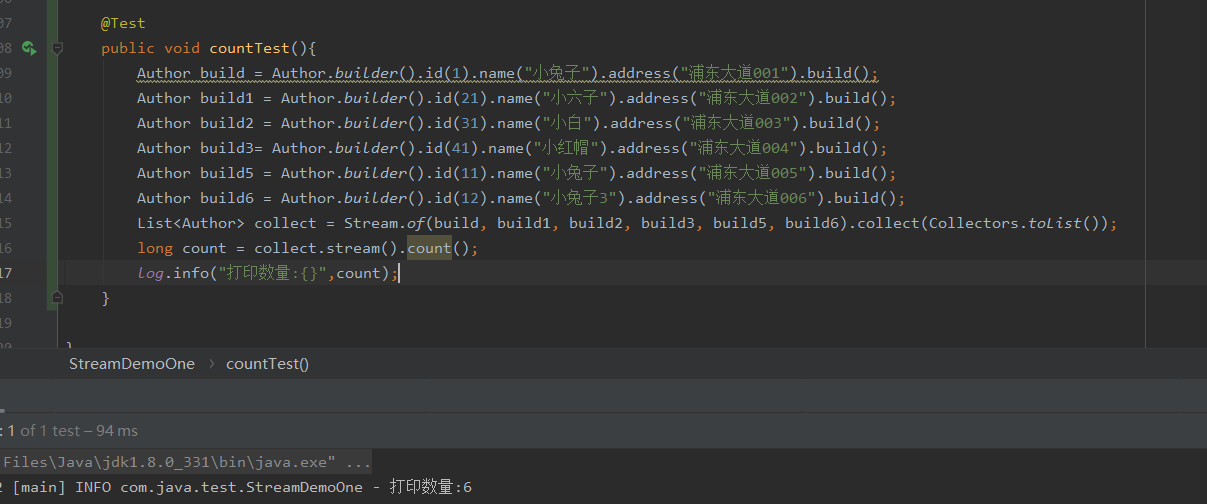
使用min和max获取最小值和最大值
@Test
public void minTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(21).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(41).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道005").build();
Author build6 = Author.builder().id(12).name("小兔子3").address("浦东大道006").build();
List<Author> collect = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3, build5, build6).collect(Collectors.toList());
Optional<Integer> min = collect.stream().map(author -> author.getId())
.min((a, b) -> a - b);
log.info("min:{}",min.get());
Optional<Integer> max = collect.stream().map(author -> author.getId())
.max((a, b) -> a - b);
log.info("max:{}",max.get());
}
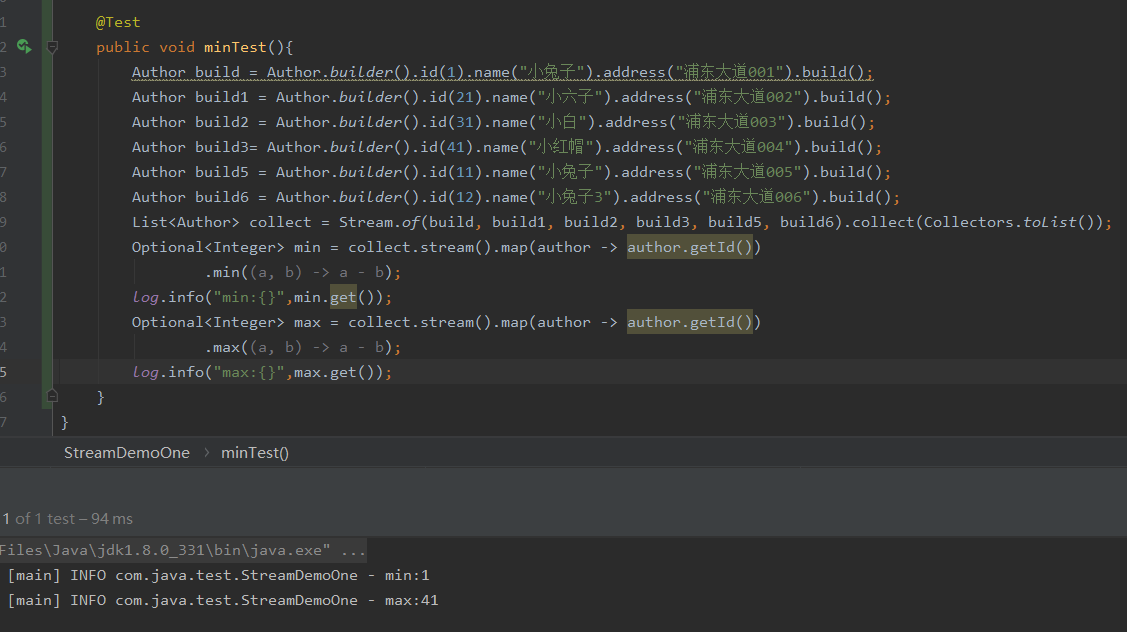
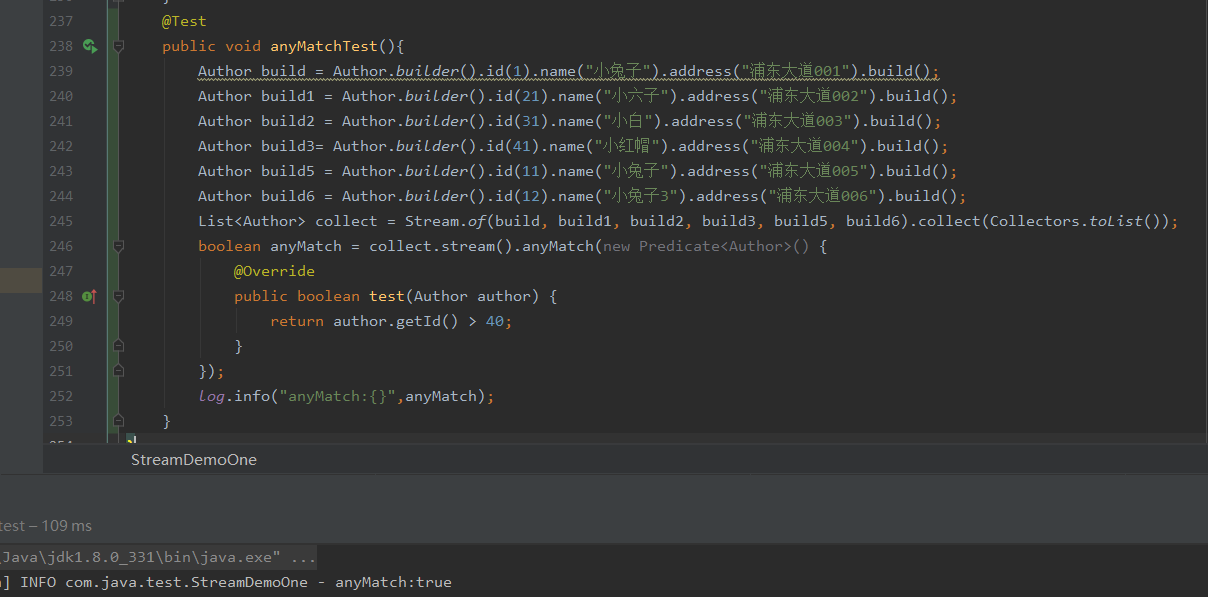
allmatchs使用,匹配满足的条件的数据,返回值为boolean
@Test
public void anyMatchTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(21).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(41).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道005").build();
Author build6 = Author.builder().id(12).name("小兔子3").address("浦东大道006").build();
List<Author> collect = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3, build5, build6).collect(Collectors.toList());
boolean anyMatch = collect.stream().anyMatch(new Predicate<Author>() {
@Override
public boolean test(Author author) {
return author.getId() > 40;
}
});
log.info("anyMatch:{}",anyMatch);
}
allmatch使用,都满足条件才会返回true
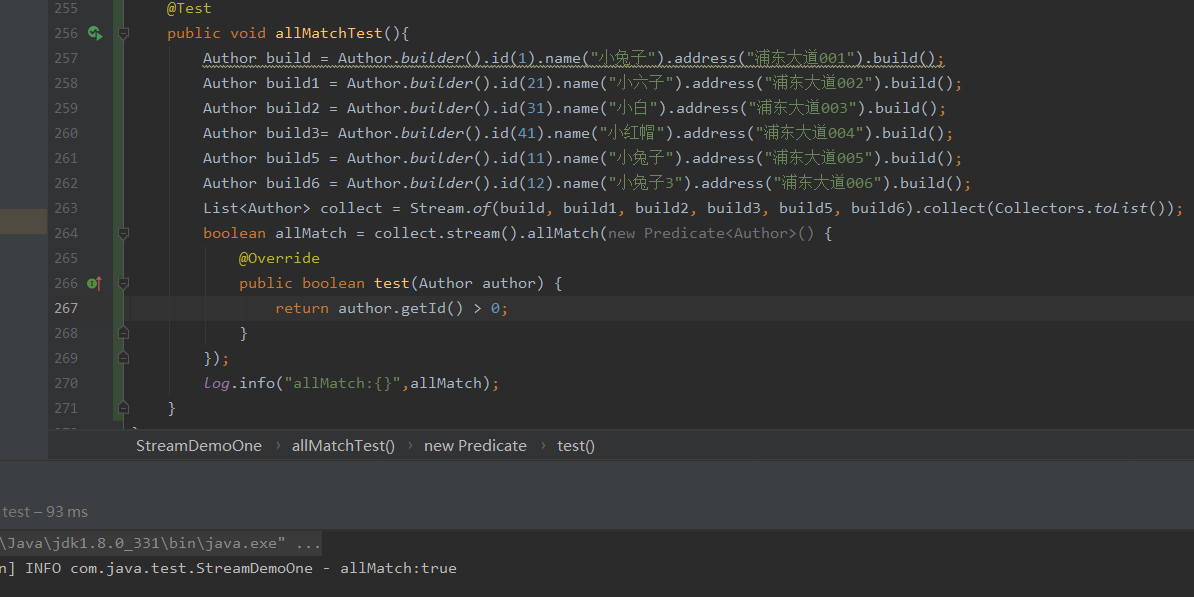
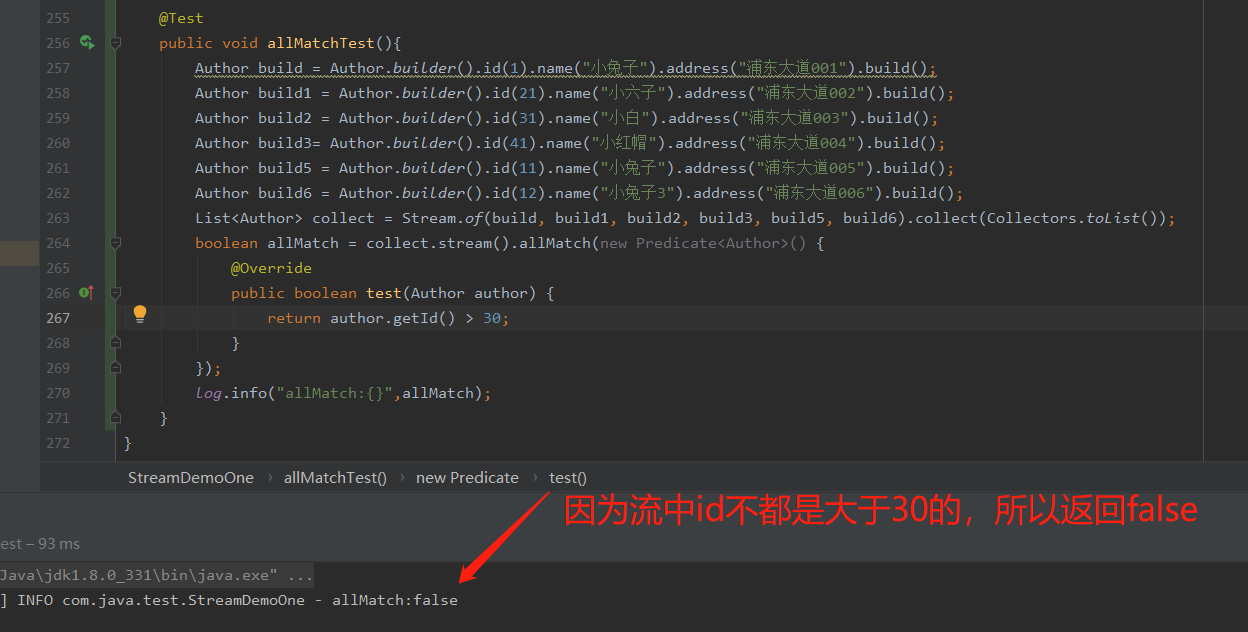
@Test
public void allMatchTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(21).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(41).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道005").build();
Author build6 = Author.builder().id(12).name("小兔子3").address("浦东大道006").build();
List<Author> collect = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3, build5, build6).collect(Collectors.toList());
boolean allMatch = collect.stream().allMatch(new Predicate<Author>() {
@Override
public boolean test(Author author) {
return author.getId() > 30;
}
});
log.info("allMatch:{}",allMatch);
}
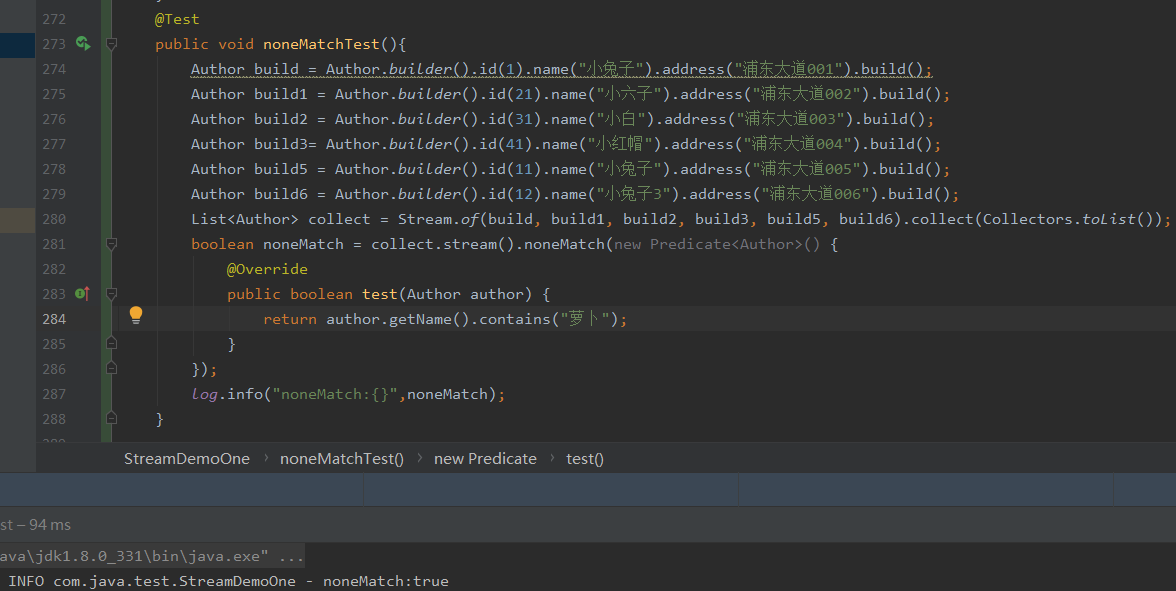
noneMatch表示都不匹配才会返回true,只要有一个返回就是false
@Test
public void noneMatchTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(21).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(41).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道005").build();
Author build6 = Author.builder().id(12).name("小兔子3").address("浦东大道006").build();
List<Author> collect = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3, build5, build6).collect(Collectors.toList());
boolean noneMatch = collect.stream().noneMatch(new Predicate<Author>() {
@Override
public boolean test(Author author) {
return author.getName().contains("小兔");
}
});
log.info("noneMatch:{}",noneMatch);
}

@Test
public void noneMatchTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(21).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(41).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道005").build();
Author build6 = Author.builder().id(12).name("小兔子3").address("浦东大道006").build();
List<Author> collect = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3, build5, build6).collect(Collectors.toList());
boolean noneMatch = collect.stream().noneMatch(new Predicate<Author>() {
@Override
public boolean test(Author author) {
return author.getName().contains("萝卜");
}
});
log.info("noneMatch:{}",noneMatch);
}
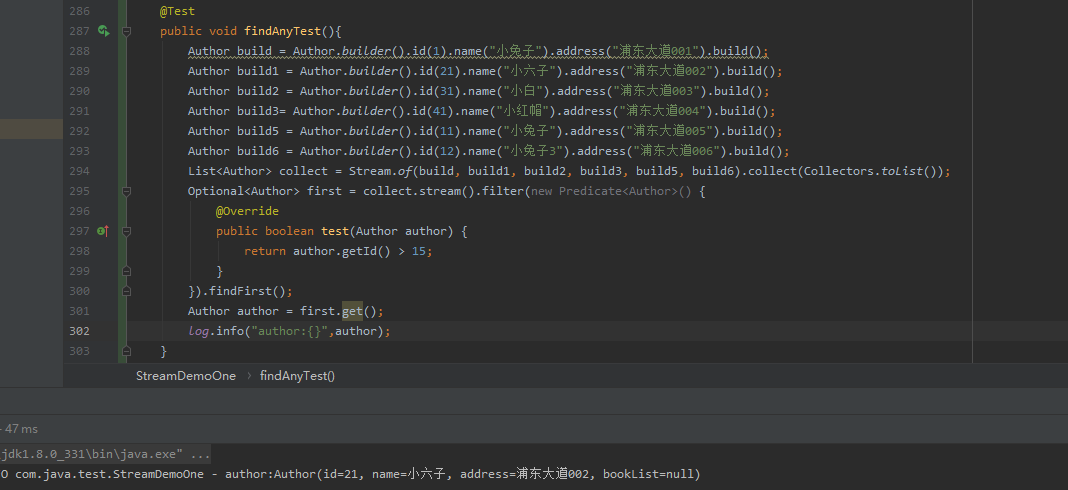
findFirst使用,查询满足条件的第一个元素
@Test
public void findAnyTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(21).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(41).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道005").build();
Author build6 = Author.builder().id(12).name("小兔子3").address("浦东大道006").build();
List<Author> collect = Stream.of(build, build1, build2, build3, build5, build6).collect(Collectors.toList());
Optional<Author> first = collect.stream().filter(new Predicate<Author>() {
@Override
public boolean test(Author author) {
return author.getId() > 15;
}
}).findFirst();
Author author = first.get();
log.info("author:{}",author);
}
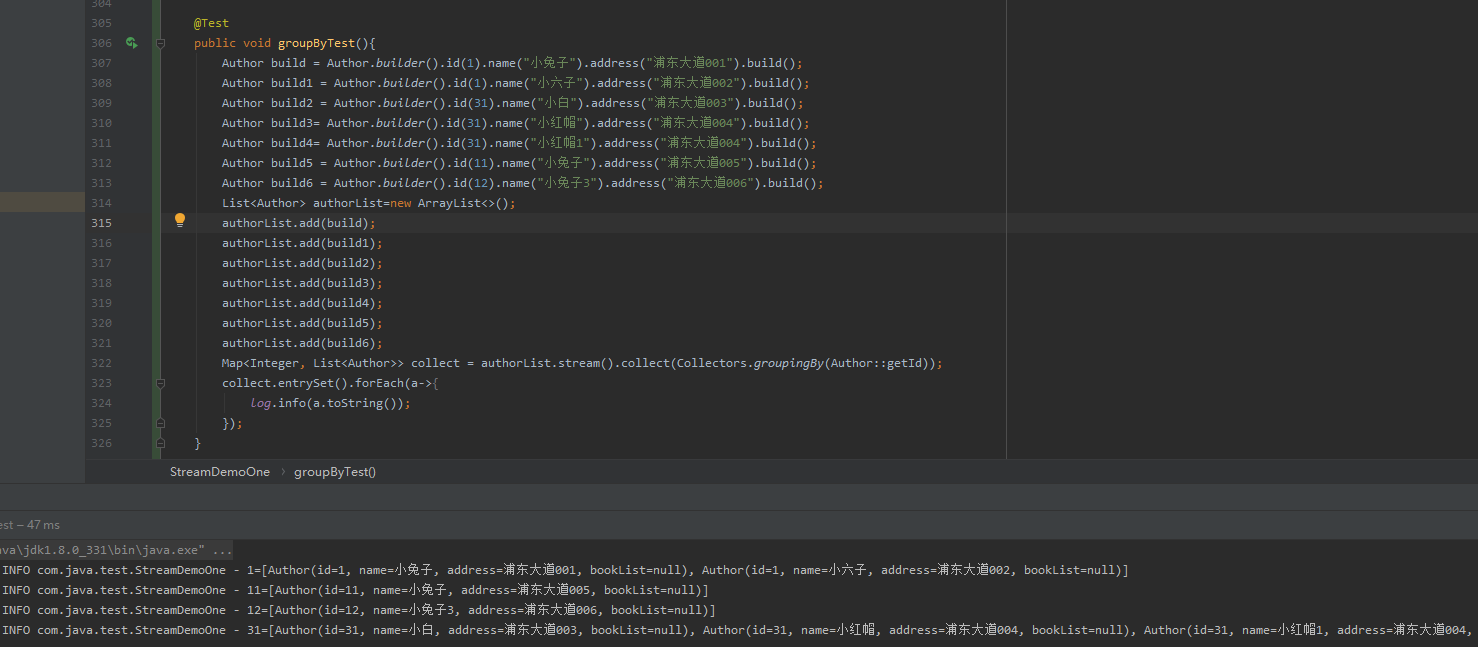
groupBy分组
@Test
public void groupByTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(1).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(31).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build4= Author.builder().id(31).name("小红帽1").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道005").build();
Author build6 = Author.builder().id(12).name("小兔子3").address("浦东大道006").build();
List<Author> authorList=new ArrayList<>();
authorList.add(build);
authorList.add(build1);
authorList.add(build2);
authorList.add(build3);
authorList.add(build4);
authorList.add(build5);
authorList.add(build6);
Map<Integer, List<Author>> collect = authorList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Author::getId));
collect.entrySet().forEach(a->{
log.info(a.toString());
});
}
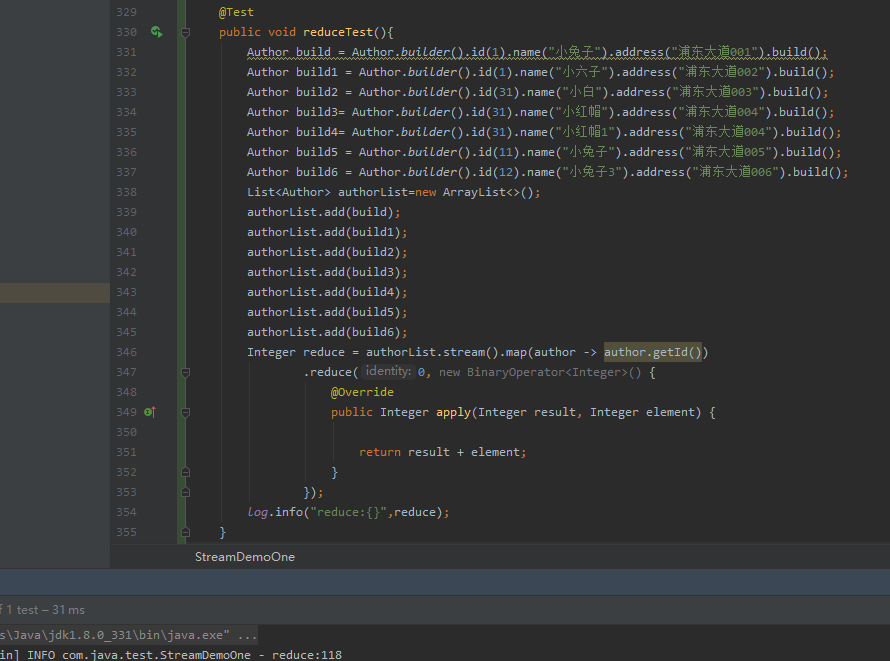
reduce使用求和
@Test
public void reduceTest(){
Author build = Author.builder().id(1).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道001").build();
Author build1 = Author.builder().id(1).name("小六子").address("浦东大道002").build();
Author build2 = Author.builder().id(31).name("小白").address("浦东大道003").build();
Author build3= Author.builder().id(31).name("小红帽").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build4= Author.builder().id(31).name("小红帽1").address("浦东大道004").build();
Author build5 = Author.builder().id(11).name("小兔子").address("浦东大道005").build();
Author build6 = Author.builder().id(12).name("小兔子3").address("浦东大道006").build();
List<Author> authorList=new ArrayList<>();
authorList.add(build);
authorList.add(build1);
authorList.add(build2);
authorList.add(build3);
authorList.add(build4);
authorList.add(build5);
authorList.add(build6);
Integer reduce = authorList.stream().map(author -> author.getId())
.reduce(0, new BinaryOperator<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer apply(Integer result, Integer element) {
return result + element;
}
});
log.info("reduce:{}",reduce);
}
最后附上pom文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.java</groupId>
<artifactId>test-study</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--lombok依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.16</version>
</dependency>
<!--引入junit单元测试依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<finalName>study</finalName>
</build>
</project>



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号