set集合以及jdk1.8集合特性简单说明
set集合中的元素没有先后顺序且不允许重复,但不是随机的
set集合包含:HashSet类,TreeSet类,LinkedHashSet类

LinkedHashSet是双向链表

叫做链表数组
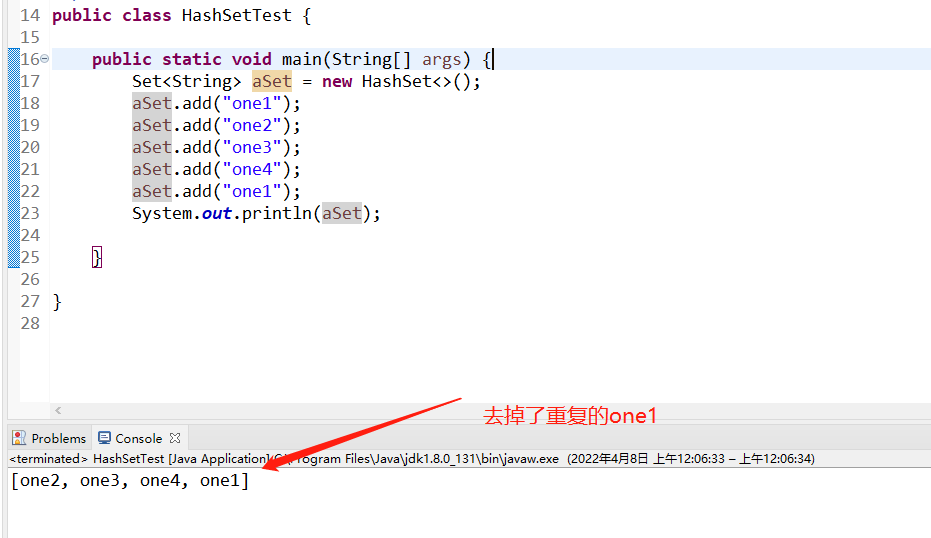
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> aSet = new HashSet<>();
aSet.add("one1");
aSet.add("one2");
aSet.add("one3");
aSet.add("one4");
aSet.add("one1");
System.out.println(aSet);
}
}
打印的顺序是乱的,但是没有显示重复的数据
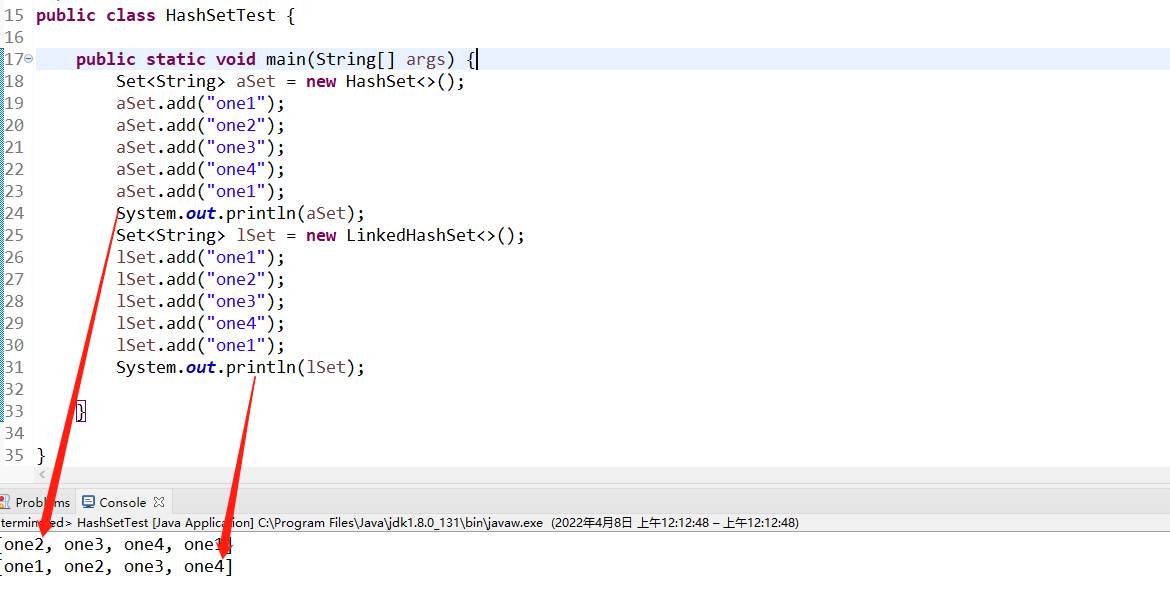
Set<String> lSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();
lSet.add("one1");
lSet.add("one2");
lSet.add("one3");
lSet.add("one4");
lSet.add("one1");
System.out.println(lSet);
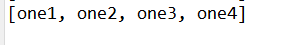
使用linkedHashSet会依次打印放入元素的顺序
存放数据的原理
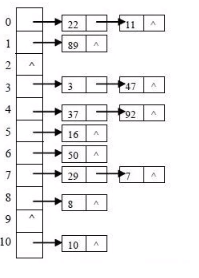
当需要新增一个数据,首先调用hashCod(),获取添加数据的哈希码值,接着调用哈希算法获取哈希值,接着去哈希表中找到索引位置 当生成的索引为0时,但是0位置已经有数据了,使用新元素和22比较哈希值是否相等,不等,插入已有元素的后面 相等的话,使用新元素调用equals()方法与22比较是否相等,相等则插入失败 不相等,插入已有元素的后面 当生成的索引是2时,直接将新元素插入索引为2的位置
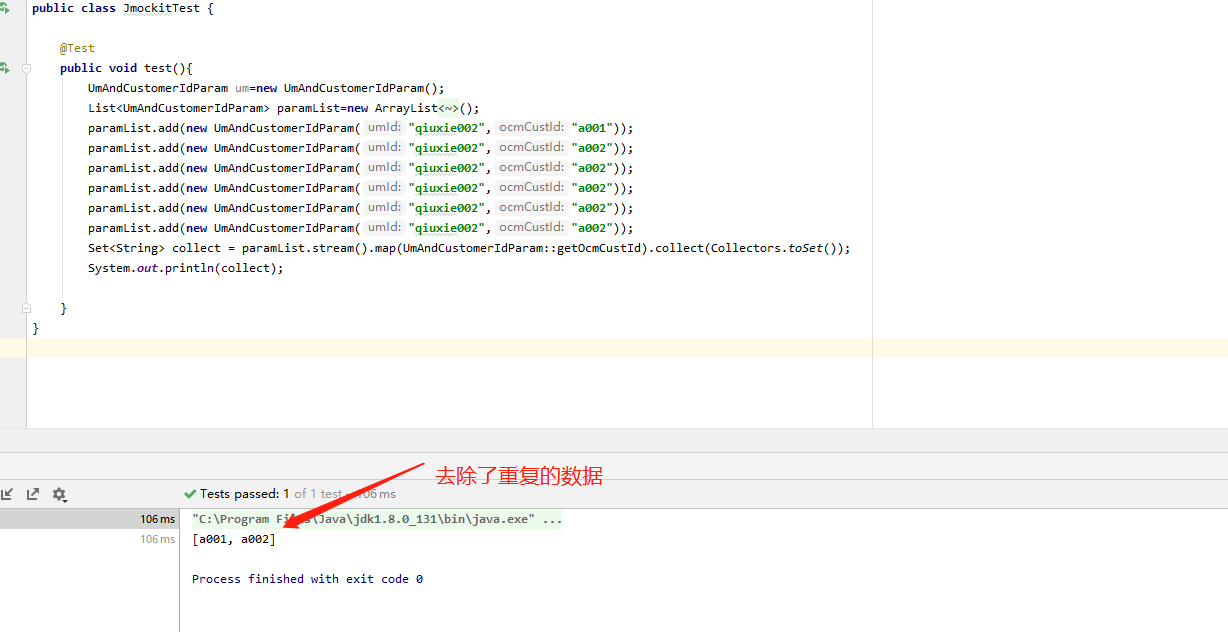
如何剔除对象中的重复数据
public class JmockitTest {
@Test
public void test(){
UmAndCustomerIdParam um=new UmAndCustomerIdParam();
List<UmAndCustomerIdParam> paramList=new ArrayList<UmAndCustomerIdParam>();
paramList.add(new UmAndCustomerIdParam("qiuxie002","a001"));
paramList.add(new UmAndCustomerIdParam("qiuxie002","a002"));
paramList.add(new UmAndCustomerIdParam("qiuxie002","a002"));
paramList.add(new UmAndCustomerIdParam("qiuxie002","a002"));
paramList.add(new UmAndCustomerIdParam("qiuxie002","a002"));
paramList.add(new UmAndCustomerIdParam("qiuxie002","a002"));
Set<String> collect = paramList.stream().map(UmAndCustomerIdParam::getOcmCustId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(collect);
}
}
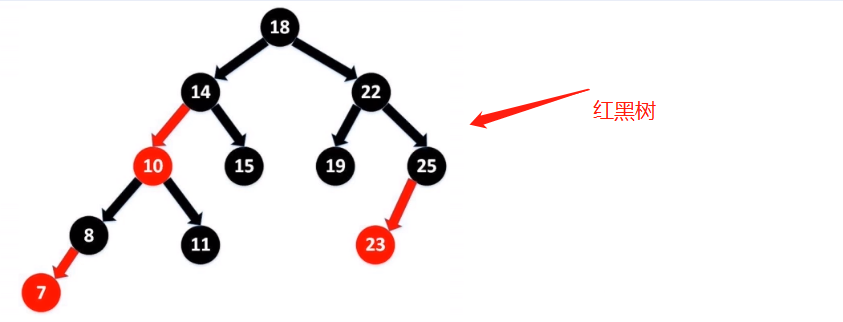
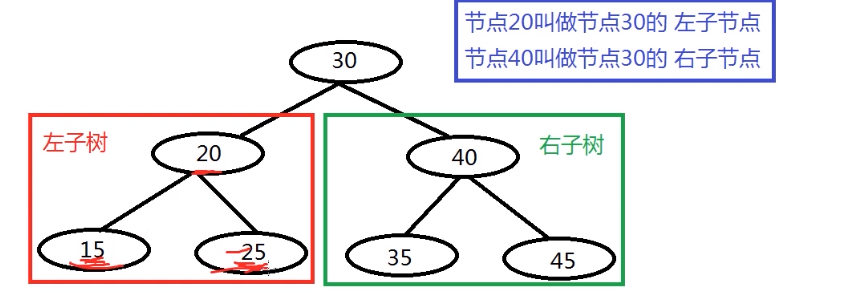
TreeSet集合底层是有序二叉树,又叫红黑树
有序二叉树的特征
1.左子树中的任意节点元素都小于根节点元素值
2.右子树中任意节点元素都大于根节点元素值
3.左子树和右子树内部都遵循上述规则
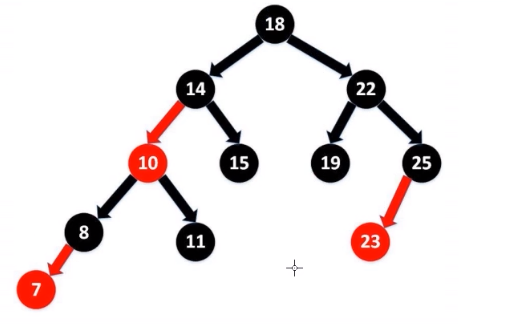
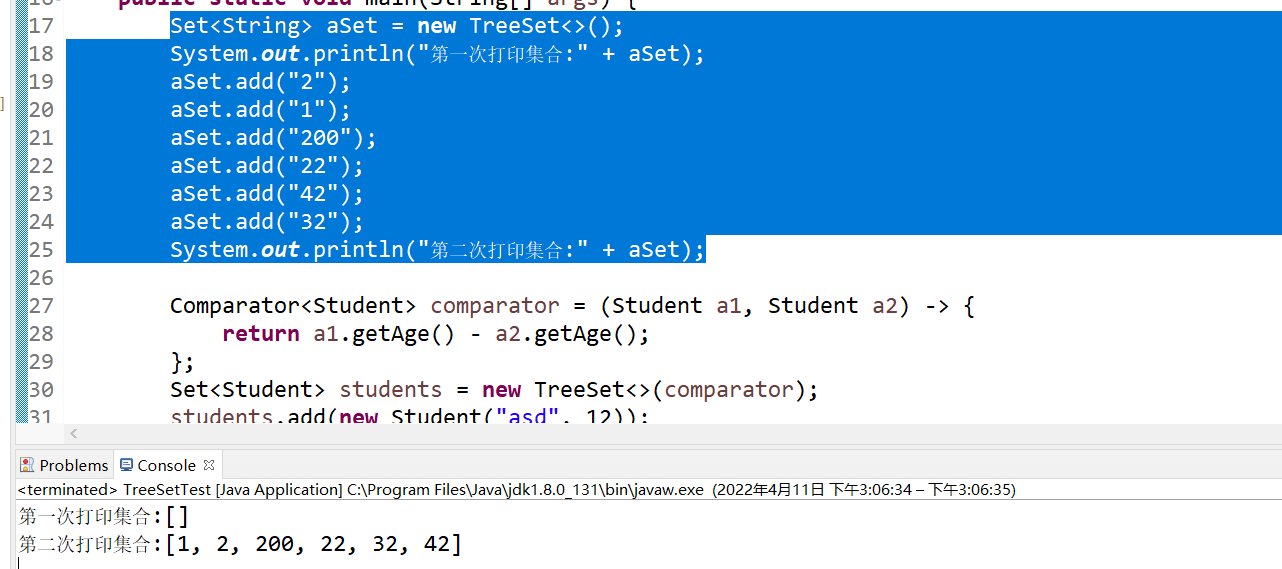
基本类型比较
Set<String> aSet = new TreeSet<>();
System.out.println("第一次打印集合:" + aSet);
aSet.add("2");
aSet.add("1");
aSet.add("200");
aSet.add("22");
aSet.add("42");
aSet.add("32");
System.out.println("第二次打印集合:" + aSet);
对象比较
当进行对象,直接去比较会出现下面的错误

下面给出三种形式解决问题
第一种是自然排序,实体类实现Comparable
/**
*
*/
package com.java.set;
/**
* @author yourheart
* @update 2022年4月11日 上午9:37:59
* @description:
*/
public class Student implements Comparable<Student> {
/**
* 学生姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 学生年龄
*/
private Integer age;
/**
* @param name
* @param age
*/
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
/**
* @return the name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* @param name the name to set
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
/**
* @return the age
*/
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* @param age the age to set
*/
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.age - o.age;
}
}
/**
*
*/
package com.java.set;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* @author yourheart
* @update 2022年4月11日 上午9:18:22
* @description:
*/
public class TreeSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Student> students = new TreeSet<>();
students.add(new Student("asd", 12));
students.add(new Student("asd", 15));
students.add(new Student("asd", 52));
students.add(new Student("asd", 82));
students.add(new Student("asd", 32));
students.add(new Student("asd", 22));
System.out.println("第三次打印集合:" + students);
}
}
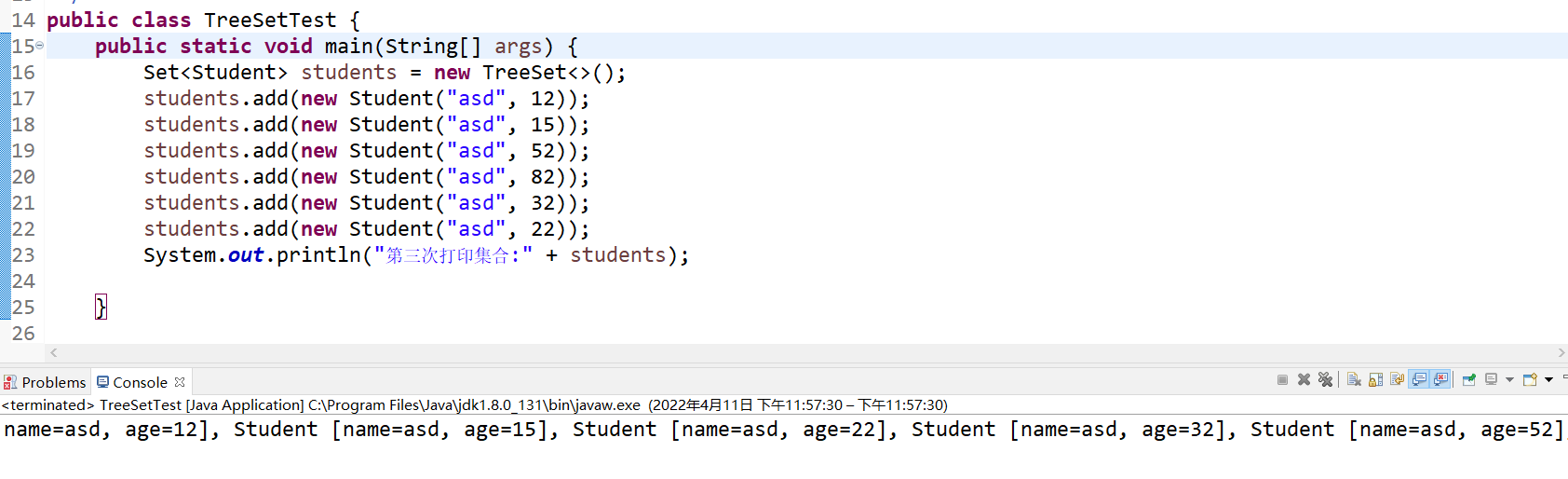
可以看到图中的数据已经排序了
姓名相同,按照年龄比较
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
if (this.name.compareTo(o.name) == 0) {
return this.age - o.age;
}
return this.name.compareTo(o.name);
}
Set<Student> students = new TreeSet<>();
students.add(new Student("asd", 12));
students.add(new Student("asd1", 15));
students.add(new Student("asd3", 52));
students.add(new Student("asd", 82));
students.add(new Student("asd4", 32));
students.add(new Student("asd", 22));
System.out.println("第三次打印集合:" + students);

第二种使用比较器规则比较进行排序,构建TreeSet集合时传入java.util.Comparator接口
使用内部类的方式创建比较器
// 准备比较器对象作为参数传递给构造方法
Comparator<Student> comparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
};
Set<Student> students = new TreeSet<>(comparator);
students.add(new Student("asd", 12));
students.add(new Student("asd1", 15));
students.add(new Student("asd3", 52));
students.add(new Student("asd", 82));
students.add(new Student("asd4", 32));
students.add(new Student("asd", 22));
students.forEach(a -> {
System.out.println(a);
});
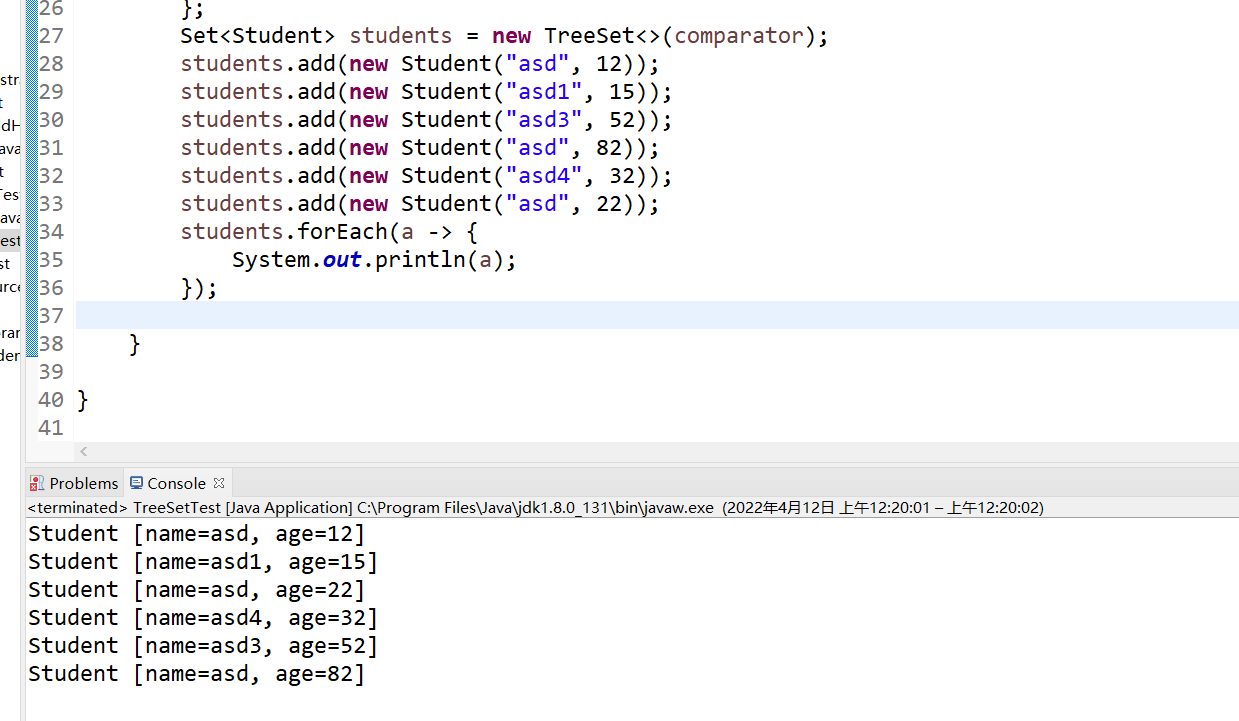
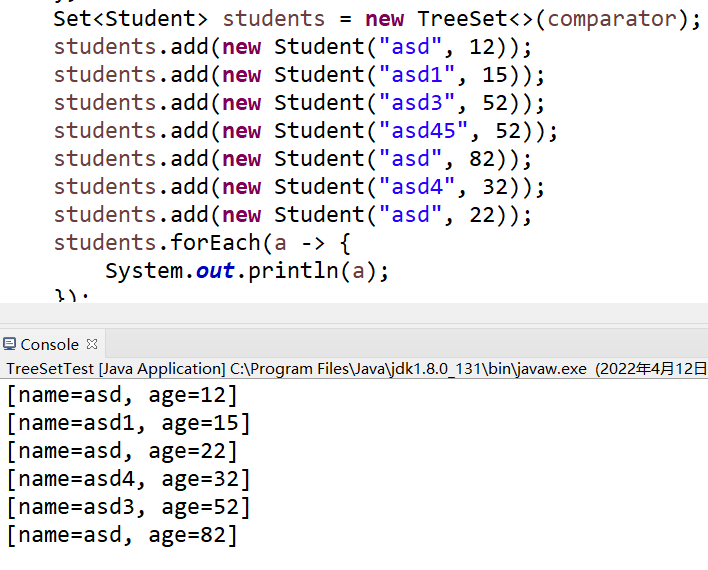
创建的比较器的优先级别大于自然排序,比较器自定义程度更高
jdk1.8开始支持lambda表达式,采用jdk1.8的特性创建构造器
使用比较器排序,引用了jdk1.8特性
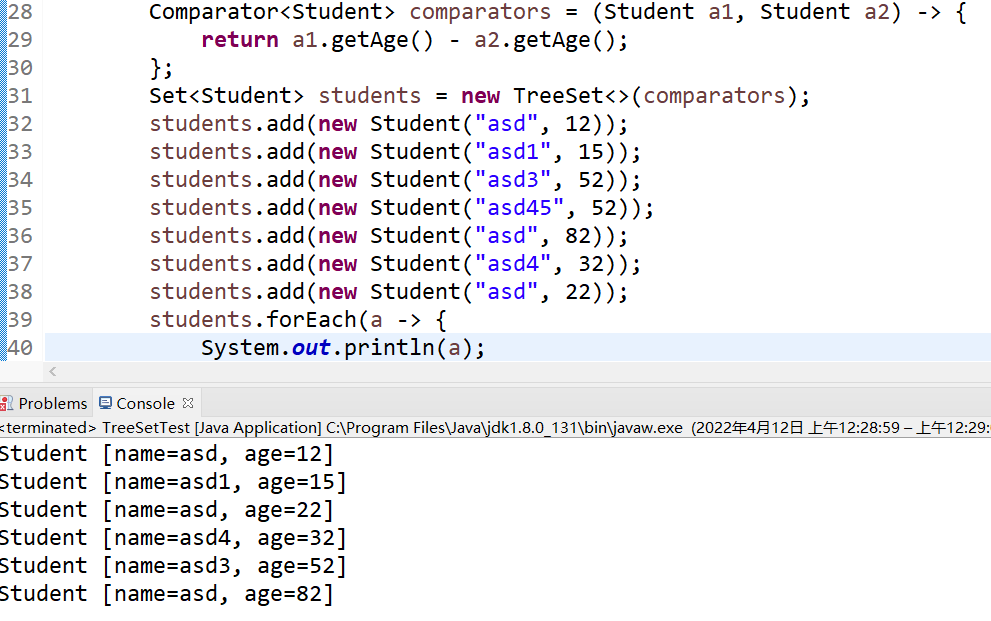
Comparator<Student> comparators = (Student a1, Student a2) -> {
return a1.getAge() - a2.getAge();
};
Set<Student> students = new TreeSet<>(comparators);
students.add(new Student("asd", 12));
students.add(new Student("asd1", 15));
students.add(new Student("asd3", 52));
students.add(new Student("asd45", 52));
students.add(new Student("asd", 82));
students.add(new Student("asd4", 32));
students.add(new Student("asd", 22));
students.forEach(a -> {
System.out.println(a);
});



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号