第4.5篇-常量池解析(2)
在parse_constant_pool()方法中调用parse_constant_pool_entries()方法对常量池中的各个项进行解析,方法的实现如下:
void ClassFileParser::parse_constant_pool_entries(int length, TRAPS) {
// Use a local copy of ClassFileStream. It helps the C++ compiler to optimize
// this function (_current can be allocated in a register, with scalar
// replacement of aggregates). The _current pointer is copied back to
// stream() when this function returns. DON'T call another method within
// this method that uses stream().
ClassFileStream* cfs0 = stream();
ClassFileStream cfs1 = *cfs0;
ClassFileStream* cfs = &cfs1;
Handle class_loader(THREAD, _loader_data->class_loader());
// Used for batching symbol allocations.
const char* names[SymbolTable::symbol_alloc_batch_size];
int lengths[SymbolTable::symbol_alloc_batch_size];
int indices[SymbolTable::symbol_alloc_batch_size];
unsigned int hashValues[SymbolTable::symbol_alloc_batch_size];
int names_count = 0;
// parsing Index 0 is unused
for (int index = 1; index < length; index++) {
// Each of the following case guarantees one more byte in the stream
// for the following tag or the access_flags following constant pool,
// so we don't need bounds-check for reading tag.
u1 tag = cfs->get_u1_fast();
switch (tag) {
case JVM_CONSTANT_Class :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(3, CHECK); // name_index, tag/access_flags
u2 name_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->klass_index_at_put(index, name_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Fieldref :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // class_index, name_and_type_index, tag/access_flags
u2 class_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u2 name_and_type_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->field_at_put(index, class_index, name_and_type_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Methodref :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // class_index, name_and_type_index, tag/access_flags
u2 class_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u2 name_and_type_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->method_at_put(index, class_index, name_and_type_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // class_index, name_and_type_index, tag/access_flags
u2 class_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u2 name_and_type_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->interface_method_at_put(index, class_index, name_and_type_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_String :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(3, CHECK); // string_index, tag/access_flags
u2 string_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->string_index_at_put(index, string_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_MethodHandle :
case JVM_CONSTANT_MethodType :
if (tag == JVM_CONSTANT_MethodHandle) {
cfs->guarantee_more(4, CHECK); // ref_kind, method_index, tag/access_flags
u1 ref_kind = cfs->get_u1_fast();
u2 method_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->method_handle_index_at_put(index, ref_kind, method_index);
} else if (tag == JVM_CONSTANT_MethodType) {
cfs->guarantee_more(3, CHECK); // signature_index, tag/access_flags
u2 signature_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->method_type_index_at_put(index, signature_index);
} else {
ShouldNotReachHere();
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // bsm_index, nt, tag/access_flags
u2 bootstrap_specifier_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u2 name_and_type_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
if (_max_bootstrap_specifier_index < (int) bootstrap_specifier_index)
_max_bootstrap_specifier_index = (int) bootstrap_specifier_index; // collect for later
_cp->invoke_dynamic_at_put(index, bootstrap_specifier_index, name_and_type_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Integer :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // bytes, tag/access_flags
u4 bytes = cfs->get_u4_fast();
_cp->int_at_put(index, (jint) bytes);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Float :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // bytes, tag/access_flags
u4 bytes = cfs->get_u4_fast();
_cp->float_at_put(index, *(jfloat*)&bytes);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Long :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(9, CHECK); // bytes, tag/access_flags
u8 bytes = cfs->get_u8_fast();
_cp->long_at_put(index, bytes);
}
index++; // Skip entry following eigth-byte constant, see JVM book p. 98
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Double :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(9, CHECK); // bytes, tag/access_flags
u8 bytes = cfs->get_u8_fast();
_cp->double_at_put(index, *(jdouble*)&bytes);
}
index++; // Skip entry following eigth-byte constant, see JVM book p. 98
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_NameAndType :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(5, CHECK); // name_index, signature_index, tag/access_flags
u2 name_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u2 signature_index = cfs->get_u2_fast();
_cp->name_and_type_at_put(index, name_index, signature_index);
}
break;
case JVM_CONSTANT_Utf8 :
{
cfs->guarantee_more(2, CHECK); // utf8_length
u2 utf8_length = cfs->get_u2_fast();
u1* utf8_buffer = cfs->get_u1_buffer();
assert(utf8_buffer != NULL, "null utf8 buffer");
// Got utf8 string, guarantee utf8_length+1 bytes, set stream position forward.
cfs->guarantee_more(utf8_length+1, CHECK); // utf8 string, tag/access_flags
cfs->skip_u1_fast(utf8_length);
if (EnableInvokeDynamic && has_cp_patch_at(index)) {
Handle patch = clear_cp_patch_at(index);
char* str = java_lang_String::as_utf8_string(patch());
// (could use java_lang_String::as_symbol instead, but might as well batch them)
utf8_buffer = (u1*) str;
utf8_length = (int) strlen(str);
}
unsigned int hash;
Symbol* result = SymbolTable::lookup_only((char*)utf8_buffer, utf8_length, hash);
if (result == NULL) {
names[names_count] = (char*)utf8_buffer;
lengths[names_count] = utf8_length;
indices[names_count] = index;
hashValues[names_count++] = hash;
if (names_count == SymbolTable::symbol_alloc_batch_size) {
SymbolTable::new_symbols(_loader_data, _cp, names_count, names, lengths, indices, hashValues, CHECK);
names_count = 0;
}
} else {
_cp->symbol_at_put(index, result);
}
}
break;
default:
classfile_parse_error("Unknown constant tag %u in class file %s", tag, CHECK);
break;
}
}
// Allocate the remaining symbols
if (names_count > 0) {
SymbolTable::new_symbols(_loader_data, _cp, names_count, names, lengths, indices, hashValues, CHECK);
}
cfs0->set_current(cfs1.current());
}
循环处理length个常量池项,不过第一个常量池项不需要处理,所以循环下标index的值初始化为1。
如果要了解各个常量池项的具体结构,代码的逻辑理解起来其实并不难。所有项的第一个字节都是用来描述常量池元素类型,调用cfs->get_u1_fast()获取元素类型后,就可以通过switch语句分情况进行处理。
1、JVM_CONSTANT_Class项的解析
JVM_CONSTANT_Class格式如下:
CONSTANT_Class_info {
u1 tag;
u2 name_index;
}
调用cfs->get_u2_fast()方法获取name_index,然后调用_cp->klass_index_at_put()方法进行存储。_cp的类型为ConstantPool*,ConstantPool类中的klass_index_at_put()方法的实现如下:
// For temporary use while constructing constant pool
void klass_index_at_put(int which, int name_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_ClassIndex);
*int_at_addr(which) = name_index;
}
void tag_at_put(int which, jbyte t) {
tags()->at_put(which, t);
}
jint* int_at_addr(int which) const {
assert(is_within_bounds(which), "index out of bounds");
return (jint*) &base()[which];
}
intptr_t* base() const {
return (intptr_t*) (
( (char*) this ) + sizeof(ConstantPool)
);
}
常量池项的下标与数组的下标是相同的,也就是说,如果当前JVM_CONSTANT_Class存储在常量池中的下标为1处,则也要存储到tags数组中下标为1的地方。同时要将名称索引name_index保存到ConstantPool中存储数据区的对应位置上。
举个例子如下:
#1 = Class #5 // TestClass ... #5 = Utf8 TestClass
假设JVM_CONSTANT_Class是常量池第一项,则解析完这一顶后的ConstantPool对象如下图所示。
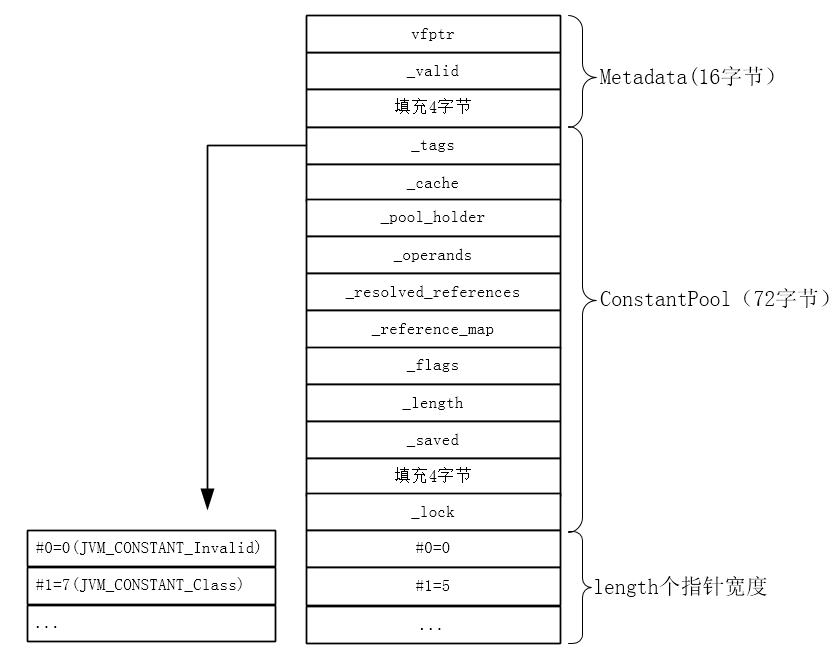
其中#0(表示常量池索引0)的值为0是因为在分配内存时会将其内存清零。
2、CONSTANT_Fieldref_info项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_Fieldref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
调用field_at_put()存储class_index与name_and_type_index,方法的实现如下:
void field_at_put(int which, int class_index, int name_and_type_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Fieldref);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) name_and_type_index<<16) | class_index;
}
name_and_type_index存储在高16位,class_index存储在低16位。
3、JVM_CONSTANT_Methodref项的解析
JVM_CONSTANT_Methodref项的格式如下:
CONSTANT_Methodref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
按照格式读取Class文件,获取到相关属性值后调用ConstantPool的method_at_put()方法进行存储,这个方法的实现如下:
void method_at_put(int which, int class_index, int name_and_type_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Methodref);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) name_and_type_index<<16) | class_index;
}
由于ConstantPool数据区一个槽是一个指针类型的宽度,所以至少有32个位,又由于class_index与name_and_type_index属性的类型为u2,这时候就可以使用高16位存储name_and_type_index,低16位存储class_index即可。
4、JVM_CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref_info {
u1 tag;
u2 class_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
调用的interface_method_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void interface_method_at_put(int which, int class_index, int name_and_type_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) name_and_type_index<<16) | class_index; // Not so nice
}
5、JVM_CONSTANT_String项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_String_info {
u1 tag;
u2 string_index;
}
调用的string_index_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void string_index_at_put(int which, int string_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_StringIndex);
*int_at_addr(which) = string_index;
}
6、JVM_CONSTANT_MethodHandle项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_MethodHandle_info {
u1 tag;
u1 reference_kind;
u2 reference_index;
}
调用的method_handle_index_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void method_handle_index_at_put(int which, int ref_kind, int ref_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_MethodHandle);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) ref_index<<16) | ref_kind;
}
7、JVM_CONSTANT_MethodType项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_MethodType_info {
u1 tag;
u2 descriptor_index;
}
调用的method_type_index_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void method_type_index_at_put(int which, int ref_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_MethodType);
*int_at_addr(which) = ref_index;
}
8、JVM_CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic_info {
u1 tag;
u2 bootstrap_method_attr_index;
u2 name_and_type_index;
}
调用的invoke_dynamic_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void invoke_dynamic_at_put(int which, int bootstrap_specifier_index, int name_and_type_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) name_and_type_index<<16) | bootstrap_specifier_index;
}
9、JVM_CONSTANT_Integer、JVM_CONSTANT_Float项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_Integer_info {
u1 tag;
u4 bytes;
}
CONSTANT_Float_info {
u1 tag;
u4 bytes;
}
调用的方法分别为int_at_put()和float_at_put()方法,实现如下:
void int_at_put(int which, jint i) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Integer);
*int_at_addr(which) = i;
}
void float_at_put(int which, jfloat f) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Float);
*float_at_addr(which) = f;
}
10、JVM_CONSTANT_Long、JVM_CONSTANT_Double项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_Long_info {
u1 tag;
u4 high_bytes;
u4 low_bytes;
}
CONSTANT_Double_info {
u1 tag;
u4 high_bytes;
u4 low_bytes;
}
调用的long_at_put()和double_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void long_at_put(int which, jlong l) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Long);
// *long_at_addr(which) = l;
Bytes::put_native_u8((address)long_at_addr(which), *( (u8*) &l ));
}
void double_at_put(int which, jdouble d) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Double);
// *double_at_addr(which) = d;
// u8 temp = *(u8*) &d;
Bytes::put_native_u8((address) double_at_addr(which), *((u8*) &d));
}
调用的Bytes::put_native_u8()方法的实现如下:
static inline void put_native_u8(address p, u8 x) { *(u8*)p = x; }
11、JVM_CONSTANT_NameAndType项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_NameAndType_info {
u1 tag;
u2 name_index;
u2 descriptor_index;
}
调用的name_and_type_at_put()方法的实现如下:
void name_and_type_at_put(int which, int name_index, int signature_index) {
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_NameAndType);
*int_at_addr(which) = ((jint) signature_index<<16) | name_index; // Not so nice
}
12、JVM_CONSTANT_Utf8项的解析
格式如下:
CONSTANT_Utf8_info {
u1 tag;
u2 length;
u1 bytes[length];
}
在HotSpot虚拟机中,字符串通常都会表示为Symbol对象,这样有利于使用符号表来存储字符串,对于2个相同的字符串来说,完全可以使用同一个Symbol对象来表示。这样就可以在ConstantPool数据区相应槽位上存储指向Symbol的指针即可。
调用SymbolTable::lookup_only()方法从符号表中查找对应的Symbol对象,如果查找不到需要暂时将相关的信息存储到临时的names、lengths、indices与hashValues数组中,这样就可以调用SymbolTable::new_symbols()进行批量添加Symbol对象来提高效率;如果找到对应的Symbol对象,则调用symbol_at_put()方法,实现如下:
void symbol_at_put(int which, Symbol* s) {
assert(s->refcount() != 0, "should have nonzero refcount");
tag_at_put(which, JVM_CONSTANT_Utf8);
*symbol_at_addr(which) = s;
}
Symbol** symbol_at_addr(int which) const {
assert(is_within_bounds(which), "index out of bounds");
return (Symbol**) &base()[which];
}
将指向Symbol对象的指针存储到指定的位置。
如果Symbol对象表示的是类名称,那么后面是类连接后,相应索引位置上的值会更新为指向InstanceKlass实例的指针,后面会详细介绍。

参考:
(1)https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jvms/se8/html/jvms-4.html#jvms-4.4
(2)《Java虚拟机原理图解》 1.2.2、Class文件中的常量池详解(上)


