关于自动装箱与拆箱在反射调用中引起的注意
1:首先先说一下什么是自动装箱与拆箱?
太基本的概念就不说了,直接百度就可以,直接丢上来一个例子就可以知道了。
int one = 1;
// compile error 编译错误就可以确定变量one不是Integer类型,因此Integer类型由getClass方法
//System.out.println(one.getClass());
Object oneObject = one;
//输出:class java.lang.Integer
System.out.println(oneObject.getClass());
2:反射中获取方法时候支持自动装箱或者拆箱吗?先说结论:不支持。
public class User {
private int age;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
反射获取setAge方法:
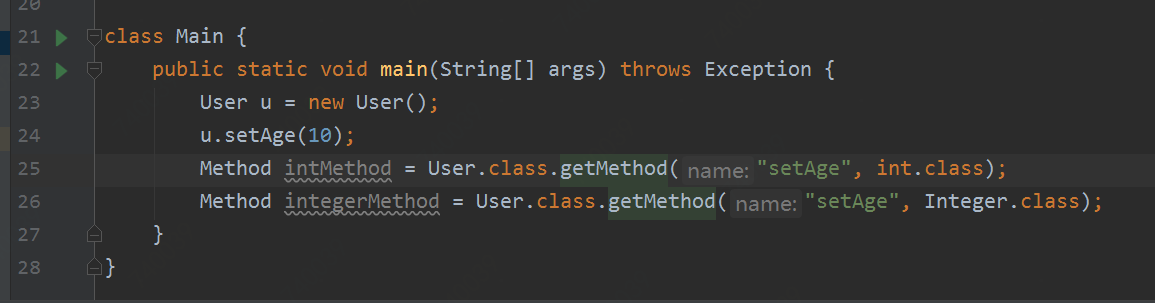
代码抛异常:

可以看出反射获取方法时不支持泛型的。具体是什么原因呢?可以跟中JDK源码,jdk源码位置: java.lang.Class#searchMethods ,感兴趣可以自已一步一步的跟踪。
直接看一下java.lang.Class#searchMethods源码:
private static Method searchMethods(Method[] methods,
String name,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes)
{
Method res = null;
String internedName = name.intern();
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) {
Method m = methods[i];
//arrayContentsEq(parameterTypes, m.getParameterTypes()) 重点代码:
// 此时parameterTypes是一个Class数组,里面只有一个Integer值(是我们反射时候指定的), m.getParameterTypes()是真是参数类型由于我们定义的age是int,所以m.getParameterTypes()是只有一个int的class数组
// 由于两个数组类型内容不相同所以不等
if (m.getName() == internedName&& arrayContentsEq(parameterTypes, m.getParameterTypes())
&& (res == null
|| res.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(m.getReturnType())))
res = m;
}
return (res == null ? res : getReflectionFactory().copyMethod(res));
}
具体原因参考源码注释即可明白。反射获取方法不支持自动装箱或拆箱,那反射调用方法是否支持自动装箱或拆箱呢?答案:支持。
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
User u = new User();
u.setAge(10);
Method intMethod = User.class.getMethod("setAge", int.class);
int one =1;
intMethod.invoke(u,one);
System.out.println(u.getAge());
intMethod.invoke(u,new Integer(2));
System.out.println(u.getAge());
}
}
可以成功输出。
3:由于获取方法不支持自动装箱或拆箱,那么我们在使用反射时候很容易错误,如何避免这个问题呢?答案:智者借力而行,当然是用现有的轮子了。那就是apache common beanutils.
可以使用BeanUtils中MethodUtils的invokeMethod方法,这个方法内部在org.apache.commons.beanutils.MethodUtils.getMatchingAccessibleMethod()中做了类型兼容判断(就是兼容int与Integer等装拆箱问题)。
MethodUtils中还有invokeExactMethod,这个方法时精准调用的意思,没有做兼容,在User中的setAge是无法通过该方法进行反射调用的,原因如下:
invokeExactMethod方法定义如下:
public static Object invokeExactMethod( final Object object,final String methodName, final Object arg)
由于User的age是int类型,但是当我们给arg传入int时候会自动转为Integer类型(上面问题1的情况),因此就会出现上面问题2中的问题。但是如果我们的age是Integer类型的话则两者就可以进行调用了。
org.apache.commons.beanutils.MethodUtils#getMatchingAccessibleMethod中的兼容处理重点代码:
public static Method getMatchingAccessibleMethod(
final Class<?> clazz,
final String methodName,
final Class<?>[] parameterTypes) {
// trace logging
final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(MethodUtils.class);
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Matching name=" + methodName + " on " + clazz);
}
final MethodDescriptor md = new MethodDescriptor(clazz, methodName, parameterTypes, false);
// see if we can find the method directly
// most of the time this works and it's much faster
try {
// Check the cache first
Method method = getCachedMethod(md);
if (method != null) {
return method;
}
method = clazz.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Found straight match: " + method);
log.trace("isPublic:" + Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers()));
}
setMethodAccessible(method); // Default access superclass workaround
cacheMethod(md, method);
return method;
} catch (final NoSuchMethodException e) { /* SWALLOW */ }
// search through all methods
final int paramSize = parameterTypes.length;
Method bestMatch = null;
final Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
float bestMatchCost = Float.MAX_VALUE;
float myCost = Float.MAX_VALUE;
for (Method method2 : methods) { //兼容处理开始
if (method2.getName().equals(methodName)) {
// log some trace information
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Found matching name:");
log.trace(method2);
}
// compare parameters
final Class<?>[] methodsParams = method2.getParameterTypes();
final int methodParamSize = methodsParams.length;
if (methodParamSize == paramSize) { // 参数个数相同
boolean match = true;
for (int n = 0 ; n < methodParamSize; n++) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Param=" + parameterTypes[n].getName());
log.trace("Method=" + methodsParams[n].getName());
}
if (!isAssignmentCompatible(methodsParams[n], parameterTypes[n])) { //重点:判断参数是否兼容
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace(methodsParams[n] + " is not assignable from "
+ parameterTypes[n]);
}
match = false;
break;
}
}
if (match) {
// get accessible version of method
final Method method = getAccessibleMethod(clazz, method2);
if (method != null) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace(method + " accessible version of "
+ method2);
}
setMethodAccessible(method); // Default access superclass workaround
myCost = getTotalTransformationCost(parameterTypes,method.getParameterTypes());
if ( myCost < bestMatchCost ) {
bestMatch = method;
bestMatchCost = myCost;
}
}
log.trace("Couldn't find accessible method.");
}
}
}
}
if ( bestMatch != null ){
cacheMethod(md, bestMatch);
} else {
// didn't find a match
log.trace("No match found.");
}
return bestMatch;
}
org.apache.commons.beanutils.MethodUtils#isAssignmentCompatible 兼容判断逻辑:
public static final boolean isAssignmentCompatible(final Class<?> parameterType, final Class<?> parameterization) {
// try plain assignment
if (parameterType.isAssignableFrom(parameterization)) {
return true;
}
if (parameterType.isPrimitive()) {// isPrimitive是jdk提供的方法
// this method does *not* do widening - you must specify exactly
// is this the right behaviour?
final Class<?> parameterWrapperClazz = getPrimitiveWrapper(parameterType); // 工具类库自己实现的
if (parameterWrapperClazz != null) {
return parameterWrapperClazz.equals(parameterization);
}
}
return false;
}
org.apache.commons.beanutils.MethodUtils#getPrimitiveWrapper 源码(很简单,没有想象的复杂):
public static Class<?> getPrimitiveWrapper(final Class<?> primitiveType) {
// does anyone know a better strategy than comparing names?
if (boolean.class.equals(primitiveType)) {
return Boolean.class;
} else if (float.class.equals(primitiveType)) {
return Float.class;
} else if (long.class.equals(primitiveType)) {
return Long.class;
} else if (int.class.equals(primitiveType)) {
return Integer.class;
} else if (short.class.equals(primitiveType)) {
return Short.class;
} else if (byte.class.equals(primitiveType)) {
return Byte.class;
} else if (double.class.equals(primitiveType)) {
return Double.class;
} else if (char.class.equals(primitiveType)) {
return Character.class;
} else {
return null;
}
}
就是一堆if else 判断。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号