大脑结构 | 前脑 | 中脑 | 后脑 | 脑干 | 大脑发育
搞生物医学的,肯定要先从结构和功能搞起,再深入分子机制的研究,这个研究的逻辑顺序是不可能被颠倒的。
现在在参与一个人类大脑类器官的项目【神经系统疾病】,自然要深入大脑发育中了。
这个疾病影响的是一个叫RTN的region,控制了孩童病人的呼吸。
先从零开始科普一下大脑的结构和功能:
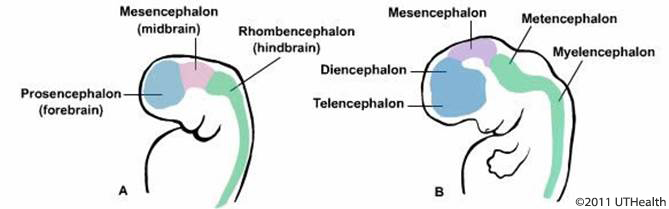
大脑的分类有很多种,这里可以从发育的角度来分为三大类:
- Telencephalon,端脑【】
- Forebrain,前脑,prosencephalon,感觉处理、内分泌结构和高级推理,大脑皮层;
- Midbrain,中脑,mesencephalon,运动和音频/视觉处理,中间的很小一部分;
- Hindbrain,后脑,rhombencephalon,自主功能,如呼吸节律和睡眠,连接脊髓;
大脑皮层按方位分:
- 颅骨,Cranial,上
- 尾部,Caudal,下
- 侧,Lateral,左右
- 腹侧,Ventral,前
- 背部,Dorsal,后
Telencephalon,端脑
The telencephalon, commonly called the cerebral hemispheres, is the largest portion of the central nervous system (CNS) and consists of the cerebral cortex, subcortical white matter (commissural, association, and projection fibers), and basal nuclei.
Forebrain,前脑
前脑最大,最外层就是大脑皮层cerebral cortex
有两个脑半球cerebral hemispheres,每个脑半球可以被分为四个脑叶lobes:
- frontal,额部,额头;自主运动、推理、冲动控制、语言和言语
- parietal,头顶;处理触觉、肢体位置和空间意识
- temporal,颞部,下巴;处理听觉刺激
- occipital,枕骨,后脑勺;视觉处理中心
每个脑叶都有自己不同的功能。
皮层下面是一些其他结构:
- 丘脑thalamus,感觉传递,我们所有的感官,除了嗅觉,都经过丘脑,然后被引导到大脑的其他区域进行处理【高速公路站】意识、警觉性和睡眠
- 下丘脑hypothalamus,快乐、食物、体温和性,调节脑下垂体pituitary gland,主腺
- 垂体pituitary gland,
- 基底神经节basal ganglia,
- 海马hippocampus,长期记忆的形成
- 杏仁核amygdala,处理恐惧
边缘系统limbic system:
- 海马体
- 杏仁核
- 下丘脑
Midbrain,中脑
前脑之下,脑干之上。
听觉和视觉处理,眼动。
分为三个部分:
- 丘,colliculi,处理视觉和听觉信号
- 被盖,tegmentum,运动协调性和警觉性
- 脑脚,cerebral peduncles,中枢神经系统
Hindbrain,后脑
又叫脑干,脊髓的延伸或者起始
协调对生存至关重要的自主功能【也是我们研究的CCHS的主要特征】
分为三个部分:
- 延髓,medulla oblongata,参与呼吸、心率、消化、吞咽、心律和打喷嚏,调节呼吸、血压和心率
- 脑桥,pons,觉醒、睡眠、运动控制和肌肉张力
- 小脑,cerebellum,接收来自我们耳朵的肌肉、肌腱、关节和结构的信息,以控制平衡、协调、运动并促进运动学习,程序记忆
深入呼吸功能的神经基础【我正在做的项目】:
Breathing is an integrated motor behavior that is driven by a respiratory rhythm generator located in the ventrolateral medulla腹外侧的髓质.
Stimulatory inputs from chemoreceptors化学感受器 that monitor CO2 and O2 in the blood provide a tonic drive to breathe and adapt it to exercise and the environment
There is general agreement that the main receptors sensing O2 are located in the carotid body (CB)颈动脉体, whereas responsiveness to CO2/pH is mainly mediated by chemoreceptors in the brainstem脑干
There are two main contenders for this role:
- serotonergic血清素能 (5HT) medullary raphe neurons 髓中缝神经元
- the retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN) 后梯形核, a group of glutamatergic谷氨酸能 neurons located near the medullary髓质 surface ventral to the facial nucleus面核 (nVII)
The RTN neurons receive input from O2-sensitive receptors in the CB via the nucleus of the solitary tract孤束核 (nTS) and connect to the respiratory centers in the lower medulla下髓质
总结RTN的核心作用:Thus, they are in a position to integrate metabolic information on blood gases and to transmit this information to the respiratory centers.
The RTN, which is mainly defined in the adult, overlaps anatomically with a potential oscillator network振荡器网络 identified in neonates新生儿 called the parafacial respiratory group面旁呼吸组 (pFRG)
研究的核心意义:Thus, understanding the molecular and cellular underpinnings of CCHS offers the promise of illuminating the mechanisms that are essential for CO2 sensitivity and, more generally, proper breathing at birth
Given that the mutant allele is expressed from the Phox2b locus, the location of the defect should be sought primarily in Phox2b-expressing structures应主要在表达 Phox2b 的结构中寻找缺陷的位置, although we cannot exclude that Phox2b-negative respiratory neurons are secondarily affected by a non-cell-autonomous mechanism.
一些指标:
高碳酸血症(英语:Hypercapnia)是血液中二氧化碳(CO2)水平异常升高的情况。二氧化碳是身体代谢的气态产物,通常通过肺排出体外。 高碳酸血症通常会引发增强呼吸和接触氧气反应,例如当睡眠时觉醒和转头。如果无法进行这类反应,将有可能致命,就像婴儿突然死亡.
继续深入development的形态研究
神经外胚层neuro-ectoderm
是形成神经系统的第一步,包含了三个发育阶段:
- transformation into the neural plate
- transformation into the neural groove (with associated neural folds)
- transformation into the neural tube.
形成神经管neural tube后,大脑会形成三个部分:前脑、中脑、后脑。
神经上皮阶段neuroepithelial stages
Neuroepithelial cells are the stem cells of the central nervous system, known as neural stem cells, and generate the intermediate progenitor cells known as radial glial cells, that differentiate into neurons and glia in the process of neurogenesis.
跟印象中的表皮细胞没有关系了,是一种CNS干细胞,NSC,neural stem cell,会生成IP,intermediate progenitor,然后分化为CN,cortical neurons。
分化分区阶段neuronal fates
divergence into neuronal fates within the dorsal and ventral forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain regions
CNS里几种常见的细胞类型:
- neural stem cells, NSC(pluripotency、neuroectoderm、neuroepithelium等)
- neural progenitor cells, NPC
- radial glial cells, RGC
- Astrocytes,星形胶质细胞
- Intermediate progenitors, IP
- neurons (CN, cortical neuron)
- Mesenchyme
neurons
- excitatory
- inhibitory
- sensory
- motor
- Interneurons
afferent传入的
efferent传出的
要大致知道这些neuron的marker,以及这些neuron在类器官中的空间分布。
常识:
different iPSC lines的大脑组成差异很大,但基因表达模式基本相同。
primate:
- chimpanzee,黑猩猩
- macaque,猕猴
- ape,猿
cell lines:
- embryonic stem cells (ESC, H9) line
- iPSC (409b2) line
参考:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号