Set重写hashCode和equals方法实现引用对象去重
运作原理:
首先判断hashCode是否相同,如果不同,直接判定为两个不同的对象。如果hashCode相同,再去比较equals是否一样,如果一样,则为同一个对象。如果不一样,则是两个不同对象。
那么直接上代码:
Book.java
package SetNoDoubleFuction01; public class Book { private String name; private Integer price; private String press; private String author; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(Integer price) { this.price = price; } public String getPress() { return press; } public void setPress(String press) { this.press = press; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public Book() { super(); } public Book(String name, Integer price, String press, String author) { this.name = name; this.price = price; this.press = press; this.author = author; } //hashCode判断结果不同才会执行equals //所以hashCode和equals都会参与判断(而且hashCode会先行进行判断) public int hashCode(){ return name.hashCode()+price.hashCode()+press.hashCode()+author.hashCode(); }; //equals不能省略(hashCode并不能起到完全判断) public boolean equals(Object obj){ System.out.println("++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++"); //用来查看equals运行了几次 if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if(this.getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Book book=(Book) obj; if (this.name.equals(book.name)&& this.price.equals(book.price)) return true; return false; }; @Override public String toString() { return "Book{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", price=" + price + ", press='" + press + '\'' + ", author='" + author + '\'' + '}'+ this.hashCode(); } }
Test01.java
package SetNoDoubleFuction01; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Set; public class test01 { static Set<Book> set = new HashSet<>(); //随便加几条数据 static Book book1 =new Book("laogao", 2, "憨批", "学生01"); static Book book2= new Book("wangfei", 1, "2233", "学生02"); static Book book3= new Book("123", 3, "报刊", "学生03"); static Book book4= new Book("33", 5, "2333", "学生04"); static Book book5= new Book("老色批", 4, "2报", "学生05"); //加入重复数据用来测试 static Book book6= new Book("33", 5, "2333", "学生04"); static Book book7= new Book("33", 5, "2333", "学生04"); public static void main(String[] args) { set.add(book1); set.add(book2); set.add(book3); set.add(book4); set.add(book5); set.add(book6); set.add(book7); System.out.println("已有数据!!2"); for (Book it:set) { System.out.println(it.toString()); } System.out.println("增加新内容?"); /* System.out.println(book4.equals(book7));*/ //控制台输入数据测试 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Book book99=new Book(); System.out.println("请输入姓名:"); book99.setName(sc.next()); System.out.println("请输入编号:"); book99.setPrice(sc.nextInt()); System.out.println("请输入类型:"); book99.setPress(sc.next()); System.out.println("请输入作者:"); book99.setAuthor(sc.next()); set.add(book99); for (Book it:set) { System.out.println(it.toString()); } } }
结果(去重成功!!)
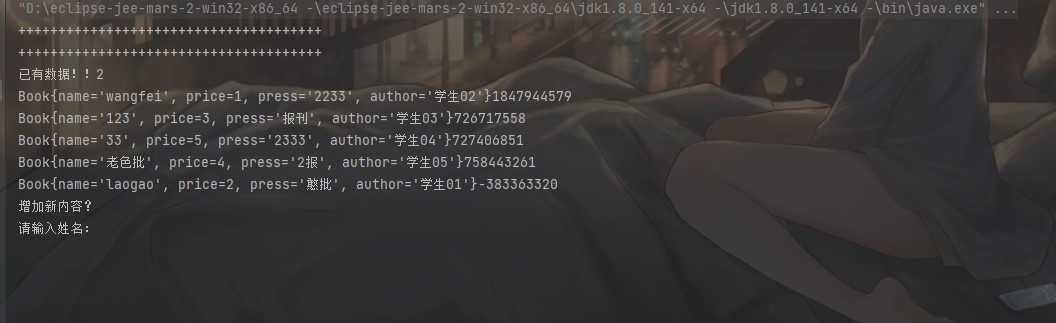
人生永远无法回头,就连这平淡不惊的一幕,终有一日也会碎落满地


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号