Python数据分析库pandas ------ merge、concatenation 、pd.concat、combine_first、stack、unstack(0)、pivot、drop;合并、拼接、组合、轴向旋转、长格式转宽格式、删除
对于合并操作,熟悉SQL的读者可以将其理解为JOIN操作,它使用一个或多个键把多行数据 结合在一起.
事实上,跟关系型数据库打交道的开发人员通常使用SQL的JOIN查询,用几个表共有的引用 值(键)从不同
的表获取数据。以这些键为基础,我们能够获取到列表形式的新数据,这些数据是对几个表中的数据进行组合
得到的。pandas库中这类操作叫作合并,执行合并操作的函数为 merge().
1 import pandas as pd
2 import numpy as np
3
4 frame1 = pd.DataFrame({
5 'color': ['white', 'red', 'red', 'black', 'green'],
6 'id':['ball','pencil','pen','mug','ashtray'],
7 'brand':['OMG','ABC','ABC','POD','POD']
8 })
9
10 frame2 = pd.DataFrame({
11 'id':['pencil','pencil','ball','pen'],
12 'brand':['OMG','POD','ABC','POD']
13 })
14
15 print(pd.merge(frame1,frame2,on='id')) # frame1,frame2的位置没有影响
16 print(pd.merge(frame2,frame1,on='id'))
17 print(pd.merge(frame2,frame1))
18 输出:
19 color id brand_x brand_y
20 0 white ball OMG ABC
21 1 red pencil ABC OMG
22 2 red pencil ABC POD
23 3 red pen ABC POD
24 id brand_x color brand_y
25 0 pencil OMG red ABC
26 1 pencil POD red ABC
27 2 ball ABC white OMG
28 3 pen POD red ABC
29 Empty DataFrame
30 Columns: [id, brand, color]
31 Index: []
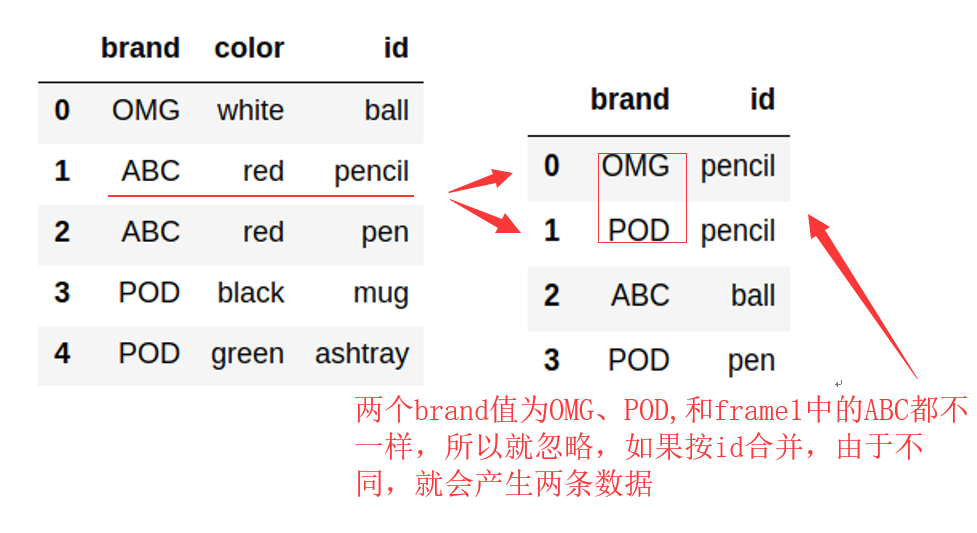
没有指定按id合并的时候,合并为空,因为id,和brand两个值不能完全一致,如pencil对应的brand值,两个
表都没有一样的所以该字段就没有了。
假如两个DataFrame基准列的名称不一致,该怎样进行合并呢?为 了解决这个问题,你可以用
left_on和right_on选项指定第一个和第二个DataFrame的基准列。
1 frame2_test = frame2
2 frame2_test.columns = ['sid', 'brand'] # 这一步也会将frame2的列名改变,对比浅复制
3 print(frame1)
4 print(frame2_test)
5 print("-----*-----\n", pd.merge(frame1,frame2_test,left_on='id',right_on='sid'))
6 输出:
7 color id brand
8 0 white ball OMG
9 1 red pencil ABC
10 2 red pen ABC
11 3 black mug POD
12 4 green ashtray POD
13 sid brand
14 0 pencil OMG
15 1 pencil POD
16 2 ball ABC
17 3 pen POD
18 -----*-----
19 color id brand_x sid brand_y
20 0 white ball OMG ball ABC
21 1 red pencil ABC pencil OMG
22 2 red pencil ABC pencil POD
23 3 red pen ABC pen POD
merge()函数默认执行的是内连接操作;上述结果中的键是由交叉操作(intersection)得到的。
其他选项有左连接、右连接和外连接。外连接把所有的键整合到一起,其效果相当于左连接 和右
连接的效果之和。连接类型用how选项指定。
1 frame4 = frame1
2 print(frame2, '\n-----*frame2*-----\n') # 前面改变列名的操作已经注释掉
3 print(frame4, '\n-----*frame4*-----\n')
4 print(pd.merge(frame4,frame2,on='id'), '\n-----*内连接*-----\n')
5 print(pd.merge(frame4,frame2,on='id',how='outer'), '\n-----*外连接*-----\n')
6 print(pd.merge(frame4,frame2,on='id',how='right'), '\n-----*右连接*-----\n')
7 输出:
8 id brand
9 0 pencil OMG
10 1 pencil POD
11 2 ball ABC
12 3 pen POD
13 -----*frame2*-----
14
15 color id brand
16 0 white ball OMG
17 1 red pencil ABC
18 2 red pen ABC
19 3 black mug POD
20 4 green ashtray POD
21 -----*frame4*-----
22
23 color id brand_x brand_y
24 0 white ball OMG ABC
25 1 red pencil ABC OMG
26 2 red pencil ABC POD
27 3 red pen ABC POD
28 -----*内连接*-----
29
30 color id brand_x brand_y
31 0 white ball OMG ABC
32 1 red pencil ABC OMG
33 2 red pencil ABC POD
34 3 red pen ABC POD
35 4 black mug POD NaN
36 5 green ashtray POD NaN
37 -----*外连接*-----
38
39 color id brand_x brand_y
40 0 white ball OMG ABC
41 1 red pencil ABC OMG
42 2 red pencil ABC POD
43 3 red pen ABC POD
44 -----*右连接*-----
指定按多个列合并:
1 print(pd.merge(frame4,frame2,on=['id','brand'],how='outer'))
2 输出:
3 color id brand
4 0 white ball OMG
5 1 red pencil ABC
6 2 red pen ABC
7 3 black mug POD
8 4 green ashtray POD
9 5 NaN pencil OMG
10 6 NaN pencil POD
11 7 NaN ball ABC
12 8 NaN pen POD
这个地方如果是内连接就会是空。
根据索引合并
1 print(frame4, '\n-----*frame4*-----\n')
2 print(frame2, '\n-----*frame2*-----\n')
3 print(pd.merge(frame4,frame2,right_index=True,left_index=True))
4 # 也可以使用jion合并
5 frame2.columns = ['id2', 'brand2']
6 print(frame4.join(frame2))
7 输入:
8 color id brand
9 0 white ball OMG
10 1 red pencil ABC
11 2 red pen ABC
12 3 black mug POD
13 4 green ashtray POD
14 -----*frame4*-----
15
16 id brand
17 0 pencil OMG
18 1 pencil POD
19 2 ball ABC
20 3 pen POD
21 -----*frame2*-----
22
23 color id_x brand_x id_y brand_y
24 0 white ball OMG pencil OMG
25 1 red pencil ABC pencil POD
26 2 red pen ABC ball ABC
27 3 black mug POD pen POD
28 color id brand id2 brand2
29 0 white ball OMG pencil OMG
30 1 red pencil ABC pencil POD
31 2 red pen ABC ball ABC
32 3 black mug POD pen POD
33 4 green ashtray POD NaN NaN
两者之间的差异是非常明显的,前者不一致的就舍去,后者添加NaN补全。
拼接操作
另外一种数据整合操作叫作拼接(concatenation)。NumPy的concatenate()函数就是用于数 组的拼接操作。
1 array1 = np.arange(9).reshape((3,3))
2 array2 = np.arange(9).reshape((3,3))+6
3 # axis=0表示按行拼接,就是将array2放在array1下面
4 print(np.concatenate([array1,array2],axis=0))
5 print(np.concatenate([array1,array2],axis=1))
6 输出:
7 [[ 0 1 2]
8 [ 3 4 5]
9 [ 6 7 8]
10 [ 6 7 8]
11 [ 9 10 11]
12 [12 13 14]]
13 [[ 0 1 2 6 7 8]
14 [ 3 4 5 9 10 11]
15 [ 6 7 8 12 13 14]]
pandas库以及它的Series和DataFrame等数据结构实现了带编号的轴,它可以进一步扩展数组拼接功能。
pandas的concat()函数实现了按轴拼接的功能。
1 ser1 = pd.Series(np.random.rand(4),index=[1,2,3,4])
2 ser2 = pd.Series(np.random.rand(4),index=[5,6,7,8])
3 # pd.concat([ser1,ser2]), concat()函数默认按照axis=0这条轴拼接数据,返回Series对象。如果指定axis=l,返回结果将是DataFrame对象。
4 print(pd.concat([ser1,ser2]))
5 print(pd.concat([ser1,ser2], axis=1))
6 # 赋予新对象以等级索引
7 print(pd.concat([ser1,ser2],keys=[1,2])) #等级索引
8 frame5 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(9).reshape(3,3), index=[1,2,3],columns=['A','B','C'])
9 frame2 = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(9).reshape(3,3), index=[4,5,6],columns=['A','B','C'])
10 print(pd.concat([frame5,frame2]))
11 print(pd.concat([frame5,frame2],axis=1))
12 输出:
13 1 0.392044
14 2 0.800669
15 3 0.899750
16 4 0.853225
17 5 0.545121
18 6 0.979369
19 7 0.864454
20 8 0.338446
21 dtype: float64
22 0 1
23 1 0.392044 NaN
24 2 0.800669 NaN
25 3 0.899750 NaN
26 4 0.853225 NaN
27 5 NaN 0.545121
28 6 NaN 0.979369
29 7 NaN 0.864454
30 8 NaN 0.338446
31 1 1 0.392044
32 2 0.800669
33 3 0.899750
34 4 0.853225
35 2 5 0.545121
36 6 0.979369
37 7 0.864454
38 8 0.338446
39 dtype: float64
40 A B C
41 1 0.781247 0.927653 0.765253
42 2 0.395887 0.625049 0.509451
43 3 0.566538 0.869041 0.862552
44 4 0.877117 0.226862 0.205766
45 5 0.489178 0.054522 0.497122
46 6 0.691023 0.076475 0.965215
47 A B C A B C
48 1 0.781247 0.927653 0.765253 NaN NaN NaN
49 2 0.395887 0.625049 0.509451 NaN NaN NaN
50 3 0.566538 0.869041 0.862552 NaN NaN NaN
51 4 NaN NaN NaN 0.877117 0.226862 0.205766
52 5 NaN NaN NaN 0.489178 0.054522 0.497122
53 6 NaN NaN NaN 0.691023 0.076475 0.965215
组合操作
还有另外一种情况,我们无法通过合并或拼接方法组合数据。例如,两个数据集的索引完全或部分重合。
1 ser1 = pd.Series(np.random.rand(5),index=[1,2,3,4,5])
2 ser2 = pd.Series(np.random.rand(4),index=[2,4,5,6])
3 # ser1组合上ser2
4 print(ser1.combine_first(ser2))
5 # ser2组合上ser1
6 print(ser2.combine_first(ser1))
7 print(ser1[:3].combine_first(ser2[:3]))
8 输出:
9 1 0.174250
10 2 0.208664
11 3 0.784141
12 4 0.861739
13 5 0.373359
14 6 0.332396
15 dtype: float64
16 1 0.174250
17 2 0.061261
18 3 0.784141
19 4 0.889045
20 5 0.232429
21 6 0.332396
22 dtype: float64
23 1 0.174250
24 2 0.208664
25 3 0.784141
26 4 0.889045
27 5 0.232429
28 dtype: float64
轴向旋转操作
1 frame5 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index=['white','black','red'],columns=['ball','pen','pencil'])
2 print(frame5)
3 frame6 = frame5.stack() # 列变行,变成层级的样式,码整齐
4 print(frame6)
5 print(frame6.unstack())
6 print(frame6.unstack(0))
7 输出:
8 ball pen pencil
9 white 0 1 2
10 black 3 4 5
11 red 6 7 8
12 white ball 0
13 pen 1
14 pencil 2
15 black ball 3
16 pen 4
17 pencil 5
18 red ball 6
19 pen 7
20 pencil 8
21 dtype: int32
22 ball pen pencil
23 white 0 1 2
24 black 3 4 5
25 red 6 7 8
26 white black red
27 ball 0 3 6
28 pen 1 4 7
29 pencil 2 5 8
长格式转宽格式
1 longframe = pd.DataFrame({
2 'color':['white','white','white','red','red','red','black','black','black'],
3 'item':['ball','pen','mug','ball','pen','mug','ball','pen','mug'],
4 'value': np.random.rand(9)
5 })
6 print(longframe)
7 输出:
8 color item value
9 0 white ball 0.993608
10 1 white pen 0.522115
11 2 white mug 0.977019
12 3 red ball 0.999250
13 4 red pen 0.051223
14 5 red mug 0.345762
15 6 black ball 0.539147
16 7 black pen 0.054598
17 8 black mug 0.420309
这种记录数据的模式有几个缺点。例如其中一个缺点是,因为一些字段具有多样性和 重复性特点,所以选
取列作为键时,这种格式的数据可读性较差,尤其是无法完全理解基准列和 其他列之间的关系。除了长格式,还
有一种把数据调整为表格形式的宽格式。这种模式可读性强,也易于连接其他表,且占用空间较少。因此一般而
言,用它存储数据效率更高,虽然它的可操作性差,这一点 尤其体现在填充数据时。如要选择一列或几列作为主
键,所要遵循的规则是其中的元素必须是唯一的。讲到格式转换,pandas提供了能够把长格式DataFrame转换为
宽格式的pivot()函数,它以用 作键的一列或多列作为参数。接着上面的例子,选择color列作为主键,item列作为
第二主键,而它们所对应的元素则作 为DataFrame的新列。
1 wideframe = longframe.pivot('color','item') 2 print(wideframe) 3 # 这种格式的DataFrame对象更加紧凑,它里面的数据可读性也更强。 4 输出: 5 value 6 item ball mug pen 7 color 8 black 0.549983 0.157802 0.987871 9 red 0.685751 0.038634 0.251137 10 white 0.263787 0.291939 0.787407
删除操作
1 frame7 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(9).reshape(3,3),index=['white','black','red'],columns=['ball','pen','pencil'])
2 print(frame7)
3 del frame7['ball'] # 删除列
4 print(frame7)
5 frame7.drop('white') # 删除行
6 print(frame7)
7 frame7.drop('pen',axis=1) # 删除列
8 输出:
9 ball pen pencil
10 white 0 1 2
11 black 3 4 5
12 red 6 7 8
13 pen pencil
14 white 1 2
15 black 4 5
16 red 7 8
17 pen pencil
18 white 1 2
19 black 4 5
20 red 7 8



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号