c++继承与派生
·类的继承
定义:是新的类从已有类那里得到已有的特性,原有的类称为基类或父类。(除了构造函数,拷贝构造函数和析构函数都继承)
继承的目的:代码设计的重用,充分利用原有的类。
语法:
单继承时:
class 派生类名(子类名):继承方式 基类名
{
派生类成员声明;
};
例:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; // 基类 class Shape { public: void setWidth(int w) { width = w; } void setHeight(int h) { height = h; } protected: int width; int height; }; // 派生类 class Rectangle: public Shape { public: int getArea() { return (width * height); } }; int main(void) { Rectangle Rect; //声明一个对象 Rect.setWidth(5); //赋值 Rect.setHeight(7); // 输出对象的面积 cout << "Total area: " << Rect.getArea() << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
运行结果:

多继承时:
class 派生类名:继承方式 基类名1,继承方式 基类名2,······,继承方式 基类名n { 派生类成员声明; };
例:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; // 基类 Shape class Shape { public: void setWidth(int w) { width = w; } void setHeight(int h) { height = h; } protected: int width; int height; }; // 基类 PaintCost class PaintCost { public: int getCost(int area) { return area * 70; } }; // 派生类 class Rectangle : public Shape, public PaintCost //继承多个类 { public: int getArea() { return (width * height); } }; int main(void) { Rectangle Rect; //对象 int area; Rect.setWidth(5); Rect.setHeight(7); area = Rect.getArea(); // 输出对象的面积 cout << "Total area: " << Rect.getArea() << endl; // 输出总花费 cout << "Total paint cost: $" << Rect.getCost(area) << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
运行截图:

继承分为3类:1.公有继承(public ):基类的公有成员和保护成员的访问属性在派生类中不变,而基类的私有成员不可直接访问
2.私有继承(private):基类中的公有成员和保护成员都以私有成员身份出现在派生类中,而基类的私有成员在派生类中不可直接访问
3.保护继承(protected):基类的共有成员和保护成员都以保护成员的身份出现在派生类中,而基类的私有成员不可直接访问
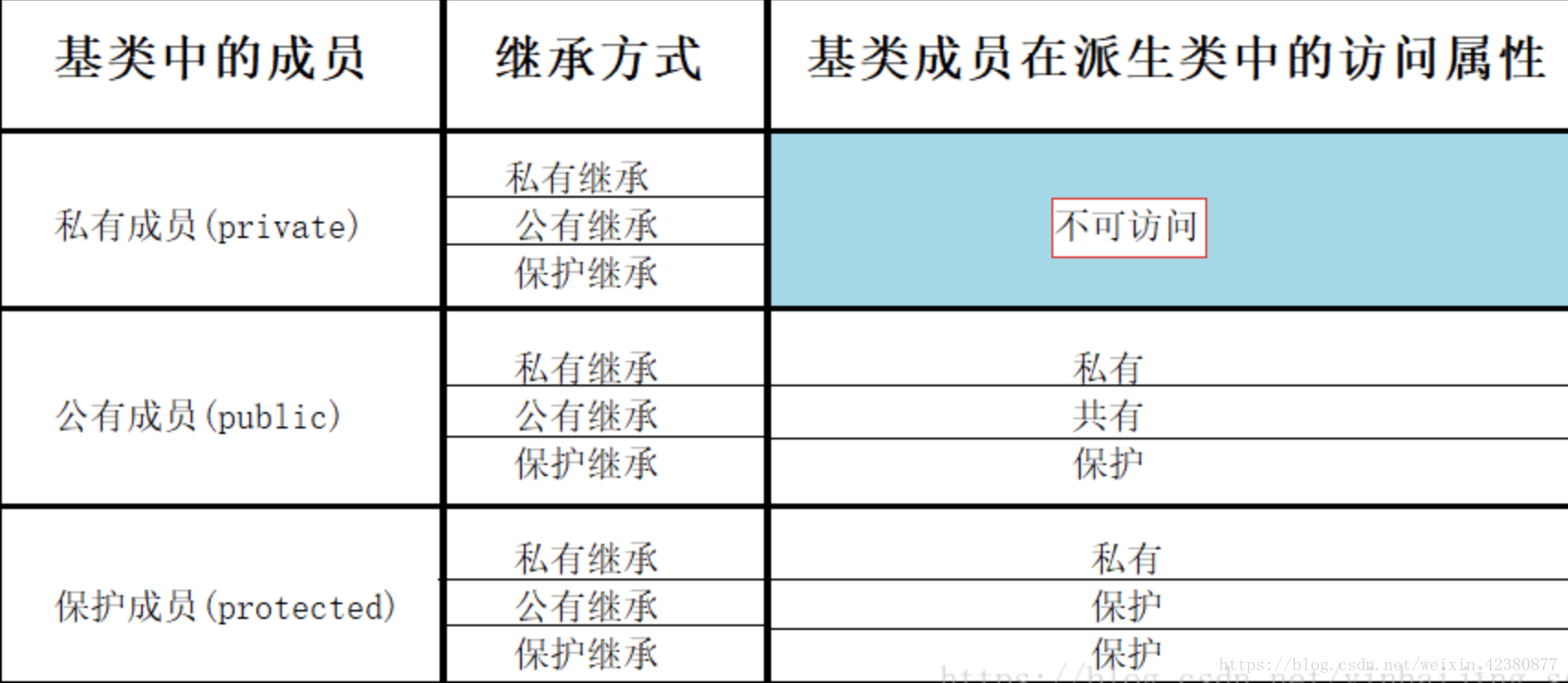
保护成员:在派生类中可以作为public,在基类中类似private。(也就是说,如果想要把基类中的私有成员给派生类用,但是却又不想将此成员作为public成员,可以设定为protected成员,这样可以达到派生类可以访问的效果)
私有继承:将除了私有成员的其他成员转换成派生类的私有成员
·类的派生
定义:从已有类产生新类的过程就是类的派生,产生的新类称为派生类或子类。
派生的目的:功能的扩展与更改。
作用:1.吸收基类成员
2.改造基类成员
3.添加新的成员
继承同名成员处理方式:
1.访问子类同名成员 直接访问即可
2.访问父类同名成员 需要加作用域
例:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; // 基类 class Shape { public: void setWidth(int w) { width = w; } void setHeight(int h) { height = h; } protected: int width; int height; int a = 10; }; // 派生类 class Rectangle : public Shape { public: int getArea() { return (width * height); } void show() { cout << a << endl; //访问子类同名成员 cout << Shape::a << endl; //访问父类同名成员 } private: int a = 20; }; int main(void) { Rectangle Rect; //声明一个对象 Rect.setWidth(5); //赋值 Rect.setHeight(7); // 输出对象的面积 cout << "Total area: " << Rect.getArea() << endl; Rect.show(); system("pause"); return 0; }
运行结果:





