GTest源码分析——用例注册与执行过程
GTest源码分析——用例注册与执行过程
Google Test(GTest)使用方法和源码解析——自动调度机制分析_&test::testbody-CSDN博客
本文不是按照阅读源码时的分析顺序,而是在阅读源码后,将涉及到的数据结构、函数放在最前面,最后再分析执行流程的。所以在分析执行流程时,不再分析函数逻辑了,不记得了就在上文找。
本文给出的源码,都经过了删减,只展示部分逻辑。
HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported() 函数
兼容C++异常/Windows SEH异常的函数,内部就是帮你执行 object::method() :
template <class T, typename Result>
Result HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(T* object, Result (T::*method)(),
const char* location) {
if (internal::GetUnitTestImpl()->catch_exceptions()) {
// ...
return (object->*method)();
}
}
UnitTest 类
就是一个存储了一堆 TestSuites 的容器。这个类对象以单例形式存在,是GTest框架中其他类之间沟通的桥梁。
这个类采用 Pimpl 设计,所以还有一个 UnitTestImpl 实现类。
UnitTestImpl::AddTestInfo() 函数
void AddTestInfo(internal::SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc,
internal::TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc,
TestInfo* test_info) {
GetTestSuite(test_info->test_suite_name_, test_info->type_param(),
set_up_tc, tear_down_tc)
->AddTestInfo(test_info);
}
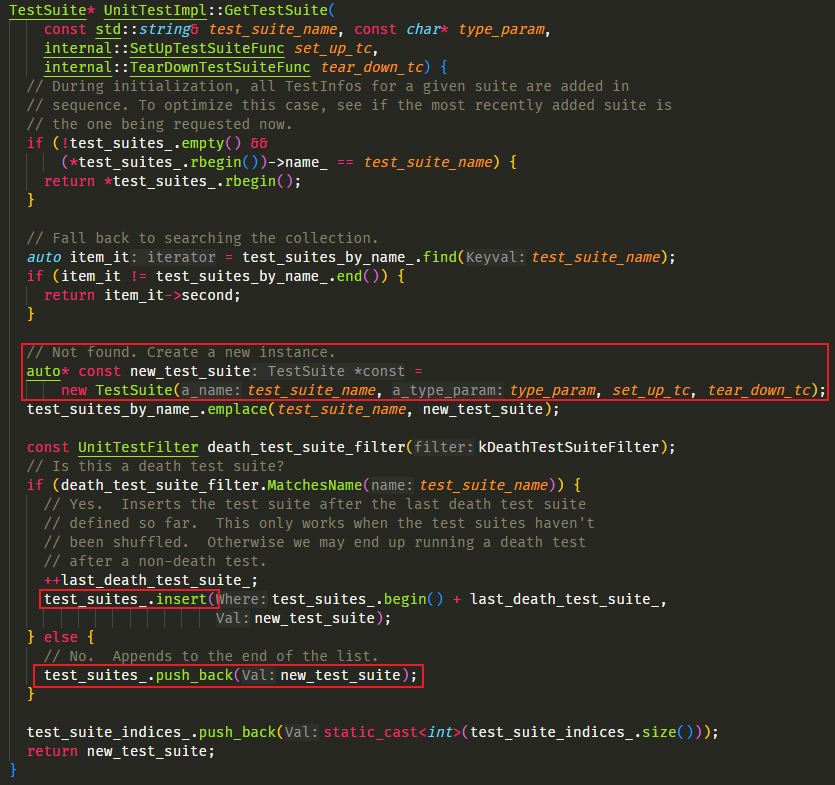
UniTestImpl::GetTestSuite() 函数
UnitTestImpl::GetTestSuite() 会尝试查找是否存在已有的同名 TestSuite 对象,没有就新建一个:
UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() 函数
bool UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() {
// 启动监听器
TestEventListener* repeater = listeners()->repeater();
repeater->OnTestProgramStart(*parent_);
// How many times to repeat the tests? We don't want to repeat them
// when we are inside the subprocess of a death test.
const int repeat = in_subprocess_for_death_test ? 1 : GTEST_FLAG_GET(repeat);
// Repeats forever if the repeat count is negative.
const bool gtest_repeat_forever = repeat < 0;
// 每轮循环是一遍全量测试
for (int i = 0; gtest_repeat_forever || i != repeat; i++) {
// Tells the unit test event listeners that the tests are about to start.
repeater->OnTestIterationStart(*parent_, i);
// Runs each test suite if there is at least one test to run.
if (has_tests_to_run) {
// Sets up all environments beforehand. If test environments aren't
// recreated for each iteration, only do so on the first iteration.
if (i == 0 || recreate_environments_when_repeating) {
repeater->OnEnvironmentsSetUpStart(*parent_);
ForEach(environments_, SetUpEnvironment);
repeater->OnEnvironmentsSetUpEnd(*parent_);
}
// Runs the tests only if there was no fatal failure or skip triggered
// during global set-up.
if (Test::IsSkipped()) {
// Emit diagnostics when global set-up calls skip, as it will not be
// emitted by default.
TestResult& test_result =
*internal::GetUnitTestImpl()->current_test_result();
for (int j = 0; j < test_result.total_part_count(); ++j) {
const TestPartResult& test_part_result =
test_result.GetTestPartResult(j);
}
fflush(stdout);
} else if (!Test::HasFatalFailure()) {
// 遍历所有 TestSuite 并调用其 Run 方法
for (int test_index = 0; test_index < total_test_suite_count();
test_index++) {
GetMutableSuiteCase(test_index)->Run(); // 执行测试
if (GTEST_FLAG_GET(fail_fast) &&
GetMutableSuiteCase(test_index)->Failed()) {
for (int j = test_index + 1; j < total_test_suite_count(); j++) {
GetMutableSuiteCase(j)->Skip();
}
break;
}
}
} else if (Test::HasFatalFailure()) {
// If there was a fatal failure during the global setup then we know we
// aren't going to run any tests. Explicitly mark all of the tests as
// skipped to make this obvious in the output.
for (int test_index = 0; test_index < total_test_suite_count();
test_index++) {
GetMutableSuiteCase(test_index)->Skip();
}
}
// Tears down all environments in reverse order afterwards. If test
// environments aren't recreated for each iteration, only do so on the
// last iteration.
if (i == repeat - 1 || recreate_environments_when_repeating) {
repeater->OnEnvironmentsTearDownStart(*parent_);
std::for_each(environments_.rbegin(), environments_.rend(),
TearDownEnvironment);
repeater->OnEnvironmentsTearDownEnd(*parent_);
}
}
// Tells the unit test event listener that the tests have just finished.
repeater->OnTestIterationEnd(*parent_, i);
// Gets the result and clears it.
if (!Passed()) {
failed = true;
}
}
repeater->OnTestProgramEnd(*parent_);
// Destroy environments in normal code, not in static teardown.
bool delete_environment_on_teardown = true;
if (delete_environment_on_teardown) {
ForEach(environments_, internal::Delete<Environment>);
environments_.clear();
}
return !failed;
}
TestFactory 类
其是一个类工厂,利用多态和模板:
// Defines the abstract factory interface that creates instances
// of a Test object.
class TestFactoryBase {
public:
virtual ~TestFactoryBase() = default;
// Creates a test instance to run. The instance is both created and destroyed
// within TestInfoImpl::Run()
virtual Test* CreateTest() = 0;
protected:
TestFactoryBase() {}
private: // 禁止拷贝
TestFactoryBase(const TestFactoryBase&) = delete;
TestFactoryBase& operator=(const TestFactoryBase&) = delete;
};
// This class provides implementation of TestFactoryBase interface.
// It is used in TEST and TEST_F macros.
template <class TestClass>
class TestFactoryImpl : public TestFactoryBase {
public:
Test* CreateTest() override { return new TestClass; }
};
Test 类
代表一个测试用例本身。是纯粹的测试逻辑。
Test::Run() 函数
就是执行宏生成/自己写的 Test 子类的钩子函数:SetUp() --> TestBody() --> TearDown()
void Test::Run() {
internal::UnitTestImpl* const impl = internal::GetUnitTestImpl();
impl->os_stack_trace_getter()->UponLeavingGTest();
internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(this, &Test::SetUp, "SetUp()");
// We will run the test only if SetUp() was successful and didn't call
// GTEST_SKIP().
if (!HasFatalFailure() && !IsSkipped()) {
impl->os_stack_trace_getter()->UponLeavingGTest();
internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(this, &Test::TestBody,
"the test body");
}
// However, we want to clean up as much as possible. Hence we will
// always call TearDown(), even if SetUp() or the test body has
// failed.
impl->os_stack_trace_getter()->UponLeavingGTest();
internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(this, &Test::TearDown,
"TearDown()");
}
TestInfo 类
TestInfo 类存储了一个测试的名字、是否应该被执行等元信息,并负责管理用户的测试类的生命周期。
其地位是连接 Test 类与 TestSuite 类,持有注入的工厂实例来负责 Test 类实例的构造与销毁。
TestInfo::Run() 函数
该函数负责创建用户通过 TEST/TEST_F 宏生成的测试类的对象,并执行该对象的 TestBody() 函数并报告执行结果,最后释放内存。
void TestInfo::Run() {
TestEventListener* repeater = UnitTest::GetInstance()->listeners().repeater();
UnitTest::GetInstance()->set_current_test_info(this);
// Notifies the unit test event listeners that a test is about to start.
repeater->OnTestStart(*this);
result_.set_start_timestamp(internal::GetTimeInMillis());
UnitTest::GetInstance()->UponLeavingGTest();
// 创建Test对象
Test* const test = internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(
factory_, &internal::TestFactoryBase::CreateTest,
"the test fixture's constructor");
// 执行测试
if (!Test::HasFatalFailure() && !Test::IsSkipped()) {
test->Run();
}
if (test != nullptr) {
// Deletes the test object.
UnitTest::GetInstance()->UponLeavingGTest();
internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(
test, &Test::DeleteSelf_, "the test fixture's destructor");
}
// Notifies the unit test event listener that a test has just finished.
repeater->OnTestEnd(*this);
UnitTest::GetInstance()->set_current_test_info(nullptr);
}
TestSuite 类
就是一个存储了一堆 TestInfo 的容器。
TestSuite::AddTestInfo() 函数
void TestSuite::AddTestInfo(TestInfo* test_info) {
test_info_list_.push_back(test_info);
test_indices_.push_back(static_cast<int>(test_indices_.size()));
}
TestSuite::Run() 函数
void TestSuite::Run() {
UnitTest::GetInstance()->set_current_test_suite(this);
TestEventListener* repeater = UnitTest::GetInstance()->listeners().repeater();
repeater->OnTestSuiteStart(*this);
UnitTest::GetInstance()->UponLeavingGTest();
// 调用绑定的 SetUp 方法
internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(
this, &TestSuite::RunSetUpTestSuite, "SetUpTestSuite()");
// 开始执行测试
for (int i = 0; i < total_test_count(); i++) {
if (skip_all) {
GetMutableTestInfo(i)->Skip();
} else {
GetMutableTestInfo(i)->Run();
}
if (GTEST_FLAG_GET(fail_fast) &&
GetMutableTestInfo(i)->result()->Failed()) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < total_test_count(); j++) {
GetMutableTestInfo(j)->Skip();
}
break;
}
}
UnitTest::GetInstance()->UponLeavingGTest();
// 调用绑定的 TearDown 方法
internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(
this, &TestSuite::RunTearDownTestSuite, "TearDownTestSuite()");
repeater->OnTestSuiteEnd(*this);
UnitTest::GetInstance()->set_current_test_suite(nullptr);
}
TEST / TEST_F 宏
这两个宏会展开为:
#define GTEST_TEST(test_suite_name, test_name) \
GTEST_TEST_(test_suite_name, test_name, ::testing::Test, \
::testing::internal::GetTestTypeId())
#define GTEST_TEST_F(test_fixture, test_name) \
GTEST_TEST_(test_fixture, test_name, test_fixture, \
::testing::internal::GetTypeId<test_fixture>())
可以看到,其实使用 TEST 还是 TEST_F 本质都是一样的,只不过差在继承关系和是否重写了 SetUp()/TearDown() 方法:
GTEST_TEST_ 宏
而 GTEST_TEST_ 会展开如下:
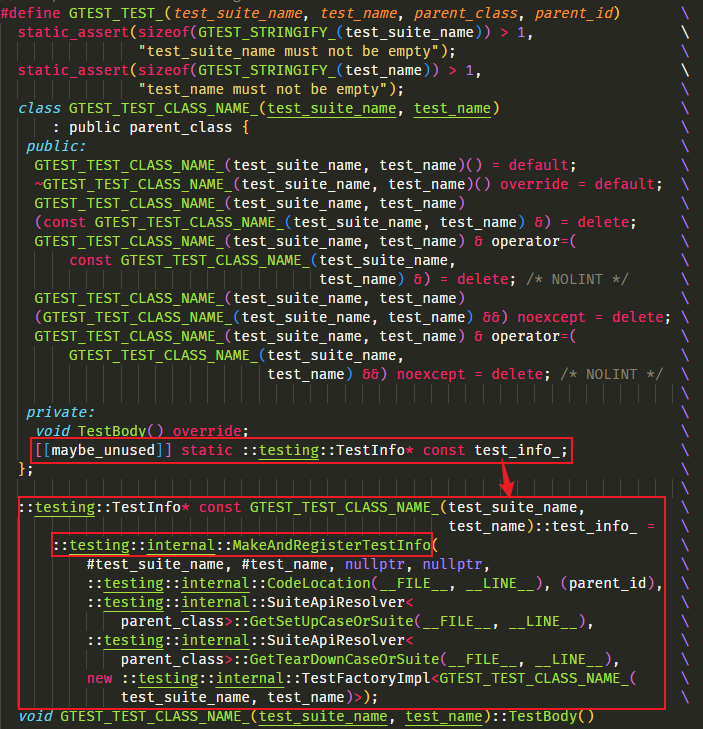
它是为每个“用例函数”生成了一个用例类,类禁用了拷贝和移动语义,继承自 ::testing::Test ,具有一个虚函数 TestBody() 并放在宏最后用于承接 TEST() { ... } 的函数体。且定义了一个静态变量 test_info_ ,利用静态变量在 main 执行之前被初始化的规则,将注册用例的操作 MakeAndRegisterTestInfo() 作为 test_info_ 的初始化过程,从而能自动在程序开始前执行注册逻辑。
MakeAndRegisterTestInfo() 函数
它是就地通过 __FILE__ 和 __LINE__ 保存了代码位置到 CodeLocation ,通过 TestFactory 创建了 TestInfo ,然后调用 UnitTestImpl::AddTestInfo() 记录这个 TestInfo 。
// Creates a new TestInfo object and registers it with Google Test;
// returns the created object.
//
// Arguments:
//
// test_suite_name: name of the test suite
// name: name of the test
// type_param: the name of the test's type parameter, or NULL if
// this is not a typed or a type-parameterized test.
// value_param: text representation of the test's value parameter,
// or NULL if this is not a value-parameterized test.
// code_location: code location where the test is defined
// fixture_class_id: ID of the test fixture class
// set_up_tc: pointer to the function that sets up the test suite
// tear_down_tc: pointer to the function that tears down the test suite
// factory: pointer to the factory that creates a test object.
// The newly created TestInfo instance will assume
// ownership of the factory object.
TestInfo* MakeAndRegisterTestInfo(
std::string test_suite_name, const char* name, const char* type_param,
const char* value_param, CodeLocation code_location,
TypeId fixture_class_id, SetUpTestSuiteFunc set_up_tc,
TearDownTestSuiteFunc tear_down_tc, TestFactoryBase* factory) {
TestInfo* const test_info =
new TestInfo(std::move(test_suite_name), name, type_param, value_param,
std::move(code_location), fixture_class_id, factory);
GetUnitTestImpl()->AddTestInfo(set_up_tc, tear_down_tc, test_info);
return test_info;
}
RUN_ALL_TESTS() 函数
在此之前还有个用于解析命令行参数的 InitGoogleTest() ,那个不重要。通过 UniTest 单例来执行:
inline int RUN_ALL_TESTS() { return ::testing::UnitTest::GetInstance()->Run(); }
int UnitTest::Run() {
// Captures the value of GTEST_FLAG(catch_exceptions). This value will be
// used for the duration of the program.
impl()->set_catch_exceptions(GTEST_FLAG_GET(catch_exceptions));
}
return internal::HandleExceptionsInMethodIfSupported(
impl(), &internal::UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests,
"auxiliary test code (environments or event listeners)")
? 0
: 1;
}
所以就相当于 UnitTest::impl()->RunAllTests() 。
其中 impl_ 对象在 UnitTest 单例创建时被创建:
UnitTest::UnitTest() { impl_ = new internal::UnitTestImpl(this); }
UnitTestImpl::RunAllTests() 分析见上文。
整体流程
类图
执行流
总结
类之间的关系
在 GoogleTest 的架构中,类之间的关系是:
- UnitTest (单例) → 管理多个 TestSuite → 每个包含多个 TestInfo → 每个通过其构造时注入的工厂类实例来创建 Test 实例。
- 即通过所有属于同一个 text fixture 的用例,每个都对应一个自己的
Test子类实例和TestInfo实例,最终都会存储在同一个TestSuite实例中。而所有的TestSuite实例又存储在UnitTest单例中。
用例注册过程
TEST/TEST_F宏展开声明了一个最终继承于Test的子类- 声明了一个虚函数
TestBody() - 声明了一个静态成员变量
::testing::TestInfo* const test_info_
- 声明了一个虚函数
- 在类外,利用
MakeAndRegisterTestInfo初始化了静态成员变量test_info_- 其中访问
UnitTest单例会使得在main函数执行前就将所有测试用例都注册到UnitTest单例中。
- 其中访问
- 最后输出了
TestBody()的函数签名,此时会连上我们测试用例的函数体。
用例执行过程
TestSuite::Run() 方法遍历所有 TestInfo,为每个测试:
- 调用
SetUpTestSuite()(整个套件执行一次) - 为每个测试创建新的
Test实例 - 调用
Test::SetUp() - 执行
Test::TestBody()(测试逻辑) - 调用
Test::TearDown() - 删除
Test实例 - 调用
TearDownTestSuite()(整个套件执行一次)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号