一、课上的代码

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 int main() 3 { void funstr(char str); 4 char str[12]={"hello world!"}; 5 str[0]='H'; 6 funstr(str); 7 return 0; 8 } 9 void funstr(char str) 10 { 11 int t; 12 printf("%s\n",str); 13 while(t!='\0') 14 { 15 printf("%c\n",str); 16 t++; 17 } 18 }
显然,课上的代码是不对的。编译器显示正确,但却未能运行。

二、课下的工作
有许多细节部位致错,课下通过查书p76页表3.8,明确了%c是字符输出函数,%s是字符串输出函数。
p260页可得知,需要定义一个指针变量去指向数组。且该代码没while的循环变量定义初始条件
数组没有定义至足够长度也是另一个方面。循环条件(为t)及输出有\n也出现了错误,所以致错。
三、正确的代码

1 #include<stdio.h> 2 int main() 3 { void funstr(char str[12]); 4 char str[12]={"hello world"}; 5 char *a=str; 6 str[0]='H'; 7 funstr(a); 8 return 0; 9 } 10 void funstr(char str[12]) 11 { 12 int t=0; 13 printf("%s\n",str); 14 while(str[t]!='\0') 15 { 16 printf("%c",str[t]); 17 t++; 18 } 19 }
更改并纠正了以上错误,进行了反思
四、
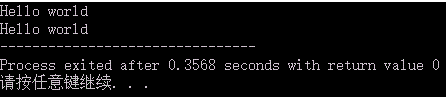
五、
编程时需要有足够的细心程度,用脑且用心,字符串需要多定义一个长度 需要初始化地址及变量。
六、尊重正版、谨防假冒伪劣:( 哼!!!!




