基于面向对象的字符图像设计
基于面向对象的字符图像设计
——《C++沉思录》第10章 一个课堂练习的分析(下)
发表一下个人看法。面向对象的一大特点就是提供了句柄,句柄的的作用一是隐藏了具体的继承层次细节,二是实现自动管理内存,省去客户端管理内存的烦恼。
之前《字符图像》介绍了一个字符图像的设计。面向对象具有数据抽象、封装、动态绑定等特性,下面我们采用面向对象的思想来重新设计字符图像。
具体细节详见代码和注释。
// 基于面向对象的字符图像设计 #include <iostream> using namespace std; // 前置声明,因为Picture中需要定义P_Node*指针 class P_Node; // 定义句柄类(代理) class Picture { private: P_Node* p; public: Picture(); Picture(const char* const*, int); Picture(const Picture&); ~Picture(); Picture& operator = (const Picture&); // 增加一构造函数,用于由P_Node*到Picture的隐式类型转换 Picture(P_Node*); private: int height() const; int width() const; void display(ostream&, int, int) const; // 输出 // 友元 friend ostream& operator << (ostream&, const Picture&); // 边框函数 friend Picture frame(const Picture&); // 纵向拼接 friend Picture operator & (const Picture&, const Picture&); // 横向拼接 friend Picture operator | (const Picture&, const Picture&); // 友元类 friend class String_Pic; friend class Frame_Pic; friend class HCat_Pic; friend class VCat_Pic; }; // 定义实际图像抽象基类 class P_Node { private: private: int use; // 引用计数,用来记录实际被代理个数 protected: P_Node(); // 用来初始化引用计数 // 由于Picture析构函数中用到了delete,所以这里需要一个虚析构函数 virtual ~P_Node(); virtual int height() const = 0; virtual int width() const = 0; virtual void display(ostream&, int, int) const = 0; protected: // 求较大的数 int max(int, int) const; // 友元 friend class Picture; }; P_Node::P_Node() : use(1) {} P_Node::~P_Node() {} int P_Node::max(int x, int y) const { return x > y ? x : y; } // 字符图像 class String_Pic : public P_Node { private: char** data; int size; private: String_Pic(const char* const*, int); ~String_Pic(); int height() const; int width() const; void display(ostream&, int, int) const; friend class Picture; }; String_Pic::String_Pic(const char* const* p, int n) : data(new char*[n]), size(n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { data[i] = new char[strlen(p[i]) + 1]; strcpy(data[i], p[i]); } } String_Pic::~String_Pic() { for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { delete [] data[i]; } delete [] data; } int String_Pic::height() const { return size; } int String_Pic::width() const { int n = 0; for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { n = max(n, strlen(data[i])); } return n; } static void pad(ostream& os, int x, int y) { for (int i = x; i < y; ++i) { os << ' '; } } void String_Pic::display(ostream& os, int row, int width) const { int start = 0; if (row >= 0 && row < height()) { os << data[row]; start = strlen(data[row]); } pad(os, start, width); } // 边框图像 class Frame_Pic : public P_Node { private: Picture p; private: Frame_Pic(const Picture&); int height() const; int width() const; void display(ostream&, int, int) const; // 该友元函数对该类进行一次封装 friend Picture frame(const Picture&); friend class Picture; }; Frame_Pic::Frame_Pic(const Picture& pic) : p(pic) {} int Frame_Pic::height() const { return p.height() + 2; } int Frame_Pic::width() const { return p.width() + 2; } void Frame_Pic::display(ostream& os, int row, int wd) const { if (row < 0 || row >= height()) { // 越界 pad(os, 0, wd); } else { if (row == 0 || row == height() - 1) // 上边或下边 { os << '+'; int i = p.width(); while (--i >= 0) { os << '-'; } os << '+'; } else // 中间行 { os << '|'; p.display(os, row - 1, p.width()); os << '|'; } // 打印width()到wd之间的空格 // wd是入参 pad(os, width(), wd); } } // 纵向拼接 class VCat_Pic : public P_Node { private: Picture top; Picture bottom; private: VCat_Pic(const Picture&, const Picture&); int height() const; int width() const; void display(ostream&, int, int) const; // 该友元函数对该类进行封装 friend Picture operator & (const Picture&, const Picture&); friend class Picture; }; VCat_Pic::VCat_Pic(const Picture& t, const Picture& b) : top(t), bottom(b) {} int VCat_Pic::height() const { return top.height() + bottom.height(); } int VCat_Pic::width() const { return max(top.width(), bottom.width()); } void VCat_Pic::display(ostream& os, int row, int wd) const { if (row >= 0 && row < top.height()) // 打印上部分 { top.display(os, row, wd); } else if (row < top.height() + bottom.height() && row >= top.height()) // 打印下部分 { bottom.display(os, row - top.height(), wd); } else { pad(os, 0, wd); } } // 横向拼接 class HCat_Pic : public P_Node { private: Picture left; Picture right; private: HCat_Pic(const Picture&, const Picture&); int height() const; int width() const; void display(ostream&, int, int) const; // 该友元函数对该类进行封装 friend Picture operator | (const Picture&, const Picture&); friend class Picture; }; HCat_Pic::HCat_Pic(const Picture& l, const Picture& r) : left(l), right(r) {} int HCat_Pic::height() const { return max(left.height(), right.height()); } int HCat_Pic::width() const { return left.width() + right.width(); } // 打印横向拼接 void HCat_Pic::display(ostream& os, int row, int wd) const { left.display(os, row, left.width()); right.display(os, row, right.width()); pad(os, width(), wd); } // 定义Picture的成员函数,需要在P_Node等类定义之后,因为用到起内部成员use等 Picture::Picture(const Picture& orig) : p(orig.p) { ++orig.p->use; } Picture::~Picture() { if (--p->use == 0) { delete p; } } Picture& Picture::operator = (const Picture& orig) { // 先拷贝再删除 ++orig.p->use; if (--p->use == 0) { delete p; } p = orig.p; return *this; } // 构造字符图像 Picture::Picture(const char* const* str, int n) : p(new String_Pic(str, n)) {} // 用于隐式类型转换 Picture::Picture(P_Node* p_node) : p(p_node) {} // 定义Picture的几个私有成员函数 int Picture::height() const { return p->height(); } int Picture::width() const { return p->width(); } void Picture::display(ostream& o, int x, int y) const { p->display(o, x, y); } // 加边框函数 // 实质是对Frame_Pic类进行封装一下 // 该函数的逻辑流程是: // 入参为Picture对象,通过该对象生成一个Frame_Pic对象 // 得到Frame_Pic对象的地址,然后由该地址隐式转换为Picture对象 // 所以流程为:Picture->Frame_Pic->Frame_Pic*->Picture Picture frame(const Picture& pic) { return new Frame_Pic(pic); } // 纵向拼接 Picture operator & (const Picture& t, const Picture& b) { return new VCat_Pic(t, b); } // 横向拼接 Picture operator | (const Picture& l, const Picture& r) { return new HCat_Pic(l, r); } // 输出 // 按行打印,按行打印可以很好的处理拼接打印 ostream& operator << (ostream& os, const Picture& picture) { int ht = picture.height(); int wt = picture.width(); for (int i = 0; i < ht;++i) { picture.display(os, i, wt); os << endl; } return os; } int main() { char* init[] = {"Paris", "in the", "Spring"}; Picture p1(init, 3); cout << p1 << endl; Picture p2 = frame(p1); cout << p2 << endl; Picture p3 = p1 & p2; Picture p4 = p1 | p2; Picture p5 = frame(p1 & p4); cout << p3 << endl; cout << p4 << endl; cout << p5 << endl; return 0; }
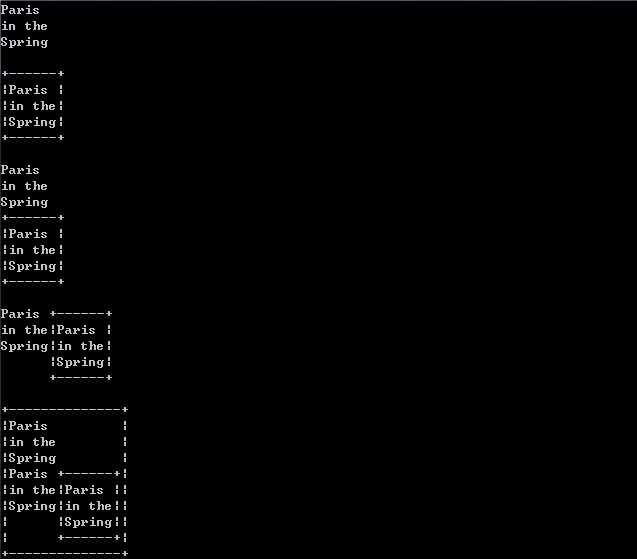
对边框进行修改
上面的边框我们采用的是+、|、-等字符。下面我们根据用户自定义的字符随意的更改。
详见代码和注释。
// 对边框进行修改 #include <iostream> using namespace std; // 前置声明,因为Picture中需要定义P_Node*指针 class P_Node; // 定义句柄类(代理) class Picture { private: P_Node* p; public: Picture(); Picture(const char* const*, int); Picture(const Picture&); ~Picture(); Picture& operator = (const Picture&); // 增加一构造函数,用于由P_Node*到Picture的隐式类型转换 Picture(P_Node*); private: int height() const; int width() const; void display(ostream&, int, int) const; // 输出 // 友元 friend ostream& operator << (ostream&, const Picture&); // 边框函数 friend Picture frame(const Picture&); // 更改边框 friend Picture reframe(const Picture&, char, char, char); // 纵向拼接 friend Picture operator & (const Picture&, const Picture&); // 横向拼接 friend Picture operator | (const Picture&, const Picture&); // 友元类 friend class String_Pic; friend class Frame_Pic; friend class HCat_Pic; friend class VCat_Pic; }; // 定义实际图像抽象基类 class P_Node { private: protected: // 原来为private,由于派生类String_Pic的reframe成员函数需要修改use,所以更改访问权限 int use; // 引用计数,用来记录实际被代理个数 protected: P_Node(); // 用来初始化引用计数 // 由于Picture析构函数中用到了delete,所以这里需要一个虚析构函数 virtual ~P_Node(); virtual int height() const = 0; virtual int width() const = 0; virtual void display(ostream&, int, int) const = 0; protected: // 求较大的数 int max(int, int) const; virtual Picture reframe(char, char, char) = 0; // 全局reframe函数 friend Picture reframe(const Picture&, char, char, char); // 友元 friend class Picture; }; P_Node::P_Node() : use(1) {} P_Node::~P_Node() {} int P_Node::max(int x, int y) const { return x > y ? x : y; } // 字符图像 class String_Pic : public P_Node { private: char** data; int size; private: String_Pic(const char* const*, int); ~String_Pic(); int height() const; int width() const; void display(ostream&, int, int) const; protected: Picture reframe(char, char, char); friend Picture reframe(const Picture&, char, char, char); friend class Picture; }; String_Pic::String_Pic(const char* const* p, int n) : data(new char*[n]), size(n) { for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { data[i] = new char[strlen(p[i]) + 1]; strcpy(data[i], p[i]); } } String_Pic::~String_Pic() { for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { delete [] data[i]; } delete [] data; } int String_Pic::height() const { return size; } int String_Pic::width() const { int n = 0; for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { n = max(n, strlen(data[i])); } return n; } static void pad(ostream& os, int x, int y) { for (int i = x; i < y; ++i) { os << ' '; } } void String_Pic::display(ostream& os, int row, int width) const { int start = 0; if (row >= 0 && row < height()) { os << data[row]; start = strlen(data[row]); } pad(os, start, width); } // String_Pic的reframe函数 Picture String_Pic::reframe(char, char, char) { ++use; // 这里没有new一个新的对象,还是代理原来的对象,所以需要自加use return this; // 隐式类型转换 } // 边框图像 class Frame_Pic : public P_Node { private: Picture p; char corner; char sideborder; char topborder; private: Frame_Pic(const Picture&, char = '+', char = '|', char = '-'); int height() const; int width() const; void display(ostream&, int, int) const; protected: Picture reframe(char, char, char); friend Picture reframe(const Picture&, char, char, char); // 该友元函数对该类进行一次封装 friend Picture frame(const Picture&); friend class Picture; }; Frame_Pic::Frame_Pic(const Picture& pic, char c, char s, char t) : p(pic), corner(c), sideborder(s), topborder(t) {} int Frame_Pic::height() const { return p.height() + 2; } int Frame_Pic::width() const { return p.width() + 2; } // 修改display函数,将+、|、-改为corner、sideborder、topborder void Frame_Pic::display(ostream& os, int row, int wd) const { if (row < 0 || row >= height()) { // 越界 pad(os, 0, wd); } else { if (row == 0 || row == height() - 1) // 上边或下边 { os << corner; int i = p.width(); while (--i >= 0) { os << topborder; } os << corner; } else // 中间行 { os << sideborder; p.display(os, row - 1, p.width()); os << sideborder; } // 打印width()到wd之间的空格 // wd是入参 pad(os, width(), wd); } } Picture Frame_Pic::reframe(char c, char s, char t) { return new Frame_Pic(::reframe(p, c, s, t), c, s, t); } // 纵向拼接 class VCat_Pic : public P_Node { private: Picture top; Picture bottom; private: VCat_Pic(const Picture&, const Picture&); int height() const; int width() const; void display(ostream&, int, int) const; protected: Picture reframe(char, char, char); friend Picture reframe(const Picture&, char, char, char); // 该友元函数对该类进行封装 friend Picture operator & (const Picture&, const Picture&); friend class Picture; }; VCat_Pic::VCat_Pic(const Picture& t, const Picture& b) : top(t), bottom(b) {} int VCat_Pic::height() const { return top.height() + bottom.height(); } int VCat_Pic::width() const { return max(top.width(), bottom.width()); } void VCat_Pic::display(ostream& os, int row, int wd) const { if (row >= 0 && row < top.height()) // 打印上部分 { top.display(os, row, wd); } else if (row < top.height() + bottom.height() && row >= top.height()) // 打印下部分 { bottom.display(os, row - top.height(), wd); } else { pad(os, 0, wd); } } Picture VCat_Pic::reframe(char c, char s, char t) { // 调用全局reframe函数 return new VCat_Pic(::reframe(top, c, s, t), ::reframe(bottom, c, s, t)); } // 横向拼接 class HCat_Pic : public P_Node { private: Picture left; Picture right; private: HCat_Pic(const Picture&, const Picture&); int height() const; int width() const; void display(ostream&, int, int) const; protected: Picture reframe(char, char, char); friend Picture reframe(const Picture&, char, char, char); // 该友元函数对该类进行封装 friend Picture operator | (const Picture&, const Picture&); friend class Picture; }; HCat_Pic::HCat_Pic(const Picture& l, const Picture& r) : left(l), right(r) {} int HCat_Pic::height() const { return max(left.height(), right.height()); } int HCat_Pic::width() const { return left.width() + right.width(); } // 打印横向拼接 void HCat_Pic::display(ostream& os, int row, int wd) const { left.display(os, row, left.width()); right.display(os, row, right.width()); pad(os, width(), wd); } Picture HCat_Pic::reframe(char c, char s, char t) { return new HCat_Pic(::reframe(left, c, s, t), ::reframe(right, c, s, t)); } // 定义Picture的成员函数,需要在P_Node等类定义之后,因为用到起内部成员use等 Picture::Picture(const Picture& orig) : p(orig.p) { ++orig.p->use; } Picture::~Picture() { if (--p->use == 0) { delete p; } } Picture& Picture::operator = (const Picture& orig) { // 先拷贝再删除 ++orig.p->use; if (--p->use == 0) { delete p; } p = orig.p; return *this; } // 构造字符图像 Picture::Picture(const char* const* str, int n) : p(new String_Pic(str, n)) {} // 用于隐式类型转换 Picture::Picture(P_Node* p_node) : p(p_node) {} // 定义Picture的几个私有成员函数 int Picture::height() const { return p->height(); } int Picture::width() const { return p->width(); } void Picture::display(ostream& o, int x, int y) const { p->display(o, x, y); } // 加边框函数 // 实质是对Frame_Pic类进行封装一下 // 该函数的逻辑流程是: // 入参为Picture对象,通过该对象生成一个Frame_Pic对象 // 得到Frame_Pic对象的地址,然后由该地址隐式转换为Picture对象 // 所以流程为:Picture->Frame_Pic->Frame_Pic*->Picture Picture frame(const Picture& pic) { return new Frame_Pic(pic); // 注意,这里返回操作是将new出来的P_Node指针隐式转换为Picture // new时,其内部的use已经置为1,不需要再对use自加 // 这里对应于P_Node的更改边框成员函数的操作: // 更改边框是直接return this,并没有new一个新对象,所以需要对其内部use自加 } // 更改边框,全局函数 Picture reframe(const Picture& pic, char c, char s, char t) { return pic.p->reframe(c, s, t); } // 纵向拼接 Picture operator & (const Picture& t, const Picture& b) { return new VCat_Pic(t, b); } // 横向拼接 Picture operator | (const Picture& l, const Picture& r) { return new HCat_Pic(l, r); } // 输出 // 按行打印,按行打印可以很好的处理拼接打印 ostream& operator << (ostream& os, const Picture& picture) { int ht = picture.height(); int wt = picture.width(); for (int i = 0; i < ht;++i) { picture.display(os, i, wt); os << endl; } return os; } int main() { char* init[] = {"Paris", "in the", "Spring"}; Picture p1(init, 3); cout << p1 << endl; Picture p2 = frame(p1); cout << p2 << endl; Picture p3 = p1 & p2; Picture p4 = p1 | p2; Picture p5 = frame(p1 & p4); cout << p3 << endl; cout << p4 << endl; cout << p5 << endl; Picture p6 = reframe(p5, '*', '*', '*'); cout << p6 << endl; return 0; }
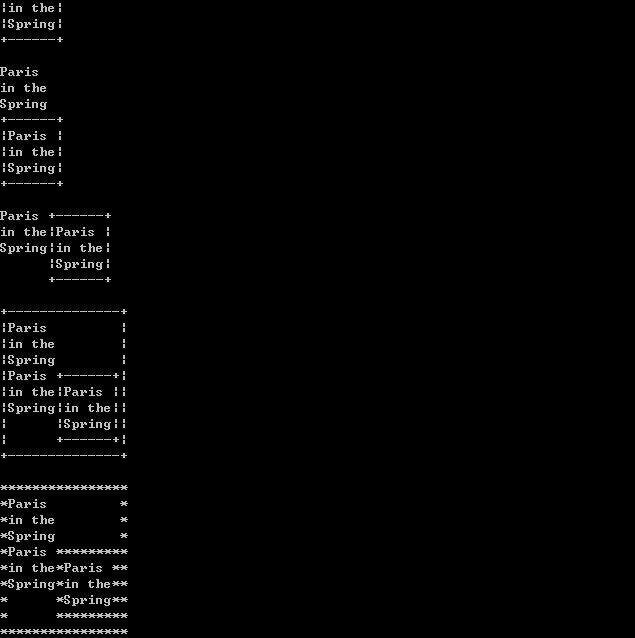
更改边框添加的操作有:
增加全局函数:reframe,该函数用于调用Picture对象中的P_Node指针指向的对象中的reframe成员函数。
在P_Node继承层次中添加reframe成员函数,实现P_Node的几个派生类的reframe成员函数。
修改Frame_Pic类的定义,几个表示边框的成员
修改Frame_Pic的display成员函数。
全局函数reframe和类成员函数reframe调用关系其实是一个递归操作,终止条件时String_Pic的reframe函数,Frame_Pic、VCat_Pic、HCat_Pic都会递归下去。
其他扩展
之前的《字符图像》中,我们进行了几个扩展:去边框、靠右拼接、靠下拼接等。同样我们可以在此基础上进行这几个扩展。
去边框:设置一个标示量,用于记录边框的个数。对于Frame_Pic函数来说,直接返回其成员p,并需要对use自加,表示被代理个数增加1。
靠右拼接,需要先打印左边的空格,然后再打印真正的图像字符行。为了先打印左边的空格,可以修改display函数,添加一个参数,用于表示每行先打印的空格数。对于靠右拼接(纵向拼接)时,对于宽度小的图像,每行先打印空格,之后再打印本行。这样不影响其他三种拼接,因为对于其他三种拼接,我们只需将display的打印空格参数置为0即可。
靠下拼接,row参数的实参值为row-(max-width)即可。
(完)
文档信息
·版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名 | Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 3.0
·博客地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/unixfy
·博客作者:unixfy
·作者邮箱:goonyangxiaofang(AT)163.com
·如果你觉得本博文的内容对你有价值,欢迎对博主 小额赞助支持



