在做MVVM各种框架对比之前,我觉得有必要先自己做一个简单的MVVM实现案例比较好,这样就可以看到自己实现的时候有那些不方便的地方。而各种框架又是怎么解决我们这些麻烦的。
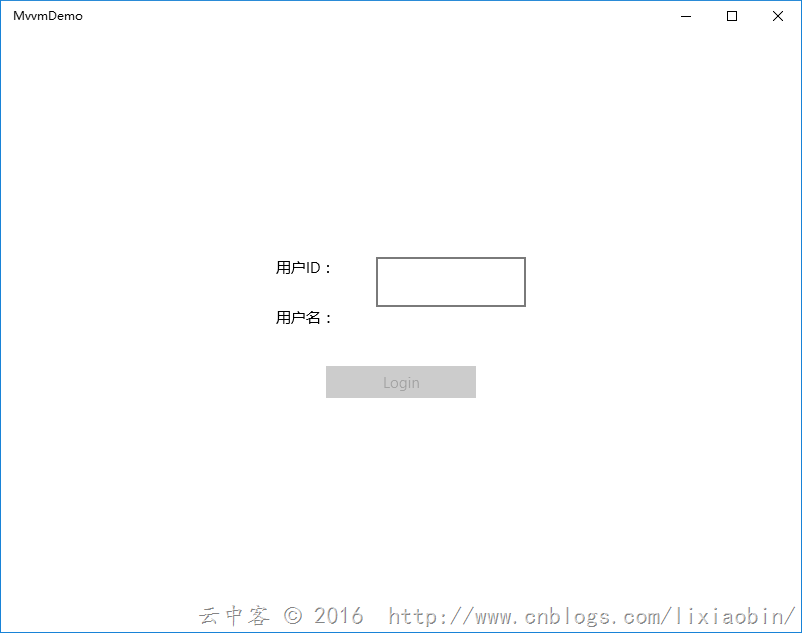
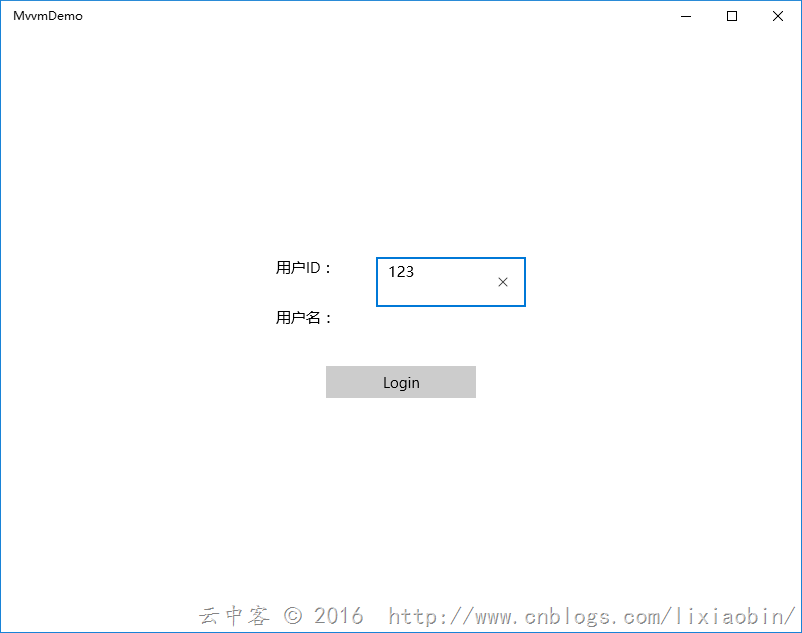
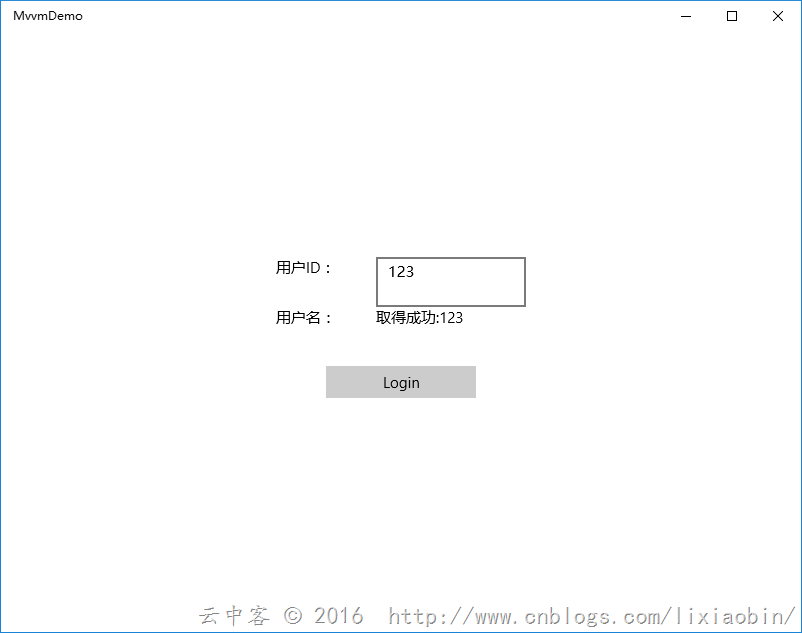
案例介绍:用户登录画面,没有输入用户ID数据时按钮不可用,输入用户ID数据后按钮可以使用。点击按钮获取用户名信息。
案例下载:https://github.com/NewBLife/UWP/tree/master/MvvmDemo
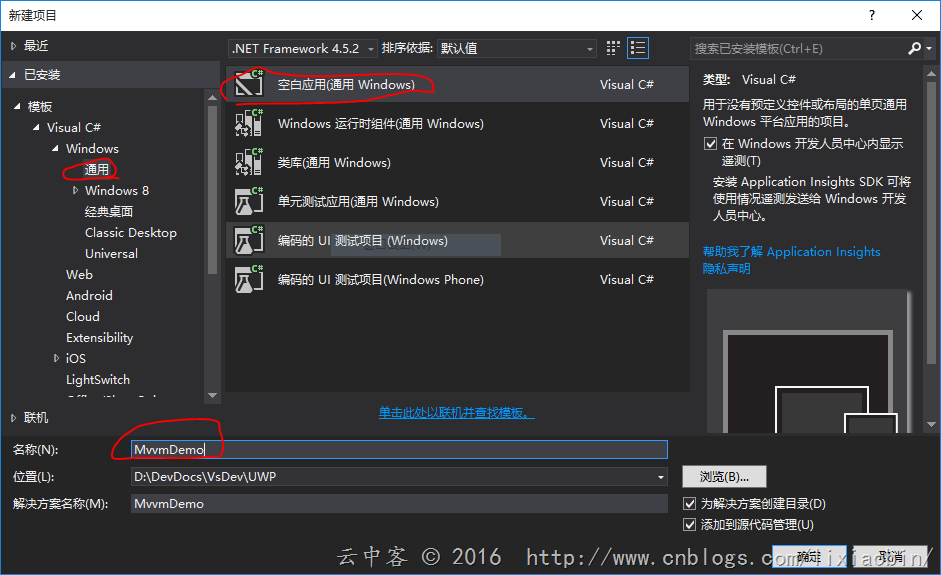
1、创建UWP空项目
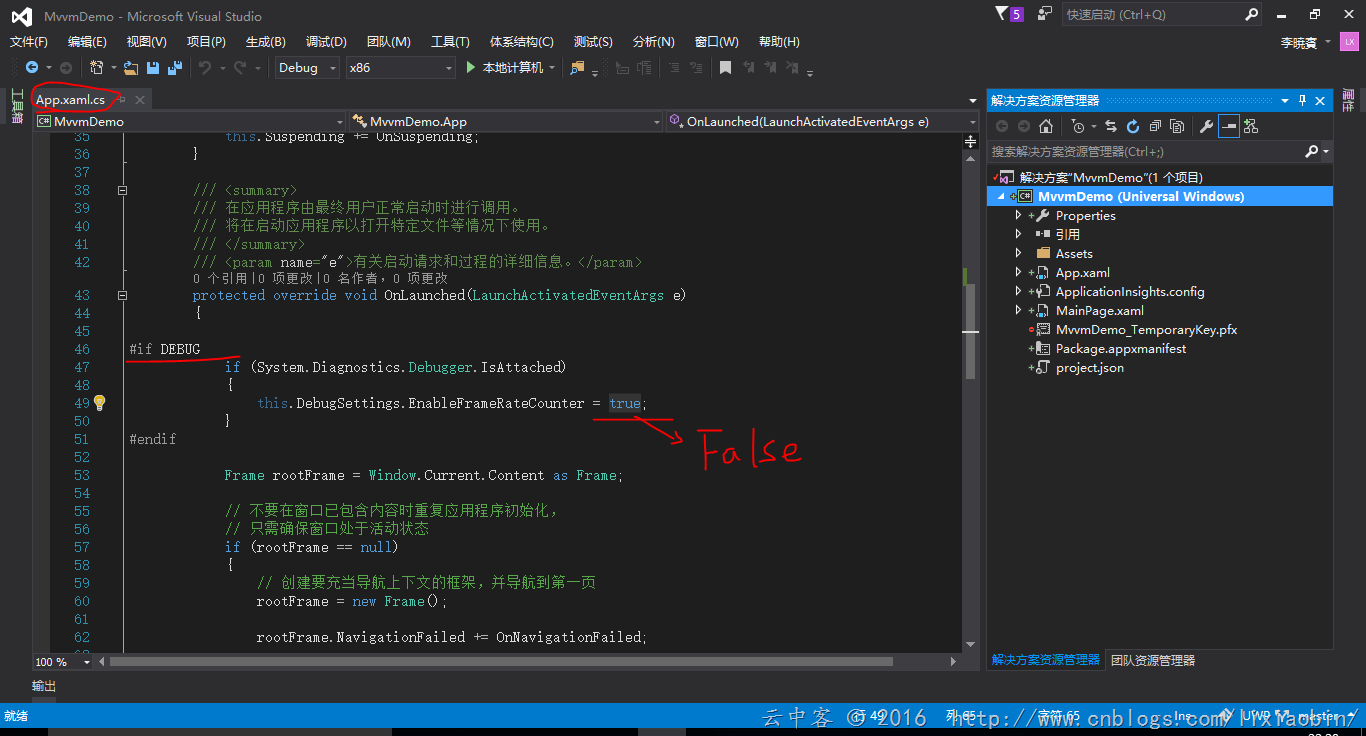
将False改成True,这应该都懂的
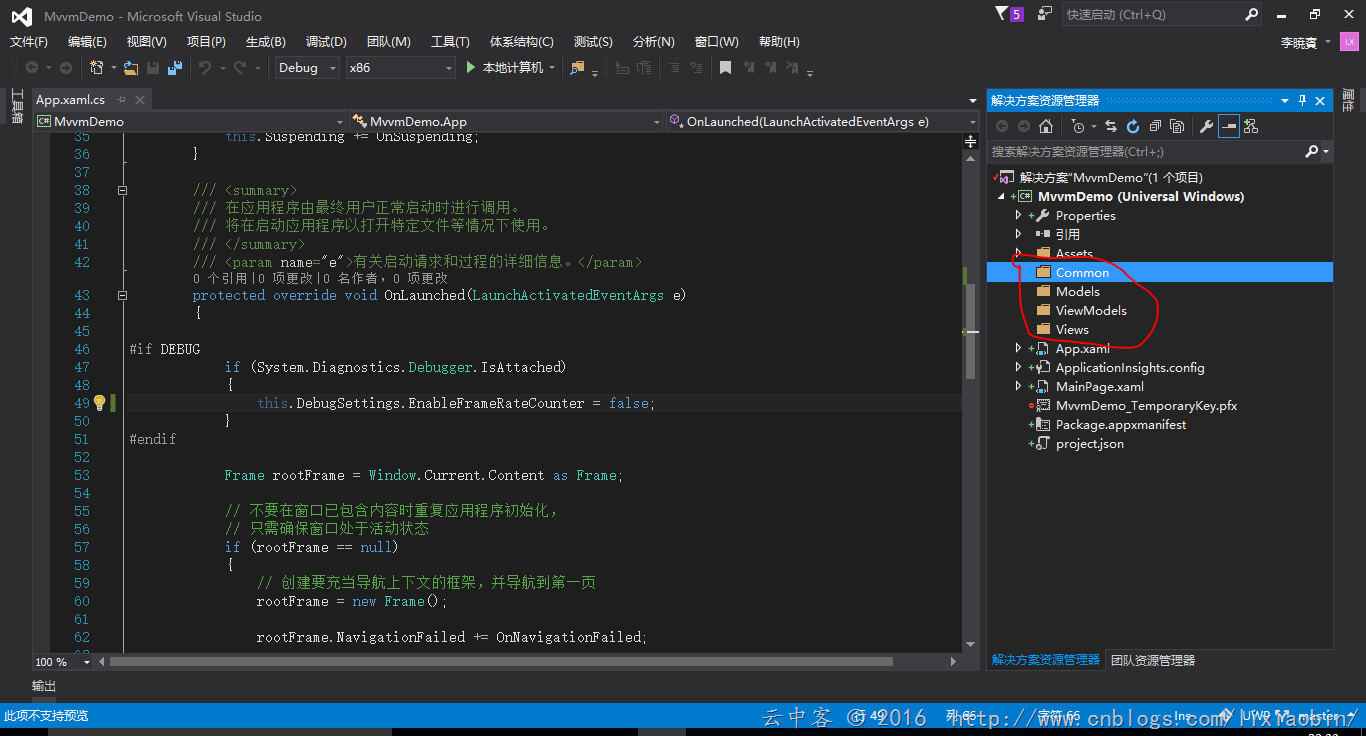
2、构建项目结构
按照MVVM模式思想,一般都会包含Views,ViewModels,Models,如果项目比较复杂在ViewModel和Model之间还会有Service层。
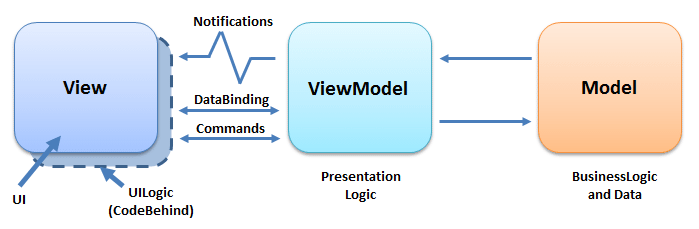
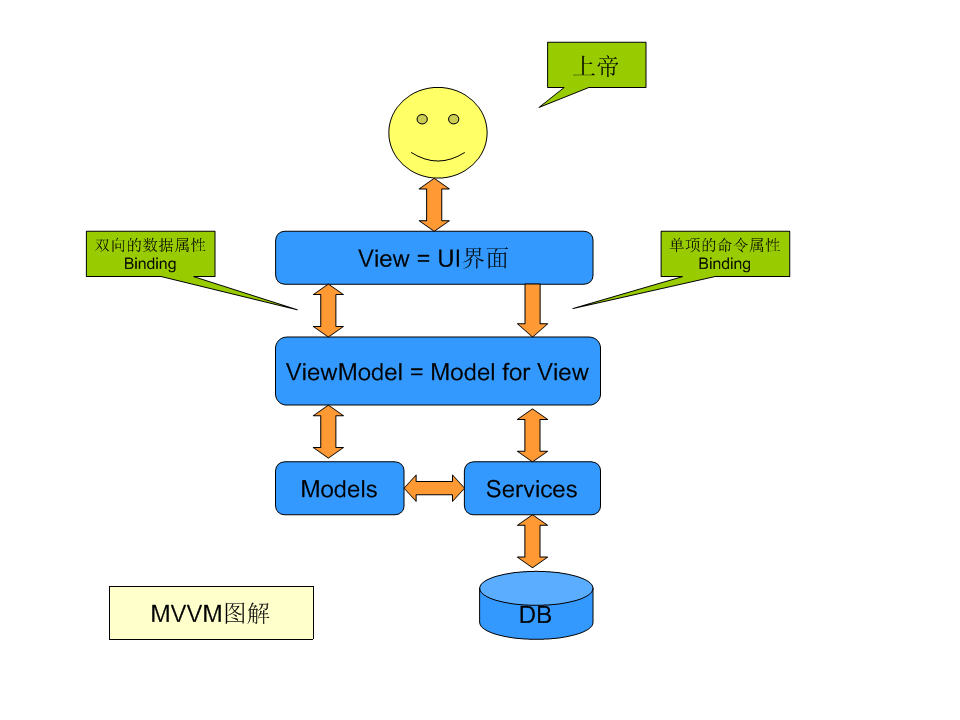
复杂系统情况:
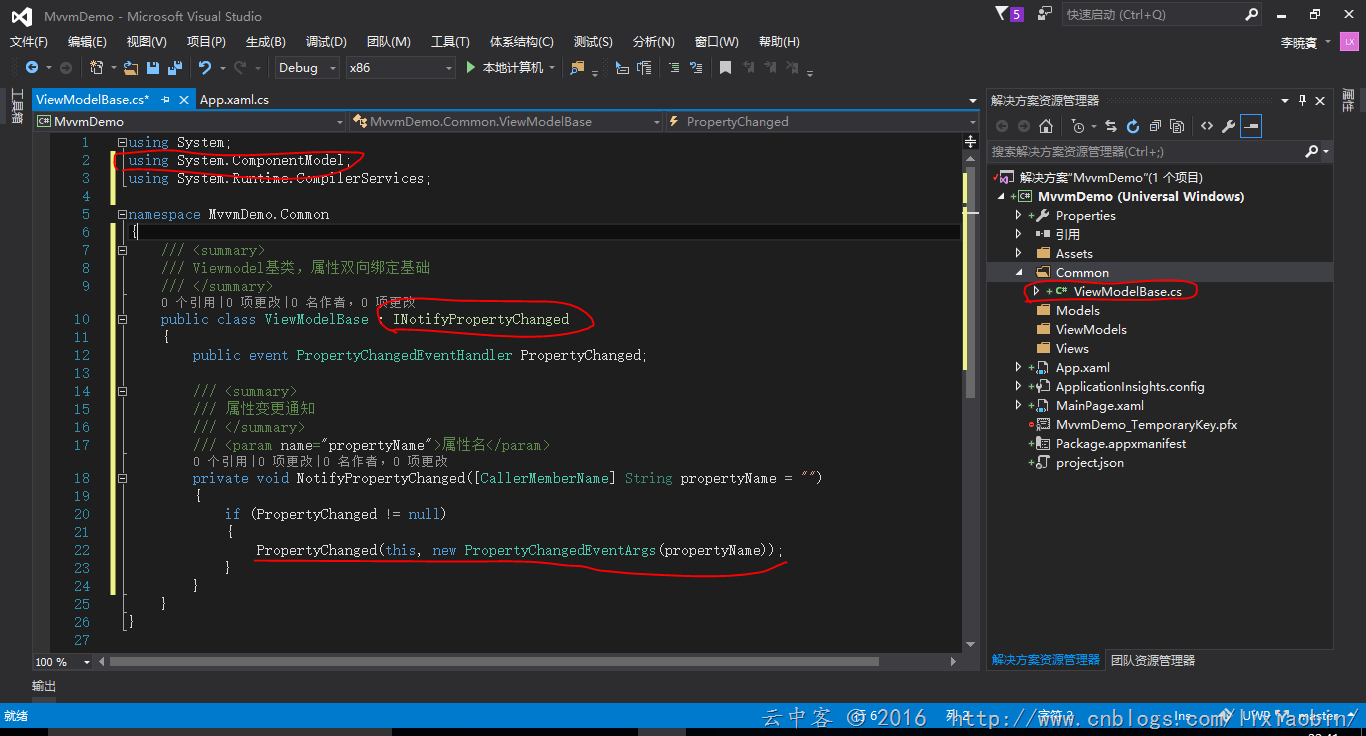
3、创建Binding基类
MVVM核心技能之一:绑定。如果是单向显示数据的话直接使用类属性就可以,如果想交互双向绑定的实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口。其中的PropertyChanged事件会通知UI改变绑定值状态。
代码如下:
using System; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Runtime.CompilerServices; namespace MvvmDemo.Common { /// <summary> /// Viewmodel基类,属性双向绑定基础 /// </summary> public class ViewModelBase : INotifyPropertyChanged { public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; /// <summary> /// 属性变更通知 /// </summary> /// <param name="propertyName">属性名</param> public void NotifyPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] String propertyName = "") { if (PropertyChanged != null) { PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName)); } } } }
4、创建Command基类
MVVM核心技能二:ICommand。这个的存在使我们的UI逻辑可以搬迁到其他地方处理,给自动化单体测试与分工设计带来了可能。按钮的Click事件,Combox选择,列表选择等等都可以使用Command形式绑定到ViewModel的Command属性做处理。
代码如下:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Input; namespace MvvmDemo.Common { public class DelegateCommand<T>: ICommand { /// <summary> /// 命令 /// </summary> private Action<T> _Command; /// <summary> /// 命令可否执行判断 /// </summary> private Func<T, bool> _CanExecute; /// <summary> /// 可执行判断结束后通知命令执行 /// </summary> public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged; /// <summary> /// 构造函数 /// </summary> /// <param name="command">命令</param> public DelegateCommand(Action<T> command):this(command,null) { } /// <summary> /// 构造函数 /// </summary> /// <param name="command">命令</param> /// <param name="canexecute">命令可执行判断</param> public DelegateCommand(Action<T> command,Func<T,bool> canexecute) { if(command==null) { throw new ArgumentException("command"); } _Command = command; _CanExecute = canexecute; } /// <summary> /// 命令执行判断 /// </summary> /// <param name="parameter">判断数据</param> /// <returns>判定结果(True:可执行,False:不可执行)</returns> public bool CanExecute(object parameter) { return _CanExecute == null ? true : _CanExecute((T)parameter); } /// <summary> /// 执行命令 /// </summary> /// <param name="parameter">参数</param> public void Execute(object parameter) { _Command((T)parameter); } } }
5、创建ViewModel
脱离UI的数据处理中心。让我们可以单独编写它的测试程序来完成UI测试。主要目的就是将DB数据整合为用户想看的数据。
代码如下:
using MvvmDemo.Common; using MvvmDemo.Models; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MvvmDemo.ViewModels { public class MainViewModel : ViewModelBase { private string _userId; private string _userName; private DelegateCommand<string> _loginCommand; /// <summary> /// 用户名 /// </summary> public string UserId { get { return _userId; } set { _userId = value; NotifyPropertyChanged(); } } /// <summary> /// 用户名 /// </summary> public string UserName { get { return _userName; } set { _userName = value; NotifyPropertyChanged(); } } /// <summary> /// 登陆命令 /// </summary> public DelegateCommand<string> LoginCommand { get { return _loginCommand ??(_loginCommand=new DelegateCommand<string>( s=> { UserName = new UserModel().GetUserName(s); }, s=>!string.IsNullOrEmpty(s) )); } } } }
6、创建View设置绑定
绑定6.0后有X:Bind,之前有Binding。x:Bind是编译时确定绑定对象,Binding是实行时确定绑定对象。总得来说X:Bind的速度比Binding快,在程序运行前就能发现绑定错误的问题。
这里直接就拿MainView做例子,更改下布局
<Page x:Class="MvvmDemo.MainPage" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:local="using:MvvmDemo" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" mc:Ignorable="d"> <Grid Background="{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Center"> <Grid.RowDefinitions> <RowDefinition Height="50"/> <RowDefinition Height="50"/> <RowDefinition Height="50"/> </Grid.RowDefinitions> <Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" /> <ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" /> </Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <TextBlock Text="用户ID:" Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" Width="100" /> <TextBlock Text="用户名:" Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" Width="100" /> <TextBox x:Name="txtUserID" Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="1" Width="150" Text="{x:Bind VM.UserId,Mode=OneWay}" /> <TextBlock x:Name="txbUserName" Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1" Width="150" Text="{x:Bind VM.UserName,Mode=OneWay}" /> <Button x:Name="btnLogin" Content="Login" Grid.Row="2" Grid.ColumnSpan="2" Width="150" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Command="{x:Bind VM.LoginCommand,Mode=OneWay}" CommandParameter="{Binding Text,ElementName=txtUserID,Mode=OneWay}"/> </Grid> </Page>
后台添加代码
/// <summary> /// 可用于自身或导航至 Frame 内部的空白页。 /// </summary> public sealed partial class MainPage : Page { public MainViewModel VM =>new MainViewModel(); public MainPage() { this.InitializeComponent(); this.DataContext = VM; } }
7、创建Model
由于这里没有复杂逻辑,就不添加Service了。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MvvmDemo.Models { public class UserModel { public string GetUserName(string userid) { return string.Format("取得成功:{0}",userid); } } }
8、实行结果
输入内容前按钮自动不可用:
输入内容后按钮自动可用:
点击Login按钮:
9、总结
这种就是简单的登陆实现,涉及到了MVVM的View,Viewmodel,Model,以及XBind的用法。6.0后有X:Bind,之前有Binding。x:Bind是编译时确定绑定对象,Binding是实行时确定绑定对象。总得来说X:Bind的速度比Binding快,在程序运行前就能发现绑定错误的问题。登陆页面的按钮是随着输入自动判断是否可用,这个就是Icommand一个方法Canexcute的作用。可见自己实现Mvvm模式也不是很难的事情,不过随着项目的复杂加深就会有很多问题,比如Viewmode之间通信等,这个时候才是MVVM框架的优势所在。