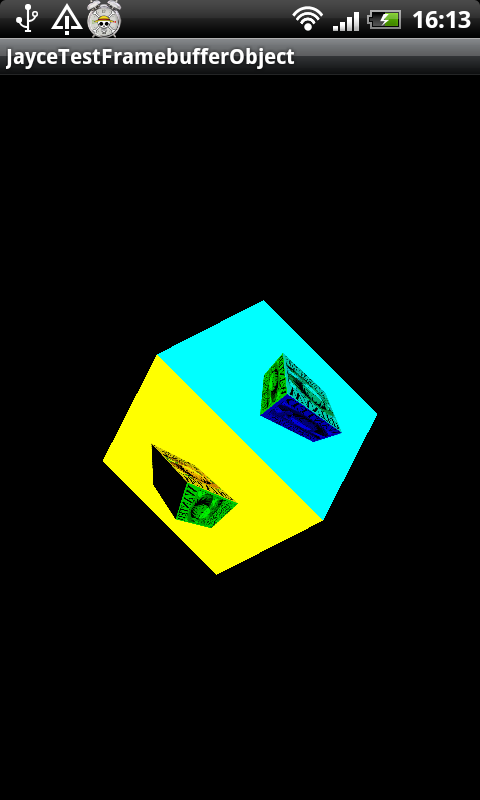
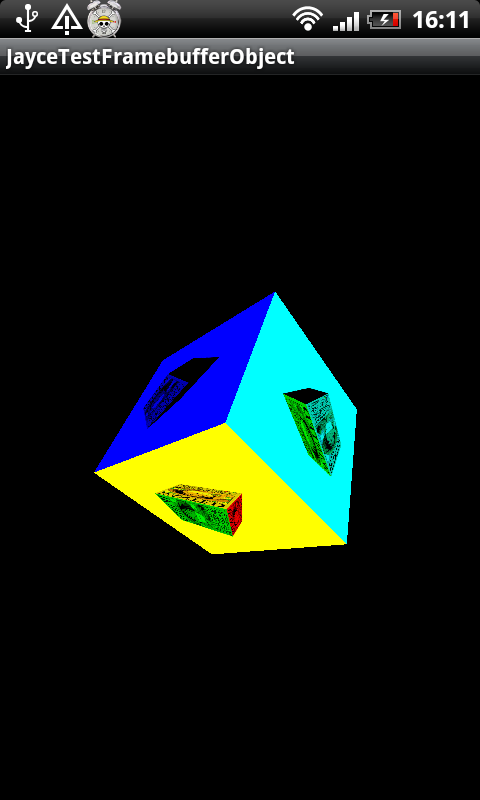
Android平台上简单的FramebufferObject示例。
FramebufferObject的概念就不说了,参考OpenGL ES 2.0 Programming Guide的第10章。
下面是render framebuffer到texture的例子。
代码的主要流程是:
创建framebuffer,绑定framebuffer,render framebuffer到texture,切换回system提供的framebuffer,利用之前产生的texture.
方便起见,两个render流程用的同样的shader.
下面是renderer的代码,Test7Renderer.java
1 package com.android.jayce.test; 2 3 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 4 import java.nio.ByteOrder; 5 import java.nio.FloatBuffer; 6 import java.nio.IntBuffer; 7 8 import javax.microedition.khronos.egl.EGLConfig; 9 import javax.microedition.khronos.opengles.GL10; 10 11 import android.content.Context; 12 import android.opengl.GLES20; 13 import android.opengl.GLSurfaceView; 14 import android.opengl.Matrix; 15 import android.os.SystemClock; 16 17 import com.android.jayce.test.R; 18 19 /** 20 * This class implements our custom renderer. Note that the GL10 parameter passed in is unused for OpenGL ES 2.0 21 * renderers -- the static class GLES20 is used instead. 22 */ 23 public class Test7Renderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer 24 { 25 /** Used for debug logs. */ 26 private static final String TAG = "Test7Renderer"; 27 28 private final Context mActivityContext; 29 30 /** 31 * Store the model matrix. This matrix is used to move models from object space (where each model can be thought 32 * of being located at the center of the universe) to world space. 33 */ 34 private float[] mModelMatrix = new float[16]; 35 36 /** 37 * Store the view matrix. This can be thought of as our camera. This matrix transforms world space to eye space; 38 * it positions things relative to our eye. 39 */ 40 private float[] mViewMatrix = new float[16]; 41 42 /** Store the projection matrix. This is used to project the scene onto a 2D viewport. */ 43 private float[] mProjectionMatrix = new float[16]; 44 45 /** Allocate storage for the final combined matrix. This will be passed into the shader program. */ 46 private float[] mMVPMatrix = new float[16]; 47 48 /** Store our model data in a float buffer. */ 49 private final FloatBuffer mCubePositions; 50 private final FloatBuffer mCubeColors; 51 private final FloatBuffer mCubeTextureCoordinates; 52 53 /** This will be used to pass in the transformation matrix. */ 54 private int mMVPMatrixHandle; 55 56 /** This will be used to pass in the modelview matrix. */ 57 private int mMVMatrixHandle; 58 59 /** This will be used to pass in the texture. */ 60 private int mTextureUniformHandle; 61 62 /** This will be used to pass in model position information. */ 63 private int mPositionHandle; 64 65 /** This will be used to pass in model color information. */ 66 private int mColorHandle; 67 68 /** This will be used to pass in model texture coordinate information. */ 69 private int mTextureCoordinateHandle; 70 71 /** How many bytes per float. */ 72 private final int mBytesPerFloat = 4; 73 74 /** Size of the position data in elements. */ 75 private final int mPositionDataSize = 3; 76 77 /** Size of the color data in elements. */ 78 private final int mColorDataSize = 4; 79 80 /** Size of the texture coordinate data in elements. */ 81 private final int mTextureCoordinateDataSize = 2; 82 83 /** This is a handle to our cube shading program. */ 84 private int mProgramHandle; 85 86 /** This is a handle to our texture data. */ 87 private int mTextureDataHandle; 88 89 /** 90 * Initialize the model data. 91 */ 92 public Test7Renderer(final Context activityContext) 93 { 94 mActivityContext = activityContext; 95 96 // Define points for a cube. 97 98 // X, Y, Z 99 final float[] cubePositionData = 100 { 101 // In OpenGL counter-clockwise winding is default. This means that when we look at a triangle, 102 // if the points are counter-clockwise we are looking at the "front". If not we are looking at 103 // the back. OpenGL has an optimization where all back-facing triangles are culled, since they 104 // usually represent the backside of an object and aren't visible anyways. 105 106 // Front face 107 -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 108 -1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 109 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 110 -1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 111 1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 112 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 113 114 // Right face 115 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 116 1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 117 1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 118 1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 119 1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 120 1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 121 122 // Back face 123 1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 124 1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 125 -1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 126 1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 127 -1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 128 -1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 129 130 // Left face 131 -1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 132 -1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 133 -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 134 -1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 135 -1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 136 -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 137 138 // Top face 139 -1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 140 -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 141 1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 142 -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 143 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 144 1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 145 146 // Bottom face 147 1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 148 1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 149 -1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 150 1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 151 -1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 152 -1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 153 }; 154 155 // R, G, B, A 156 final float[] cubeColorData = 157 { 158 // Front face (red) 159 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 160 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 161 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 162 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 163 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 164 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 165 166 // Right face (green) 167 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 168 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 169 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 170 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 171 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 172 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 173 174 // Back face (blue) 175 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 176 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 177 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 178 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 179 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 180 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 181 182 // Left face (yellow) 183 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 184 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 185 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 186 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 187 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 188 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 189 190 // Top face (cyan) 191 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 192 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 193 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 194 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 195 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 196 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 197 198 // Bottom face (magenta) 199 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 200 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 201 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 202 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 203 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 204 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f 205 }; 206 207 // S, T (or X, Y) 208 // Texture coordinate data. 209 // Because images have a Y axis pointing downward (values increase as you move down the image) while 210 // OpenGL has a Y axis pointing upward, we adjust for that here by flipping the Y axis. 211 // What's more is that the texture coordinates are the same for every face. 212 final float[] cubeTextureCoordinateData = 213 { 214 // Front face 215 0.0f, 0.0f, 216 0.0f, 1.0f, 217 1.0f, 0.0f, 218 0.0f, 1.0f, 219 1.0f, 1.0f, 220 1.0f, 0.0f, 221 222 // Right face 223 0.0f, 0.0f, 224 0.0f, 1.0f, 225 1.0f, 0.0f, 226 0.0f, 1.0f, 227 1.0f, 1.0f, 228 1.0f, 0.0f, 229 230 // Back face 231 0.0f, 0.0f, 232 0.0f, 1.0f, 233 1.0f, 0.0f, 234 0.0f, 1.0f, 235 1.0f, 1.0f, 236 1.0f, 0.0f, 237 238 // Left face 239 0.0f, 0.0f, 240 0.0f, 1.0f, 241 1.0f, 0.0f, 242 0.0f, 1.0f, 243 1.0f, 1.0f, 244 1.0f, 0.0f, 245 246 // Top face 247 0.0f, 0.0f, 248 0.0f, 1.0f, 249 1.0f, 0.0f, 250 0.0f, 1.0f, 251 1.0f, 1.0f, 252 1.0f, 0.0f, 253 254 // Bottom face 255 0.0f, 0.0f, 256 0.0f, 1.0f, 257 1.0f, 0.0f, 258 0.0f, 1.0f, 259 1.0f, 1.0f, 260 1.0f, 0.0f 261 }; 262 263 // Initialize the buffers. 264 mCubePositions = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(cubePositionData.length * mBytesPerFloat) 265 .order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()).asFloatBuffer(); 266 mCubePositions.put(cubePositionData).position(0); 267 268 mCubeColors = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(cubeColorData.length * mBytesPerFloat) 269 .order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()).asFloatBuffer(); 270 mCubeColors.put(cubeColorData).position(0); 271 272 mCubeTextureCoordinates = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(cubeTextureCoordinateData.length * mBytesPerFloat) 273 .order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()).asFloatBuffer(); 274 mCubeTextureCoordinates.put(cubeTextureCoordinateData).position(0); 275 } 276 277 protected String getVertexShader(int shader) 278 { 279 return ToolsUtil.readTextFileFromRawResource(mActivityContext, shader); 280 } 281 282 protected String getFragmentShader(int shader) 283 { 284 return ToolsUtil.readTextFileFromRawResource(mActivityContext, shader); 285 } 286 287 @Override 288 public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 glUnused, EGLConfig config) 289 { 290 // Set the background clear color to black. 291 GLES20.glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); 292 293 // Use culling to remove back faces. 294 GLES20.glEnable(GLES20.GL_CULL_FACE); 295 296 // Enable depth testing 297 GLES20.glEnable(GLES20.GL_DEPTH_TEST); 298 299 // The below glEnable() call is a holdover from OpenGL ES 1, and is not needed in OpenGL ES 2. 300 // Enable texture mapping 301 GLES20.glEnable(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D); 302 303 // Position the eye in front of the origin. 304 final float eyeX = 0.0f; 305 final float eyeY = 0.0f; 306 final float eyeZ = -0.5f; 307 308 // We are looking toward the distance 309 final float lookX = 0.0f; 310 final float lookY = 0.0f; 311 final float lookZ = -5.0f; 312 313 // Set our up vector. This is where our head would be pointing were we holding the camera. 314 final float upX = 0.0f; 315 final float upY = 1.0f; 316 final float upZ = 0.0f; 317 318 // Set the view matrix. This matrix can be said to represent the camera position. 319 // NOTE: In OpenGL 1, a ModelView matrix is used, which is a combination of a model and 320 // view matrix. In OpenGL 2, we can keep track of these matrices separately if we choose. 321 Matrix.setLookAtM(mViewMatrix, 0, eyeX, eyeY, eyeZ, lookX, lookY, lookZ, upX, upY, upZ); 322 323 final String vertexShader = getVertexShader(R.raw.per_pixel_vertex_shader); 324 final String fragmentShader = getFragmentShader(R.raw.per_pixel_fragment_shader); 325 326 final int vertexShaderHandle = ToolsUtil.compileShader(GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER, vertexShader); 327 final int fragmentShaderHandle = ToolsUtil.compileShader(GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, fragmentShader); 328 329 mProgramHandle = ToolsUtil.createAndLinkProgram(vertexShaderHandle, fragmentShaderHandle, 330 new String[] {"a_Position", "a_Color", "a_TexCoordinate"}); 331 332 // Load the texture 333 mTextureDataHandle = ToolsUtil.loadTexture(mActivityContext, R.drawable.aaa); 334 } 335 336 @Override 337 public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 glUnused, int width, int height) 338 { 339 // Set the OpenGL viewport to the same size as the surface. 340 GLES20.glViewport(0, 0, width, height); 341 342 // Create a new perspective projection matrix. The height will stay the same 343 // while the width will vary as per aspect ratio. 344 final float ratio = (float) width / height; 345 final float left = -ratio; 346 final float right = ratio; 347 final float bottom = -1.0f; 348 final float top = 1.0f; 349 final float near = 1.0f; 350 final float far = 10.0f; 351 352 Matrix.frustumM(mProjectionMatrix, 0, left, right, bottom, top, near, far); 353 } 354 355 @Override 356 public void onDrawFrame(GL10 glUnused) 357 { 358 IntBuffer framebuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(1); 359 IntBuffer depthRenderbuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(1); 360 IntBuffer texture = IntBuffer.allocate(1); 361 int texWidth = 480, texHeight = 480; 362 IntBuffer maxRenderbufferSize = IntBuffer.allocate(1); 363 GLES20.glGetIntegerv(GLES20.GL_MAX_RENDERBUFFER_SIZE, maxRenderbufferSize); 364 // check if GL_MAX_RENDERBUFFER_SIZE is >= texWidth and texHeight 365 if((maxRenderbufferSize.get(0) <= texWidth) || 366 (maxRenderbufferSize.get(0) <= texHeight)) 367 { 368 // cannot use framebuffer objects as we need to create 369 // a depth buffer as a renderbuffer object 370 // return with appropriate error 371 } 372 // generate the framebuffer, renderbuffer, and texture object names 373 GLES20.glGenFramebuffers(1, framebuffer); 374 GLES20.glGenRenderbuffers(1, depthRenderbuffer); 375 GLES20.glGenTextures(1, texture); 376 // bind texture and load the texture mip-level 0 377 // texels are RGB565 378 // no texels need to be specified as we are going to draw into 379 // the texture 380 GLES20.glBindTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture.get(0)); 381 GLES20.glTexImage2D(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GLES20.GL_RGB, texWidth, texHeight, 382 0, GLES20.GL_RGB, GLES20.GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT_5_6_5, null); 383 GLES20.glTexParameteri(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GLES20.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); 384 GLES20.glTexParameteri(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GLES20.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); 385 GLES20.glTexParameteri(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GLES20.GL_LINEAR); 386 GLES20.glTexParameteri(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GLES20.GL_LINEAR); 387 // bind renderbuffer and create a 16-bit depth buffer 388 // width and height of renderbuffer = width and height of 389 // the texture 390 GLES20.glBindRenderbuffer(GLES20.GL_RENDERBUFFER, depthRenderbuffer.get(0)); 391 GLES20.glRenderbufferStorage(GLES20.GL_RENDERBUFFER, GLES20.GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT16, 392 texWidth, texHeight); 393 // bind the framebuffer 394 GLES20.glBindFramebuffer(GLES20.GL_FRAMEBUFFER, framebuffer.get(0)); 395 // specify texture as color attachment 396 GLES20.glFramebufferTexture2D(GLES20.GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GLES20.GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0, 397 GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture.get(0), 0); 398 // specify depth_renderbufer as depth attachment 399 GLES20.glFramebufferRenderbuffer(GLES20.GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GLES20.GL_DEPTH_ATTACHMENT, 400 GLES20.GL_RENDERBUFFER, depthRenderbuffer.get(0)); 401 // check for framebuffer complete 402 int status = GLES20.glCheckFramebufferStatus(GLES20.GL_FRAMEBUFFER); 403 if(status == GLES20.GL_FRAMEBUFFER_COMPLETE) 404 { 405 // render to texture using FBO 406 GLES20.glClearColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f); 407 GLES20.glClear(GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GLES20.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); 408 409 // Do a complete rotation every 10 seconds. 410 long time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() % 10000L; 411 float angleInDegrees = (360.0f / 10000.0f) * (2 * (int) time); 412 413 GLES20.glUseProgram(mProgramHandle); 414 415 // Set program handles for cube drawing. 416 mMVPMatrixHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(mProgramHandle, "u_MVPMatrix"); 417 mMVMatrixHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(mProgramHandle, "u_MVMatrix"); 418 mTextureUniformHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(mProgramHandle, "u_Texture"); 419 mPositionHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgramHandle, "a_Position"); 420 mColorHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgramHandle, "a_Color"); 421 mTextureCoordinateHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgramHandle, "a_TexCoordinate"); 422 423 // Set the active texture unit to texture unit 0. 424 GLES20.glActiveTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE0); 425 426 // Bind the texture to this unit. 427 GLES20.glBindTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, mTextureDataHandle); 428 429 // Tell the texture uniform sampler to use this texture in the shader by binding to texture unit 0. 430 GLES20.glUniform1i(mTextureUniformHandle, 0); 431 432 Matrix.setIdentityM(mModelMatrix, 0); 433 Matrix.translateM(mModelMatrix, 0, 0.0f, -1.0f, -5.0f); 434 Matrix.rotateM(mModelMatrix, 0, angleInDegrees, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f); 435 drawCube(); 436 437 // render to window system provided framebuffer 438 GLES20.glBindFramebuffer(GLES20.GL_FRAMEBUFFER, 0); 439 GLES20.glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f); 440 GLES20.glClear(GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GLES20.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); 441 442 // Do a complete rotation every 10 seconds. 443 time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() % 10000L; 444 angleInDegrees = (360.0f / 10000.0f) * ((int) time); 445 446 GLES20.glUseProgram(mProgramHandle); 447 448 // Set program handles for cube drawing. 449 mMVPMatrixHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(mProgramHandle, "u_MVPMatrix"); 450 mMVMatrixHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(mProgramHandle, "u_MVMatrix"); 451 mTextureUniformHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(mProgramHandle, "u_Texture"); 452 mPositionHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgramHandle, "a_Position"); 453 mColorHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgramHandle, "a_Color"); 454 mTextureCoordinateHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgramHandle, "a_TexCoordinate"); 455 456 // Set the active texture unit to texture unit 0. 457 GLES20.glActiveTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE0); 458 459 // Bind the texture to this unit. 460 GLES20.glBindTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture.get(0)/*mTextureDataHandle*/); 461 462 // Tell the texture uniform sampler to use this texture in the shader by binding to texture unit 0. 463 GLES20.glUniform1i(mTextureUniformHandle, 0); 464 465 Matrix.setIdentityM(mModelMatrix, 0); 466 Matrix.translateM(mModelMatrix, 0, 0.0f, 0.0f, -5.0f); 467 Matrix.rotateM(mModelMatrix, 0, angleInDegrees, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f); 468 drawCube(); 469 GLES20.glBindTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0); 470 } 471 472 // cleanup 473 GLES20.glDeleteRenderbuffers(1, depthRenderbuffer); 474 GLES20.glDeleteFramebuffers(1, framebuffer); 475 GLES20.glDeleteTextures(1, texture); 476 } 477 478 /** 479 * Draws a cube. 480 */ 481 private void drawCube() 482 { 483 // Pass in the position information 484 mCubePositions.position(0); 485 GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(mPositionHandle, mPositionDataSize, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 486 0, mCubePositions); 487 488 GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(mPositionHandle); 489 490 // Pass in the color information 491 mCubeColors.position(0); 492 GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(mColorHandle, mColorDataSize, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 493 0, mCubeColors); 494 GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(mColorHandle); 495 496 // Pass in the texture coordinate information 497 mCubeTextureCoordinates.position(0); 498 GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(mTextureCoordinateHandle, mTextureCoordinateDataSize, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 499 0, mCubeTextureCoordinates); 500 501 GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(mTextureCoordinateHandle); 502 503 // This multiplies the view matrix by the model matrix, and stores the result in the MVP matrix 504 // (which currently contains model * view). 505 Matrix.multiplyMM(mMVPMatrix, 0, mViewMatrix, 0, mModelMatrix, 0); 506 507 // Pass in the modelview matrix. 508 GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(mMVMatrixHandle, 1, false, mMVPMatrix, 0); 509 510 // This multiplies the modelview matrix by the projection matrix, and stores the result in the MVP matrix 511 // (which now contains model * view * projection). 512 Matrix.multiplyMM(mMVPMatrix, 0, mProjectionMatrix, 0, mMVPMatrix, 0); 513 514 // Pass in the combined matrix. 515 GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(mMVPMatrixHandle, 1, false, mMVPMatrix, 0); 516 517 // Draw the cube. 518 GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36); 519 } 520 }
还有一个辅助类,ToolsUtil.java:
1 package com.android.jayce.test; 2 3 import android.content.Context; 4 import android.graphics.Bitmap; 5 import android.graphics.BitmapFactory; 6 import android.opengl.GLES20; 7 import android.opengl.GLUtils; 8 import android.util.Log; 9 10 import java.io.BufferedReader; 11 import java.io.IOException; 12 import java.io.InputStream; 13 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 14 15 public class ToolsUtil 16 { 17 public static int loadTexture(final Context context, final int resourceId) 18 { 19 final int[] textureHandle = new int[1]; 20 GLES20.glGenTextures(1, textureHandle, 0); 21 22 if(textureHandle[0] != 0) 23 { 24 final BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options(); 25 options.inScaled = false; 26 27 final Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(context.getResources(), resourceId, options); 28 GLES20.glBindTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureHandle[0]); 29 30 GLES20.glTexParameteri(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GLES20.GL_NEAREST); 31 GLES20.glTexParameteri(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GLES20.GL_NEAREST); 32 33 GLUtils.texImage2D(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, bitmap, 0); 34 bitmap.recycle(); 35 } 36 37 if(textureHandle[0] == 0) 38 { 39 throw new RuntimeException("failed to load texture"); 40 } 41 42 return textureHandle[0]; 43 } 44 45 /** 46 * Helper function to compile a shader. 47 * 48 * @param shaderType The shader type. 49 * @param shaderSource The shader source code. 50 * @return An OpenGL handle to the shader. 51 */ 52 public static int compileShader(final int shaderType, final String shaderSource) 53 { 54 int shaderHandle = GLES20.glCreateShader(shaderType); 55 56 if (shaderHandle != 0) 57 { 58 // Pass in the shader source. 59 GLES20.glShaderSource(shaderHandle, shaderSource); 60 61 // Compile the shader. 62 GLES20.glCompileShader(shaderHandle); 63 64 // Get the compilation status. 65 final int[] compileStatus = new int[1]; 66 GLES20.glGetShaderiv(shaderHandle, GLES20.GL_COMPILE_STATUS, compileStatus, 0); 67 68 // If the compilation failed, delete the shader. 69 if (compileStatus[0] == 0) 70 { 71 GLES20.glDeleteShader(shaderHandle); 72 shaderHandle = 0; 73 } 74 } 75 76 if (shaderHandle == 0) 77 { 78 throw new RuntimeException("Error creating shader."); 79 } 80 81 return shaderHandle; 82 } 83 84 /** 85 * Helper function to compile and link a program. 86 * 87 * @param vertexShaderHandle An OpenGL handle to an already-compiled vertex shader. 88 * @param fragmentShaderHandle An OpenGL handle to an already-compiled fragment shader. 89 * @param attributes Attributes that need to be bound to the program. 90 * @return An OpenGL handle to the program. 91 */ 92 public static int createAndLinkProgram(final int vertexShaderHandle, final int fragmentShaderHandle, final String[] attributes) 93 { 94 int programHandle = GLES20.glCreateProgram(); 95 96 if (programHandle != 0) 97 { 98 // Bind the vertex shader to the program. 99 GLES20.glAttachShader(programHandle, vertexShaderHandle); 100 101 // Bind the fragment shader to the program. 102 GLES20.glAttachShader(programHandle, fragmentShaderHandle); 103 104 // Bind attributes 105 if (attributes != null) 106 { 107 final int size = attributes.length; 108 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 109 { 110 GLES20.glBindAttribLocation(programHandle, i, attributes[i]); 111 } 112 } 113 114 // Link the two shaders together into a program. 115 GLES20.glLinkProgram(programHandle); 116 117 // Get the link status. 118 final int[] linkStatus = new int[1]; 119 GLES20.glGetProgramiv(programHandle, GLES20.GL_LINK_STATUS, linkStatus, 0); 120 121 // If the link failed, delete the program. 122 if (linkStatus[0] == 0) 123 { 124 GLES20.glDeleteProgram(programHandle); 125 programHandle = 0; 126 } 127 } 128 129 if (programHandle == 0) 130 { 131 throw new RuntimeException("Error creating program."); 132 } 133 134 return programHandle; 135 } 136 137 public static String readTextFileFromRawResource(final Context context, 138 final int resourceId) 139 { 140 final InputStream inputStream = context.getResources().openRawResource( 141 resourceId); 142 final InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader( 143 inputStream); 144 final BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader( 145 inputStreamReader); 146 147 String nextLine; 148 final StringBuilder body = new StringBuilder(); 149 150 try 151 { 152 while ((nextLine = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) 153 { 154 body.append(nextLine); 155 body.append('\n'); 156 } 157 } 158 catch (IOException e) 159 { 160 return null; 161 } 162 163 return body.toString(); 164 } 165 166 }
使用的shader, per_pixel_vertex_shader.glsl:
1 uniform mat4 u_MVPMatrix; // A constant representing the combined model/view/projection matrix. 2 uniform mat4 u_MVMatrix; // A constant representing the combined model/view matrix. 3 4 attribute vec4 a_Position; // Per-vertex position information we will pass in. 5 attribute vec4 a_Color; // Per-vertex color information we will pass in. 6 attribute vec2 a_TexCoordinate; // Per-vertex texture coordinate information we will pass in. 7 8 varying vec3 v_Position; // This will be passed into the fragment shader. 9 varying vec4 v_Color; // This will be passed into the fragment shader. 10 varying vec2 v_TexCoordinate; // This will be passed into the fragment shader. 11 12 // The entry point for our vertex shader. 13 void main() 14 { 15 // Transform the vertex into eye space. 16 v_Position = vec3(u_MVMatrix * a_Position); 17 18 // Pass through the color. 19 v_Color = a_Color; 20 21 // Pass through the texture coordinate. 22 v_TexCoordinate = a_TexCoordinate; 23 24 // gl_Position is a special variable used to store the final position. 25 // Multiply the vertex by the matrix to get the final point in normalized screen coordinates. 26 gl_Position = u_MVPMatrix * a_Position; 27 }
使用的shader, per_pixel_fragment_shader.glsl:
1 precision mediump float; // Set the default precision to medium. We don't need as high of a 2 // precision in the fragment shader. 3 uniform sampler2D u_Texture; // The input texture. 4 5 varying vec3 v_Position; // Interpolated position for this fragment. 6 varying vec4 v_Color; // This is the color from the vertex shader interpolated across the 7 varying vec2 v_TexCoordinate; // Interpolated texture coordinate per fragment. 8 9 // The entry point for our fragment shader. 10 void main() 11 { 12 // Multiply the color by the diffuse illumination level and texture value to get final output color. 13 gl_FragColor = (v_Color * texture2D(u_Texture, v_TexCoordinate)); 14 }
好了,就这么多了,可以看到旋转立方体每一面的texture都是用的自己创建的framebuffer render的texture,每面都有一个旋转的立方体。
看看效果图吧: