策略设计模式
策略设计模式定义:创建一个能够根据所传递的参数对象的不同而具有不同行为的方法,称为策略设计模式。策略就是传递进去的参数对象,它包含要执行的代码。
策略模式应用场景:
1.如果在一个系统里面有许多类,它们之间的区别仅在于它们的行为,那么使用策略模式可以动态地让一个对象在许多行为中选择一种行为。
2.一个系统需要动态地在几种算法中选择一种。
3.如果一个对象有很多的行为,如果不用恰当的模式,这些行为就只好使用多重的条件选择语句来实现(即使用 if...else)。
实现:
我们首先创建一个定义活动的 Strategy 接口和实现了 Strategy 接口的实体策略类,Context 是一个使用了某种策略的类。Main,我们的演示类使用 Context 和策略对象来演示 Context 在它所配置或使用的策略改变时的行为变化。
UML类图:
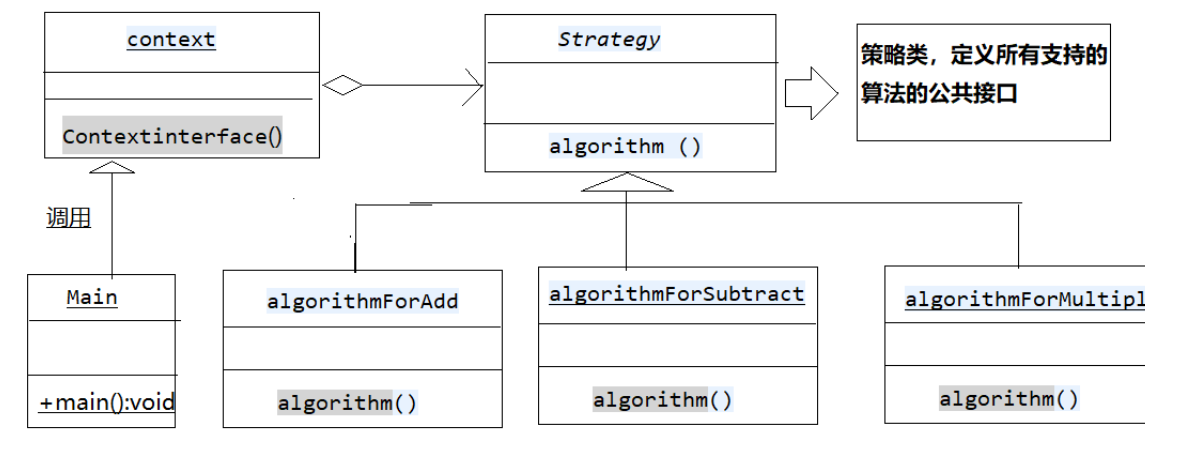
步骤1:创建定义活动的 Strategy 接口
public interface Strategy { public double algorithm (double numberA,double numberB); }
步骤2:创建实现了 Strategy 接口的实体策略类
algorithmForAdd.java
public class algorithmForAdd implements Strategy {
@Override
public double algorithm(double numberA,double numberB) {
return numberA+numberB;
}
}
algorithmForMultiply.java
public class algorithmForMultiply implements Strategy {
@Override
public double algorithm(double numberA, double numberB) {
return numberA * numberB;
}
}
algorithmForSubtract.java
public class algorithmForSubtract implements Strategy {
@Override
public double algorithm(double numberA, double numberB) {
return numberA-numberB;
}
}
步骤3:
创建 Context 类
public class context {
private Strategy strategy;
public context(Strategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public double Contextinterface(double numberA, double numberB) {
return strategy.algorithm(numberA, numberB);
}
}
步骤4:
创建Main类
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("10+20 = "+new context(new algorithmForAdd()).Contextinterface(10, 20));
System.out.println("10-20 = "+new context(new algorithmForSubtract()).Contextinterface(10, 20));
System.out.println("10*20 = "+new context(new algorithmForMultiply()).Contextinterface(10, 20));
}
}
运行结果:





