高斯滤波
高斯滤波器 (Gaussian Filter)
-
最有用的滤波器 (尽管不是最快的)。 高斯滤波是将输入数组的每一个像素点与 高斯内核 卷积将卷积和当作输出像素值。
-
还记得1维高斯函数的样子吗?
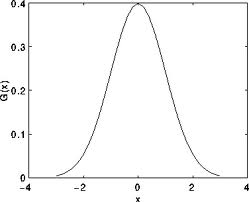
假设图像是1维的,那么观察上图,不难发现中间像素的加权系数是最大的, 周边像素的加权系数随着它们远离中间像素的距离增大而逐渐减小。
Note
2维高斯函数可以表达为 :
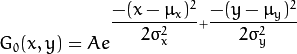
其中 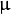 为均值 (峰值对应位置),
为均值 (峰值对应位置), 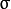 代表标准差 (变量
代表标准差 (变量 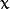 和 变量
和 变量 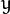 各有一个均值,也各有一个标准差)。
各有一个均值,也各有一个标准差)。
高斯滤波的实现比较简单,opencv和matlab均有函数实现,参看图像处理之滤波器
这里有一个简单的例子对比:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <vector> using namespace std; using namespace cv; void OpenCv_Gauss_Test() { Mat src = imread("lena.jpg", 0); int scale = 1; resize(src, src, Size(src.cols * scale, src.rows*scale)); Mat dst = src.clone(); cout << src.cols << "*" << src.rows << " " << src.rows * src.cols / 10000 << "M" << endl; int ksize = 11; GaussianBlur(src, dst, Size(ksize, ksize), 0, 0); namedWindow("dstopencv"); imshow("dstopencv",dst); } void mygausstest() { Mat src = imread("lena.jpg", 0); int scale = 1; resize(src, src, Size(src.cols * scale, src.rows*scale)); Mat dst = src.clone(); cout << src.cols << "*" << src.rows << " " << src.rows * src.cols / 10000 << "M" << endl; int ksize = 11; int step = ksize / 2; int m = src.rows - step * 2 - 1; int n = src.cols - step * 2 - 1; float sigma = 0.3*((ksize - 1)*0.5 - 1) + 0.8; Mat gausskernel = getGaussianKernel(ksize, sigma, CV_64F); Mat showkernel = gausskernel*gausskernel.t(); for (int i = step + 1; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = step + 1; j < n; ++j) { Mat sub =src(Range(i - step, i + step + 1), Range(j - step, j + step + 1)); sub.convertTo(sub, CV_64F); dst.at<uchar>(i, j) = cv::sum(sub.mul(showkernel))[0]; } } namedWindow("src"); namedWindow("dst"); imshow("src", src); imshow("dst", dst); waitKey(0); } void main() { OpenCv_Gauss_Test(); mygausstest(); }
这里主要讨论高斯滤波的优化加速问题。
参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/app_12062011/article/details/27082049
http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/HIPR2/gsmooth.htm
http://blog.csdn.net/app_12062011/article/details/27082049
IIR高斯递归滤波器
http://blog.csdn.net/bluecol/article/details/45584065 (IIR高斯滤波器)
http://q.cnblogs.com/q/54532/
http://www.cnblogs.com/Imageshop/archive/2013/01/07/2849782.html
gimp源码
/* * Calculate the coefficients for the recursive filter algorithm * Fast Computation of gaussian blurring. */ static void compute_coefs3 (gauss3_coefs *c, gfloat sigma) { /* * Papers: "Recursive Implementation of the gaussian filter.", * Ian T. Young , Lucas J. Van Vliet, Signal Processing 44, Elsevier 1995. * formula: 11b computation of q * 8c computation of b0..b1 * 10 alpha is normalization constant B */ gfloat q, q2, q3; q = 0; if (sigma >= 2.5) { q = 0.98711 * sigma - 0.96330; } else if ((sigma >= 0.5) && (sigma < 2.5)) { q = 3.97156 - 4.14554 * (gfloat) sqrt ((double) 1 - 0.26891 * sigma); } else { q = 0.1147705018520355224609375; } q2 = q * q; q3 = q * q2; c->b[0] = (1.57825+(2.44413*q)+(1.4281 *q2)+(0.422205*q3)); c->b[1] = ( (2.44413*q)+(2.85619*q2)+(1.26661 *q3)); c->b[2] = ( -((1.4281*q2)+(1.26661 *q3))); c->b[3] = ( (0.422205*q3)); c->B = 1.0-((c->b[1]+c->b[2]+c->b[3])/c->b[0]); c->sigma = sigma; c->N = 3; } static void gausssmooth (gfloat *in, gfloat *out, gint size, gint rowstride, gauss3_coefs *c) { /* * Papers: "Recursive Implementation of the gaussian filter.", * Ian T. Young , Lucas J. Van Vliet, Signal Processing 44, Elsevier 1995. * formula: 9a forward filter * 9b backward filter * fig7 algorithm */ gint i,n, bufsize; gfloat *w1,*w2; /* forward pass */ bufsize = size+3; size -= 1; w1 = (gfloat *) g_try_malloc (bufsize * sizeof (gfloat)); w2 = (gfloat *) g_try_malloc (bufsize * sizeof (gfloat)); w1[0] = in[0]; w1[1] = in[0]; w1[2] = in[0]; for ( i = 0 , n=3; i <= size ; i++, n++) { w1[n] = (gfloat)(c->B*in[i*rowstride] + ((c->b[1]*w1[n-1] + c->b[2]*w1[n-2] + c->b[3]*w1[n-3] ) / c->b[0])); } /* backward pass */ w2[size+1]= w1[size+3]; w2[size+2]= w1[size+3]; w2[size+3]= w1[size+3]; for (i = size, n = i; i >= 0; i--, n--) { w2[n]= out[i * rowstride] = (gfloat)(c->B*w1[n] + ((c->b[1]*w2[n+1] + c->b[2]*w2[n+2] + c->b[3]*w2[n+3] ) / c->b[0])); } g_free (w1); g_free (w2); }
opencv下面实现IIR高斯滤波器
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> using namespace cv; using namespace std; #include "Timer.h" Timer timer; // timer double elapsedTime; // time in millisecond double avgtime = 0; double testnum = 0; void timebegin() { timer.start(); } void timeend(string str) { elapsedTime = timer.getElapsedTimeInMilliSec(); avgtime += elapsedTime; str = str + "time is: ";// %lf ms\n"; cout << str << elapsedTime << "ms" << endl; } /**************************************** * src : 原始图像数据 * * dst : 模糊后图像数据 * * width : 图像宽 * * height : 图像高 * * sigma : 高斯参数 * * chan : 图像通道数 * *****************************************/ void IMG_GaussBlur(unsigned char* src, unsigned char*& dst, int width, int height, float sigma, int chan) { int i = 0; int row = 0; int col = 0; int pos = 0; int channel = 0; int n = 0; int bufsize = 0; int size = 0; int rowstride = 0; int channelsize = width*height; if (width > height) { bufsize = width + 3; } else { bufsize = height + 3; } float* w1 = (float *)malloc(bufsize * sizeof (float)); float *w2 = (float *)malloc(bufsize * sizeof (float)); float *in = (float *)malloc(channelsize * sizeof (float)); float *out = (float *)malloc(channelsize * sizeof (float)); //----------------计算高斯核---------------------------------------// //compute_coefs3(coef, sigma); float q = 0; float q2, q3; double b[4] = { 0 }; double B = 0; int N = 3; if (sigma >= 2.5) { q = 0.98711 * sigma - 0.96330; } else if ((sigma >= 0.5) && (sigma < 2.5)) { q = 3.97156 - 4.14554 * (float)sqrt((double)1 - 0.26891 * sigma); } else { q = 0.1147705018520355224609375; } q2 = q * q; q3 = q * q2; b[0] = (1.57825 + (2.44413*q) + (1.4281 *q2) + (0.422205*q3)); b[1] = ((2.44413*q) + (2.85619*q2) + (1.26661 *q3)); b[2] = (-((1.4281*q2) + (1.26661 *q3))); b[3] = ((0.422205*q3)); B = 1.0 - ((b[1] + b[2] + b[3]) / b[0]); //----------------计算高斯核结束---------------------------------------// // 处理图像的多个通道 for (channel = 0; channel < chan; channel++) { // 获取一个通道的所有像素值 for (i = 0, pos = channel; i < channelsize; i++, pos += chan) { /* 0-255 => 1-256 */ in[i] = (float)(src[pos] + 1.0); } //纵向处理 for (row = 0; row < height; row++) { pos = row * width; //gausssmooth(in + pos, out + pos, width, 1, &coef); size = width; rowstride = 1; bufsize = size + 3; size -= 1; w1[0] = (in + pos)[0]; w1[1] = (in + pos)[0]; w1[2] = (in + pos)[0]; for (i = 0, n = 3; i <= size; i++, n++) { w1[n] = (float)(B*(in + pos)[i*rowstride] + ((b[1] * w1[n - 1] + b[2] * w1[n - 2] + b[3] * w1[n - 3]) / b[0])); } /** backward pass */ w2[size + 1] = w1[size + 3]; w2[size + 2] = w1[size + 3]; w2[size + 3] = w1[size + 3]; for (i = size, n = i; i >= 0; i--, n--) { w2[n] = (out + pos)[i * rowstride] = (float)(B*w1[n] + ((b[1] * w2[n + 1] + b[2] * w2[n + 2] + b[3] * w2[n + 3]) / b[0])); } } //下面的横向处理直接将数据 out 与 in 对调 省去memcpy //memcpy(in, out, channelsize * sizeof(float)); //memset(out, 0 , channelsize * sizeof(float)); //横向处理 for (col = 0; col < width; col++) { //gausssmooth(out + col, in + col, height, width, &coef); size = height; rowstride = width; bufsize = size + 3; size -= 1; w1[0] = (out + col)[0]; w1[1] = (out + col)[0]; w1[2] = (out + col)[0]; for (i = 0, n = 3; i <= size; i++, n++) { w1[n] = (float)(B*(out + col)[i*rowstride] + ((b[1] * w1[n - 1] + b[2] * w1[n - 2] + b[3] * w1[n - 3]) / b[0])); } w2[size + 1] = w1[size + 3]; w2[size + 2] = w1[size + 3]; w2[size + 3] = w1[size + 3]; for (i = size, n = i; i >= 0; i--, n--) { w2[n] = (in + col)[i * rowstride] = (float)(B*w1[n] + ((b[1] * w2[n + 1] + b[2] * w2[n + 2] + b[3] * w2[n + 3]) / b[0])); } } //拷贝结果到函数输出指针 for (i = 0, pos = channel; i < channelsize; i++, pos += chan) { dst[pos] = in[i] - 1; } } free(w1); free(w2); free(in); free(out); } void main() { Mat src = imread("src.jpg"); Mat dst1 = src.clone(); Mat dst2 = src.clone(); float sigma = 15.0; timebegin(); IMG_GaussBlur(src.data, dst1.data, src.cols, src.rows, sigma, 3); timeend("IIR_GAUSS"); int ksize = 71; timebegin(); GaussianBlur(src, dst2, Size(ksize,ksize),0, 0); timeend("OPNECV_GAUSS"); //namedWindow("src",0); namedWindow("dst1",0); namedWindow("dst2",0); //imshow("src", src); imshow("dst1", dst1); imshow("dst2", dst2); waitKey(0); }
附加 测试时间的函数代码,这个代码可以在linux以及windows下面通用,也可以参看博文:
Time.cpp
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Timer.cpp // ========= // High Resolution Timer. // This timer is able to measure the elapsed time with 1 micro-second accuracy // in both Windows, Linux and Unix system // // AUTHOR: Song Ho Ahn (song.ahn@gmail.com) // CREATED: 2003-01-13 // UPDATED: 2006-01-13 // // Copyright (c) 2003 Song Ho Ahn ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #include "Timer.h" #include <stdlib.h> /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // constructor /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Timer::Timer() { #ifdef WIN32 QueryPerformanceFrequency(&frequency); startCount.QuadPart = 0; endCount.QuadPart = 0; #else startCount.tv_sec = startCount.tv_usec = 0; endCount.tv_sec = endCount.tv_usec = 0; #endif stopped = 0; startTimeInMicroSec = 0; endTimeInMicroSec = 0; } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // distructor /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Timer::~Timer() { } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // start timer. // startCount will be set at this point. /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void Timer::start() { stopped = 0; // reset stop flag #ifdef WIN32 QueryPerformanceCounter(&startCount); #else gettimeofday(&startCount, NULL); #endif } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // stop the timer. // endCount will be set at this point. /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// void Timer::stop() { stopped = 1; // set timer stopped flag #ifdef WIN32 QueryPerformanceCounter(&endCount); #else gettimeofday(&endCount, NULL); #endif } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // compute elapsed time in micro-second resolution. // other getElapsedTime will call this first, then convert to correspond resolution. /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// double Timer::getElapsedTimeInMicroSec() { #ifdef WIN32 if(!stopped) QueryPerformanceCounter(&endCount); startTimeInMicroSec = startCount.QuadPart * (1000000.0 / frequency.QuadPart); endTimeInMicroSec = endCount.QuadPart * (1000000.0 / frequency.QuadPart); #else if(!stopped) gettimeofday(&endCount, NULL); startTimeInMicroSec = (startCount.tv_sec * 1000000.0) + startCount.tv_usec; endTimeInMicroSec = (endCount.tv_sec * 1000000.0) + endCount.tv_usec; #endif return endTimeInMicroSec - startTimeInMicroSec; } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // divide elapsedTimeInMicroSec by 1000 /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// double Timer::getElapsedTimeInMilliSec() { return this->getElapsedTimeInMicroSec() * 0.001; } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // divide elapsedTimeInMicroSec by 1000000 /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// double Timer::getElapsedTimeInSec() { return this->getElapsedTimeInMicroSec() * 0.000001; } /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // same as getElapsedTimeInSec() /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// double Timer::getElapsedTime() { return this->getElapsedTimeInSec(); }
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Timer.h // ======= // High Resolution Timer. // This timer is able to measure the elapsed time with 1 micro-second accuracy // in both Windows, Linux and Unix system // // AUTHOR: Song Ho Ahn (song.ahn@gmail.com) // CREATED: 2003-01-13 // UPDATED: 2006-01-13 // // Copyright (c) 2003 Song Ho Ahn ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// #ifndef TIMER_H_DEF #define TIMER_H_DEF #ifdef WIN32 // Windows system specific #include <windows.h> #else // Unix based system specific #include <sys/time.h> #endif class Timer { public: Timer(); // default constructor ~Timer(); // default destructor void start(); // start timer void stop(); // stop the timer double getElapsedTime(); // get elapsed time in second double getElapsedTimeInSec(); // get elapsed time in second (same as getElapsedTime) double getElapsedTimeInMilliSec(); // get elapsed time in milli-second double getElapsedTimeInMicroSec(); // get elapsed time in micro-second protected: private: double startTimeInMicroSec; // starting time in micro-second double endTimeInMicroSec; // ending time in micro-second int stopped; // stop flag #ifdef WIN32 LARGE_INTEGER frequency; // ticks per second LARGE_INTEGER startCount; // LARGE_INTEGER endCount; // #else timeval startCount; // timeval endCount; // #endif }; #endif // TIMER_H_DEF



